Meinolf's SMART-GRID-Thread - 500 Beiträge pro Seite
eröffnet am 19.01.09 13:35:57 von
neuester Beitrag 12.09.19 14:12:39 von
neuester Beitrag 12.09.19 14:12:39 von
Beiträge: 307
ID: 1.147.666
ID: 1.147.666
Aufrufe heute: 0
Gesamt: 33.825
Gesamt: 33.825
Aktive User: 0
Top-Diskussionen
| Titel | letzter Beitrag | Aufrufe |
|---|---|---|
| vor 29 Minuten | 6649 | |
| vor 8 Minuten | 4232 | |
| vor 22 Minuten | 3526 | |
| vor 14 Minuten | 3514 | |
| vor 49 Minuten | 3324 | |
| heute 08:59 | 3256 | |
| vor 25 Minuten | 2551 | |
| vor 42 Minuten | 2332 |
Meistdiskutierte Wertpapiere
| Platz | vorher | Wertpapier | Kurs | Perf. % | Anzahl | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1. | 17.741,77 | -0,83 | 220 | |||
| 2. | 2. | 155,11 | -3,94 | 130 | |||
| 3. | 3. | 6,3680 | -3,69 | 100 | |||
| 4. | 5. | 6,6880 | -4,73 | 73 | |||
| 5. | 4. | 2.373,12 | -0,34 | 63 | |||
| 6. | 20. | 23,970 | -2,68 | 49 | |||
| 7. | 8. | 7,6300 | +0,66 | 40 | |||
| 8. | 15. | 26,75 | -0,45 | 40 |
Mit fortschreitendem Ausbau der Erneuerbaren Energien wird es immer wichtiger werden, die Entwicklung des ganzen Systems der Strom- und Energieerzeugung zu betrachten und zu optimieren.
Fossile Energien sind "dispatchable", d.h. im Wesentlichen dann einsetzbar, wenn der Bedarf da ist.
Erneuerbare stehen dann zur Verfügung, wenn die Natur sie bereitstellt.
Um Nachfrage und Angebot zur Deckung zu bringen, werden alle Arten von Technologien zu
-Speicherung
-Netzmanagement
-Demand Management
etc.
zum Einsatz kommen müssen.
Ich verfolge bereits eine kleine anzahl von Firmen, die Angebote in dieser richtung machen, würde aber gerne auch eine Diskussionsplattform für nicht-firmenspezifische Thmen haben.
Deshalb dieser Thread.
Fossile Energien sind "dispatchable", d.h. im Wesentlichen dann einsetzbar, wenn der Bedarf da ist.
Erneuerbare stehen dann zur Verfügung, wenn die Natur sie bereitstellt.
Um Nachfrage und Angebot zur Deckung zu bringen, werden alle Arten von Technologien zu
-Speicherung
-Netzmanagement
-Demand Management
etc.
zum Einsatz kommen müssen.
Ich verfolge bereits eine kleine anzahl von Firmen, die Angebote in dieser richtung machen, würde aber gerne auch eine Diskussionsplattform für nicht-firmenspezifische Thmen haben.
Deshalb dieser Thread.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 36.402.747 von meinolf67 am 19.01.09 13:35:57Ein paar konkrete Fragen habe ich auch schon.
Weiß jemand was über:
1) konkrete Kosten von Batterietechnologien; Invest pro kWh, Lebensdauer, Betriebskosten,...
2) GROßE konkrete Projekte zum Demand Management; so nach dem Motto: riesiges Kühlhaus wird genau dann runtergekühlt , wenn Last-Tal und weniger gekühlt, wenn Lastspitze...
3) Quellen zur Struktur der Elektrizitätsnetze, der Engpässe, künftige Entwicklungsrichtungen,...
Weiß jemand was über:
1) konkrete Kosten von Batterietechnologien; Invest pro kWh, Lebensdauer, Betriebskosten,...
2) GROßE konkrete Projekte zum Demand Management; so nach dem Motto: riesiges Kühlhaus wird genau dann runtergekühlt , wenn Last-Tal und weniger gekühlt, wenn Lastspitze...
3) Quellen zur Struktur der Elektrizitätsnetze, der Engpässe, künftige Entwicklungsrichtungen,...
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 36.402.775 von meinolf67 am 19.01.09 13:39:57Beispiel für einen dezentralen Ansatz nach 2):
Ice Bear 30 Hybrid Air Conditioner
Discover the Power of Ice
Ice Energy’s Ice Bear® Hybrid Air Conditioner is the industry's first integrated energy storage and HVAC solution specifically designed for small to medium-sized commercial buildings.
By using cleaner, more efficient and less expensive nighttime power to produce and store energy for use the next day, the Ice Bear 30 Hybrid Air Conditioner provides efficient cooling using only a fraction of the peak energy required by conventional systems, dramatically lowering electricity costs and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Air conditioning energy demand – typically 40-50% of a building’s electricity use during expensive peak hours – can be reduced by as much as 95%.
Combining conventional air conditioning with Ice Energy’s ground-breaking energy storage technology and using each when it’s most efficient and cost-effective, hybrid cooling saves money and reduces the impact on the environment. Together, this unique hybrid system surpasses the overall efficiency and performance of conventional equipment alone.
Together, this unique hybrid system surpasses the overall efficiency and performance of conventional equipment alone.
Ice Bear 30 Hybrid Air Conditioner
Discover the Power of Ice
Ice Energy’s Ice Bear® Hybrid Air Conditioner is the industry's first integrated energy storage and HVAC solution specifically designed for small to medium-sized commercial buildings.
By using cleaner, more efficient and less expensive nighttime power to produce and store energy for use the next day, the Ice Bear 30 Hybrid Air Conditioner provides efficient cooling using only a fraction of the peak energy required by conventional systems, dramatically lowering electricity costs and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Air conditioning energy demand – typically 40-50% of a building’s electricity use during expensive peak hours – can be reduced by as much as 95%.
Combining conventional air conditioning with Ice Energy’s ground-breaking energy storage technology and using each when it’s most efficient and cost-effective, hybrid cooling saves money and reduces the impact on the environment. Together, this unique hybrid system surpasses the overall efficiency and performance of conventional equipment alone.
Together, this unique hybrid system surpasses the overall efficiency and performance of conventional equipment alone.
Ice Energy Launches Utility-Scale Smart Grid Tools For RE Integration
in News Departments > FYI
by SI Staff on Thursday 15 January 2009
email the content item print the content item
Ice Energy, a provider of smart grid and distributed energy-storage solutions for leveling peak energy demand, plans expand its offerings to focus on utility-scale deployment. The company's technology involves lossless distributed energy storage with closed-loop, two-way control and a software infrastructure to permanently reshape the load curve.
Unlike load management cycling or other curtailment programs that harm customer comfort and economic productivity, Ice Energy permanently and transparently shifts cooling energy consumption to off-peak hours, with no negative impact to consumers, the company says.
The technology is designed to complement intermittent, off-peak renewable portfolio assets such as wind and solar, enabling utilities to shift significant load to off-peak hours when the energy delivery system is both underutilized and more thermally efficient.
SOURCE: Ice Energy
in News Departments > FYI
by SI Staff on Thursday 15 January 2009
email the content item print the content item
Ice Energy, a provider of smart grid and distributed energy-storage solutions for leveling peak energy demand, plans expand its offerings to focus on utility-scale deployment. The company's technology involves lossless distributed energy storage with closed-loop, two-way control and a software infrastructure to permanently reshape the load curve.
Unlike load management cycling or other curtailment programs that harm customer comfort and economic productivity, Ice Energy permanently and transparently shifts cooling energy consumption to off-peak hours, with no negative impact to consumers, the company says.
The technology is designed to complement intermittent, off-peak renewable portfolio assets such as wind and solar, enabling utilities to shift significant load to off-peak hours when the energy delivery system is both underutilized and more thermally efficient.
SOURCE: Ice Energy
Ice Energy set to change industry
By Kristen Tatti
Northern Colorado Business Report
WINDSOR - The past year has been full of accolades for Windsor-based Ice Energy Inc., but this year will be about leveraging the praise into an industry-changing, revenue-generating energy industry powerhouse.
In early June, the company officially launched its next generation of cooling technology - the Ice Bear 30 Hybrid Air Conditioner and companion Ice-Ready Rooftop Unit. The launch represents a huge milestone for the company as it moves toward mass deployment deals, fulfilling its vision of outfitting every new commercial and residential building with the Ice Bear system.
Ice Energy was founded in 2003 with the Ice Bear 50, which uses a seemingly simplistic building cooling technology - ice. The Ice Bear is designed to switch the energy used for cooling buildings from the peak-use hours of the day to off-peak hours at night. Water frozen in the evening is used during the day to cool refrigerant for the air conditioning unit.
Ice Energy's solution is unique because it works with the more efficient refrigerant rather than just water. Buildings greater than two stories use water cooling systems because the water can maintain cooler temperatures for longer distances. But buildings of two stories and smaller make up 98 percent of all structures in the United States. That translates into a market of about 80 million cooling units, according to Ice Energy President Frank Ramirez.
"The Ice Bear 30 took lessons learned from the initial deployment and integrated it into the design," he said.
The Ice Bear 50 allowed the company to prove the technology, demonstrate its efficiency and learn how the challenges presented at different sites. It also garnered recognition and awards.
In early 2004, the Ice Bear received a Gold Award at the World's Best Technology contest, over 60 competing technologies. Ice Energy was also called "Most Promising Company" at the Energy Venture Fair IV in October 2003.
Doing more with less
The attention is not too surprising. A big push now is conservation, but Ramirez said that asking consumers to give up their comfort is a fruitless endeavor.
"It's not just how much we consume; but when we consume," he said, adding that it is 50 percent more efficient to generate and transmit energy at night to be stored for daytime use. Transmission energy loss during the day averages around 20 percent but only 6 percent in the evening. Therefore, even an appliance that uses slightly more energy will be more efficient and less consuming during off-peak hours.
"It is very difficult to change the way consumers behave," Ramirez said. "We can change the way energy is consumed at a facility by having technology do the work."
Ice Energy's technology is about efficiency, not conservation. To Ramirez, conservation is doing less with less and feeling good about it; efficiency is doing more with less by being smart about how it's done.
One of the big breakthroughs for new system is its ability to work with any equipment. The Ice Bear 30 is designed so that it can be outfitted on existing HVAC systems, and available to end-users as an out-of-the-box solution. Ice Energy is also working with air-conditioning industry leaders Trane Inc. and Carrier Corp. to offer cooling units with the Ice Bear 30 already integrated through its resellers, with a similar deal with another major manufacturer in the works.
"The technology itself is only a small part of this," he said.
During the next year, Ramirez said a lot of focus will be put on developing a business model wherein there will be no expense to the consumer. And he isn't talking about a good return on investment.
"The end consumer will be the beneficiary of the technology and the host of the technology," Ramirez explained, but the utility companies will be Ice Energy's customers. Ideally, utility companies would deploy Ice Energy's technology in the same way those companies would deliver any resources to the end-users.
The company is already working with a few California utilities, including Pacific Gas & Electric Co. and Southern California Edison.
"We're in very advanced discussions with a number of large utilities for deployment (of this technology) on a utility scale," he said.
Ice Energy sees the business model as a win-win-win: good for consumers, for utilities and for the company. The company is discussing deployments of 50 to 100 megawatt with utilities. It would take about 14,000 Ice Bear 30 units to fulfill a 100-megawatt deployment. The company manufactured a few hundred units last year.
"The ramp-up in scale is huge," Ramirez said.
Funding like a power plant
In order to fund such an increase in production, Ice Energy is in discussions to land large infrastructure funds more typically used to build power plants. Ramirez said that because the Ice Bear mitigates the need to add generation capacity, it is like a power plant, just storing power rather than generating it.
"In every respect, switching from peak to off-peak demand is like building a new power plant," said Pete Higgens, Ice Energy board member. Essentially, the Ice Bear 30 is a cheaper, less regulated way to build power generation capacity.
Higgens, a former Microsoft executive, went to graduate school with Ramirez and first heard of Ice Energy at a reunion in 2003.
"I view it in a macro sense as an incredible creator of value," he said. "It solves a huge problem."
Higgens said the company is in the process of changing its accolades into revenue.
"I think it's a time of acceleration," he said.
Ice Energy's board of directors and advisory board play a big role in the company's direction and future. The roster reads like a who's who of industry and business, even counting retired U.S. Army General Norman Schwarzkopf as its leadership adviser.
Joe Desmond was able to learn about Ice Energy as a direct observer. Desmond served as the chair of the California Energy Commission when he first saw the product at work in technical evaluations in the state.
"It became clear to me that the technology could solve a lot of the energy problems in California," he said. "The ability to shift 90-plus percent of on-peak demand to off-peak is a great benefit."
Now as a member of the board of directors, Desmond is able to bring his many years of experience working in various aspects of the energy industry to Ice Energy.
"I like to think that I bring a very broad perspective about how the energy industry will evaluate the technology," he said.
For Desmond, the decision to become involved with Ice Energy was about both the experience of the management team and the strength of the technology.
"They had clearly invested a lot in the technology and in testing," he said. "Equally important is the market opportunity."
The energy industry, he explained, has been largely preoccupied with generation, transmission and demand. Energy storage is a virtually untapped aspect of the business.
"This has significant potential to change the industry," he said.
Desmond explained that the launch of the Ice Bear 30 is an accomplishment on many levels. It is a standard unit deployable on a plug-and-play basis; it decreases the cost of installation of new units and integration for existing units and includes a method for real-time communication for monitoring performance.
"Although on the surface it appears to be simplistic, they have significant intellectual property around how to intelligently store energy," Desmond said.
Ice Energy currently has seven patents, issued and owned, and more than 100 in process.
"We're not a manufacturing company," Ramirez said, explaining that research and development is the company's true competency. "The process is one of continuous improvement and refinement."
Greater aspirations
Ice Energy is already cooling the office and industrial building market, but has greater aspirations. Ramirez said that work is ongoing to develop an appropriately intelligent system for cooling residential properties. The company has had about a dozen test units operating for around two years, mining information for further development. The key is to provide consumers with an absolutely simple plug-and-play solution.
"Working with the residential marketplace has different problems and solutions," Ramirez said.
In addition to research and realizing the business model, Ice Energy is also working on landing the financing it will need to ramp up its growth. The company is in the process now of attracting a $25 million Series B round of financing.
"We're into the stretch run with three prospective partners," he said.
A $26 million Series A round came in June 2007 though a partnership led by investment banking powerhouse Goldman Sachs. Ramirez explained that about half of that funding went to debt and note conversion.
Raising capital for the company now should be a walk in the park compared to efforts in the early days.
"When we first started talking about storage five years ago, we were seen as strange people with a strange idea. Now we're seen as visionaries in the mainstream," Ramirez said. "We've just begun to get the momentum and mass to tell this story."
By Kristen Tatti
Northern Colorado Business Report
WINDSOR - The past year has been full of accolades for Windsor-based Ice Energy Inc., but this year will be about leveraging the praise into an industry-changing, revenue-generating energy industry powerhouse.
In early June, the company officially launched its next generation of cooling technology - the Ice Bear 30 Hybrid Air Conditioner and companion Ice-Ready Rooftop Unit. The launch represents a huge milestone for the company as it moves toward mass deployment deals, fulfilling its vision of outfitting every new commercial and residential building with the Ice Bear system.
Ice Energy was founded in 2003 with the Ice Bear 50, which uses a seemingly simplistic building cooling technology - ice. The Ice Bear is designed to switch the energy used for cooling buildings from the peak-use hours of the day to off-peak hours at night. Water frozen in the evening is used during the day to cool refrigerant for the air conditioning unit.
Ice Energy's solution is unique because it works with the more efficient refrigerant rather than just water. Buildings greater than two stories use water cooling systems because the water can maintain cooler temperatures for longer distances. But buildings of two stories and smaller make up 98 percent of all structures in the United States. That translates into a market of about 80 million cooling units, according to Ice Energy President Frank Ramirez.
"The Ice Bear 30 took lessons learned from the initial deployment and integrated it into the design," he said.
The Ice Bear 50 allowed the company to prove the technology, demonstrate its efficiency and learn how the challenges presented at different sites. It also garnered recognition and awards.
In early 2004, the Ice Bear received a Gold Award at the World's Best Technology contest, over 60 competing technologies. Ice Energy was also called "Most Promising Company" at the Energy Venture Fair IV in October 2003.
Doing more with less
The attention is not too surprising. A big push now is conservation, but Ramirez said that asking consumers to give up their comfort is a fruitless endeavor.
"It's not just how much we consume; but when we consume," he said, adding that it is 50 percent more efficient to generate and transmit energy at night to be stored for daytime use. Transmission energy loss during the day averages around 20 percent but only 6 percent in the evening. Therefore, even an appliance that uses slightly more energy will be more efficient and less consuming during off-peak hours.
"It is very difficult to change the way consumers behave," Ramirez said. "We can change the way energy is consumed at a facility by having technology do the work."
Ice Energy's technology is about efficiency, not conservation. To Ramirez, conservation is doing less with less and feeling good about it; efficiency is doing more with less by being smart about how it's done.
One of the big breakthroughs for new system is its ability to work with any equipment. The Ice Bear 30 is designed so that it can be outfitted on existing HVAC systems, and available to end-users as an out-of-the-box solution. Ice Energy is also working with air-conditioning industry leaders Trane Inc. and Carrier Corp. to offer cooling units with the Ice Bear 30 already integrated through its resellers, with a similar deal with another major manufacturer in the works.
"The technology itself is only a small part of this," he said.
During the next year, Ramirez said a lot of focus will be put on developing a business model wherein there will be no expense to the consumer. And he isn't talking about a good return on investment.
"The end consumer will be the beneficiary of the technology and the host of the technology," Ramirez explained, but the utility companies will be Ice Energy's customers. Ideally, utility companies would deploy Ice Energy's technology in the same way those companies would deliver any resources to the end-users.
The company is already working with a few California utilities, including Pacific Gas & Electric Co. and Southern California Edison.
"We're in very advanced discussions with a number of large utilities for deployment (of this technology) on a utility scale," he said.
Ice Energy sees the business model as a win-win-win: good for consumers, for utilities and for the company. The company is discussing deployments of 50 to 100 megawatt with utilities. It would take about 14,000 Ice Bear 30 units to fulfill a 100-megawatt deployment. The company manufactured a few hundred units last year.
"The ramp-up in scale is huge," Ramirez said.
Funding like a power plant
In order to fund such an increase in production, Ice Energy is in discussions to land large infrastructure funds more typically used to build power plants. Ramirez said that because the Ice Bear mitigates the need to add generation capacity, it is like a power plant, just storing power rather than generating it.
"In every respect, switching from peak to off-peak demand is like building a new power plant," said Pete Higgens, Ice Energy board member. Essentially, the Ice Bear 30 is a cheaper, less regulated way to build power generation capacity.
Higgens, a former Microsoft executive, went to graduate school with Ramirez and first heard of Ice Energy at a reunion in 2003.
"I view it in a macro sense as an incredible creator of value," he said. "It solves a huge problem."
Higgens said the company is in the process of changing its accolades into revenue.
"I think it's a time of acceleration," he said.
Ice Energy's board of directors and advisory board play a big role in the company's direction and future. The roster reads like a who's who of industry and business, even counting retired U.S. Army General Norman Schwarzkopf as its leadership adviser.
Joe Desmond was able to learn about Ice Energy as a direct observer. Desmond served as the chair of the California Energy Commission when he first saw the product at work in technical evaluations in the state.
"It became clear to me that the technology could solve a lot of the energy problems in California," he said. "The ability to shift 90-plus percent of on-peak demand to off-peak is a great benefit."
Now as a member of the board of directors, Desmond is able to bring his many years of experience working in various aspects of the energy industry to Ice Energy.
"I like to think that I bring a very broad perspective about how the energy industry will evaluate the technology," he said.
For Desmond, the decision to become involved with Ice Energy was about both the experience of the management team and the strength of the technology.
"They had clearly invested a lot in the technology and in testing," he said. "Equally important is the market opportunity."
The energy industry, he explained, has been largely preoccupied with generation, transmission and demand. Energy storage is a virtually untapped aspect of the business.
"This has significant potential to change the industry," he said.
Desmond explained that the launch of the Ice Bear 30 is an accomplishment on many levels. It is a standard unit deployable on a plug-and-play basis; it decreases the cost of installation of new units and integration for existing units and includes a method for real-time communication for monitoring performance.
"Although on the surface it appears to be simplistic, they have significant intellectual property around how to intelligently store energy," Desmond said.
Ice Energy currently has seven patents, issued and owned, and more than 100 in process.
"We're not a manufacturing company," Ramirez said, explaining that research and development is the company's true competency. "The process is one of continuous improvement and refinement."
Greater aspirations
Ice Energy is already cooling the office and industrial building market, but has greater aspirations. Ramirez said that work is ongoing to develop an appropriately intelligent system for cooling residential properties. The company has had about a dozen test units operating for around two years, mining information for further development. The key is to provide consumers with an absolutely simple plug-and-play solution.
"Working with the residential marketplace has different problems and solutions," Ramirez said.
In addition to research and realizing the business model, Ice Energy is also working on landing the financing it will need to ramp up its growth. The company is in the process now of attracting a $25 million Series B round of financing.
"We're into the stretch run with three prospective partners," he said.
A $26 million Series A round came in June 2007 though a partnership led by investment banking powerhouse Goldman Sachs. Ramirez explained that about half of that funding went to debt and note conversion.
Raising capital for the company now should be a walk in the park compared to efforts in the early days.
"When we first started talking about storage five years ago, we were seen as strange people with a strange idea. Now we're seen as visionaries in the mainstream," Ramirez said. "We've just begun to get the momentum and mass to tell this story."
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 36.402.775 von meinolf67 am 19.01.09 13:39:57Schau mal unter E-Energy ...
Die Bundesregierung fördert gerade ein paar Projekte in der Richtung
Die Bundesregierung fördert gerade ein paar Projekte in der Richtung
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 36.403.921 von vvogel am 19.01.09 15:56:23Danke für den Tip
hallo,
mich würden auch mal firmen bzw. startups interessieren, die in das thema smart grid reinpassen und an der börse handelbar sind.
kann mir jemand eine kleine übersicht geben?
wäre nett!
danke
h.
mich würden auch mal firmen bzw. startups interessieren, die in das thema smart grid reinpassen und an der börse handelbar sind.
kann mir jemand eine kleine übersicht geben?
wäre nett!
danke
h.
gerade bei Spiegel-Online (daher im Zweifel alles sehr ungenau bis vollkommen falsch...  )
)
Das Stromnetz der Zukunft soll eine gewaltige Kommunikationsplattform werden - daran arbeiten Firmen wie Silver Spring aus Kalifornien. Ziel: Verbraucher sollen ihren Energiebedarf selbst genau kontrollieren können. Investoren überschütten die Startups mit Geld, Experten wittern einen Mega-Boom.
http://www.spiegel.de/wirtschaft/0,1518,612827,00.html
 )
)Das Stromnetz der Zukunft soll eine gewaltige Kommunikationsplattform werden - daran arbeiten Firmen wie Silver Spring aus Kalifornien. Ziel: Verbraucher sollen ihren Energiebedarf selbst genau kontrollieren können. Investoren überschütten die Startups mit Geld, Experten wittern einen Mega-Boom.
http://www.spiegel.de/wirtschaft/0,1518,612827,00.html
habe ich auch gelesen und bin gerade auf der Suche nach entsprechenden AGs deren Aktien man handeln kann. Bin für jeden Tip dankbar.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 36.828.997 von Scar am 23.03.09 19:57:34mal ein paar Anregungen (z.T. (OTC-)MicroCaps, deswegen Handelbarkeit nicht unbedingt gegeben) für die weitere Recherche:
RuggedCom (CA78131P2017)
Telvent (ES0178495034)
Ambient (US02318N1028)
Beacon Power (US0736771066)
Itron (US4657411066)
Power-One (US7393081044)
PowerSecure (US73936N1054)
EnerNOC (US2927641074)
aber natürlich auch eine SMA (DE000A0DJ6J9) die aus meiner Sicht deutliche Potentiale auch abseits von PV hat (siehe z.B. Backup-Lösungen)
RuggedCom (CA78131P2017)
Telvent (ES0178495034)
Ambient (US02318N1028)
Beacon Power (US0736771066)
Itron (US4657411066)
Power-One (US7393081044)
PowerSecure (US73936N1054)
EnerNOC (US2927641074)
aber natürlich auch eine SMA (DE000A0DJ6J9) die aus meiner Sicht deutliche Potentiale auch abseits von PV hat (siehe z.B. Backup-Lösungen)
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 36.828.997 von Scar am 23.03.09 19:57:34aus meinen musterdepot:
ITRON INC. 888379
Enernoc Inc. A0MSDC
Duke Energy Corp. A0JJ5P
Ruggedcom Inc. A0MVSY
Xcel Energy, Inc. 2614807
WHIRLPOOL CORP. 856331
Echelon Corporation 2285377
DIGI INTERNATIONAL INC. 878008
Comverge Inc. A0MN5C
Telvent GIT A0DK9P
ITRON INC. 888379
Enernoc Inc. A0MSDC
Duke Energy Corp. A0JJ5P
Ruggedcom Inc. A0MVSY
Xcel Energy, Inc. 2614807
WHIRLPOOL CORP. 856331
Echelon Corporation 2285377
DIGI INTERNATIONAL INC. 878008
Comverge Inc. A0MN5C
Telvent GIT A0DK9P
smart meter - smart home:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rRJJBRbq2FM
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rRJJBRbq2FM
Four utilities sign contracts with EnerNOC
March 24, 2009 09:18
EnerNOC Inc., a Boston company that helps utilities manage and conserve electricity use, said that four utilities operating in Maryland have signed contracts to avail themselves of EnerNOC services.
The utilities are Allegheny Power, Baltimore Gas and Electric, Delmarva Power and Light Co., and Potomac Electric Power Co., and the contracts will result in EnerNOC providing 250 megawatts of demand response capacity in the state of Maryland, EnerNOC said.
To read today's press release from EnerNOC, please click here.
(By Chris Reidy, Globe staff)
Gruß Karlll
March 24, 2009 09:18
EnerNOC Inc., a Boston company that helps utilities manage and conserve electricity use, said that four utilities operating in Maryland have signed contracts to avail themselves of EnerNOC services.
The utilities are Allegheny Power, Baltimore Gas and Electric, Delmarva Power and Light Co., and Potomac Electric Power Co., and the contracts will result in EnerNOC providing 250 megawatts of demand response capacity in the state of Maryland, EnerNOC said.
To read today's press release from EnerNOC, please click here.
(By Chris Reidy, Globe staff)
Gruß Karlll
das ist meine favorit
Beacon Power (US0736771066)
Beacon Power (US0736771066)
Smart Meter: Neue Standards machen dezentrale Energieversorgung effizient (31.03.2009)
Die Vorteile einer dezentralen Energieversorgung liegen auf der Hand: Die Nähe zum Endverbraucher ermöglicht verlustarme kurze Übertragungswege. Auch regenerative Energien, z.B. private Solaranlagen, können in dezentralen Stromnetzen effektiv genutzt werden. Das Forschungsprojekt SMEDEA an der TU Dortmund soll jetzt Wege und Standards erarbeiten, wie die gemessenen Daten von neuen elektronischen Zählern, welche ab 2010 auch dem Endkunden angeboten werden müssen (den so genannten Smart Metern) für die Steuerung und den wirtschaftlichen Betrieb vernetzter dezentraler Energieerzeuger genutzt werden können.
TU DdortmunNRW-Wirtschaftsministerin Christa Thoben überreichte heute, am 30. März, persönlich den Bewilligungsbescheid über eine Förderung in Höhe von 370.000 €. SMEDEA (Standardisiertes Smart Metering als Schlüsselfunktion für die Energieeffizienz von dezentralen Energieumwandlungsanlagen) konnte sich im Wettbewerb "Energie.NRW" durchsetzen und wird von Prof. Christian Rehtanz vom Lehrstuhl für Energiesysteme und Energiewirtschaft der Fakultät Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik der TU Dortmund koordiniert. Partner auf Seiten der Industrie sind die EVB Energie AG, einer der marktführenden Dienstleiter für Energieversorgungsunternehmen sowie die Energieversorgung Oelde GmbH.
"Ich freue mich, dieses Smart Metering Projekt heute auf den Weg bringen zu können. Denn, Energieeffizienz braucht auch Verbrauchstransparenz in den Haushalten. Mit intelligenten Zählern machen wir einen wichtigen Schritt hierzu", sagte Wirtschaftsministerin Christa Thoben. "Mit der Entwicklung und dem Einsatz der elektronischen Haushaltszähler eröffnen sich einerseits neue Möglichkeiten, die Effizienz des Stromverbrauchs beim Kunden zu steigern und Anreize zum Einsparen von Strom zu geben. Andererseits bringt es auch den Stromversorgern Vorteile z.B. durch die Fernablesung und eine vereinfachte Rechnungslegung."
Das Forschungsprojekt nutzt die Umsetzung der EU-Richtlinie 2006/32/EG "Energieeffizienz und Energiedienstleistungen", die eine zeitnahe Information der Endverbraucher über ihren Energieverbrauch und die individuelle Nutzung fordert. Jeder Stromkunde soll so seinen Energieverbrauch selbst beeinflussen und damit auch reduzieren können. Voraussetzung hierfür ist ein flächendeckender Einsatz von Smart Metering-Systemen, die - mit Kommunikationsschnittstellen ausgestattet - auch für ein effektives Energiemanagement insbesondere von dezentralen Energieerzeugern genutzt werden können.
In der praktischen Umsetzung sehen sich die Wissenschaftler jedoch mit einer Fülle von Problemen konfrontiert, die in diesem Zusammenhang ein optimales Zusammenwirken von Zählerdatenverarbeitung, Netzplanung und Netzbetrieb verhindert. Die informationstechnische Vernetzung der Komponenten stellt eine große technologische Herausforderung dar, insbesondere vor dem Hintergrund, dass die Hersteller von elektronischen Zählern zur Zeit unterschiedliche Kommunikationsstandards verwenden. Hierfür gilt es, Standards und Konzepte zu entwickeln und diese in der Praxis zu erproben. Zusätzlich müssen z.B. auch datenschutzrechtliche Implikationen berücksichtigt werden.
Der Projektpartner Energieversorgung Oelde GmbH wird die Inbetriebnahme eines Smart Metering-Netzes mit ca. 150 einzelnen Zählern durchführen. Dieses Pilotprojekt wird als Grundlage für die Feldversuche verwendet. Die zeitnahe automatische Verbrauchsdatenerfassung wird durch die EVB Energie AG im Rahmen dieses Pilotprojekts umgesetzt und realisiert. Die Testumgebung in den Laboren des Lehrstuhls für Energiesysteme und Energiewirtschaft der TU Dortmund bietet die Plattform für die theoretischen Untersuchungen, bevor die Anlagen im Netz installiert werden.
Insgesamt drei Jahre wollen die Projektpartner das System planen, entwickeln und in der Praxis erproben. Die Ergebnisse des Pilotprojekts sollen zu 100% auf herkömmliche Netze unabhängig von ihrer Größe übertragbar sein und sollen deren Wirtschaftlichkeit als auch den effizienten Einsatz der dezentralen Energieerzeugung wesentlich verbessern.
Quelle: TU Dortmund
Die Vorteile einer dezentralen Energieversorgung liegen auf der Hand: Die Nähe zum Endverbraucher ermöglicht verlustarme kurze Übertragungswege. Auch regenerative Energien, z.B. private Solaranlagen, können in dezentralen Stromnetzen effektiv genutzt werden. Das Forschungsprojekt SMEDEA an der TU Dortmund soll jetzt Wege und Standards erarbeiten, wie die gemessenen Daten von neuen elektronischen Zählern, welche ab 2010 auch dem Endkunden angeboten werden müssen (den so genannten Smart Metern) für die Steuerung und den wirtschaftlichen Betrieb vernetzter dezentraler Energieerzeuger genutzt werden können.
TU DdortmunNRW-Wirtschaftsministerin Christa Thoben überreichte heute, am 30. März, persönlich den Bewilligungsbescheid über eine Förderung in Höhe von 370.000 €. SMEDEA (Standardisiertes Smart Metering als Schlüsselfunktion für die Energieeffizienz von dezentralen Energieumwandlungsanlagen) konnte sich im Wettbewerb "Energie.NRW" durchsetzen und wird von Prof. Christian Rehtanz vom Lehrstuhl für Energiesysteme und Energiewirtschaft der Fakultät Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik der TU Dortmund koordiniert. Partner auf Seiten der Industrie sind die EVB Energie AG, einer der marktführenden Dienstleiter für Energieversorgungsunternehmen sowie die Energieversorgung Oelde GmbH.
"Ich freue mich, dieses Smart Metering Projekt heute auf den Weg bringen zu können. Denn, Energieeffizienz braucht auch Verbrauchstransparenz in den Haushalten. Mit intelligenten Zählern machen wir einen wichtigen Schritt hierzu", sagte Wirtschaftsministerin Christa Thoben. "Mit der Entwicklung und dem Einsatz der elektronischen Haushaltszähler eröffnen sich einerseits neue Möglichkeiten, die Effizienz des Stromverbrauchs beim Kunden zu steigern und Anreize zum Einsparen von Strom zu geben. Andererseits bringt es auch den Stromversorgern Vorteile z.B. durch die Fernablesung und eine vereinfachte Rechnungslegung."
Das Forschungsprojekt nutzt die Umsetzung der EU-Richtlinie 2006/32/EG "Energieeffizienz und Energiedienstleistungen", die eine zeitnahe Information der Endverbraucher über ihren Energieverbrauch und die individuelle Nutzung fordert. Jeder Stromkunde soll so seinen Energieverbrauch selbst beeinflussen und damit auch reduzieren können. Voraussetzung hierfür ist ein flächendeckender Einsatz von Smart Metering-Systemen, die - mit Kommunikationsschnittstellen ausgestattet - auch für ein effektives Energiemanagement insbesondere von dezentralen Energieerzeugern genutzt werden können.
In der praktischen Umsetzung sehen sich die Wissenschaftler jedoch mit einer Fülle von Problemen konfrontiert, die in diesem Zusammenhang ein optimales Zusammenwirken von Zählerdatenverarbeitung, Netzplanung und Netzbetrieb verhindert. Die informationstechnische Vernetzung der Komponenten stellt eine große technologische Herausforderung dar, insbesondere vor dem Hintergrund, dass die Hersteller von elektronischen Zählern zur Zeit unterschiedliche Kommunikationsstandards verwenden. Hierfür gilt es, Standards und Konzepte zu entwickeln und diese in der Praxis zu erproben. Zusätzlich müssen z.B. auch datenschutzrechtliche Implikationen berücksichtigt werden.
Der Projektpartner Energieversorgung Oelde GmbH wird die Inbetriebnahme eines Smart Metering-Netzes mit ca. 150 einzelnen Zählern durchführen. Dieses Pilotprojekt wird als Grundlage für die Feldversuche verwendet. Die zeitnahe automatische Verbrauchsdatenerfassung wird durch die EVB Energie AG im Rahmen dieses Pilotprojekts umgesetzt und realisiert. Die Testumgebung in den Laboren des Lehrstuhls für Energiesysteme und Energiewirtschaft der TU Dortmund bietet die Plattform für die theoretischen Untersuchungen, bevor die Anlagen im Netz installiert werden.
Insgesamt drei Jahre wollen die Projektpartner das System planen, entwickeln und in der Praxis erproben. Die Ergebnisse des Pilotprojekts sollen zu 100% auf herkömmliche Netze unabhängig von ihrer Größe übertragbar sein und sollen deren Wirtschaftlichkeit als auch den effizienten Einsatz der dezentralen Energieerzeugung wesentlich verbessern.
Quelle: TU Dortmund
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 36.830.792 von Keiretsu am 24.03.09 00:05:37
Will mich hier nur mal kurz vermerken.
Will mich hier nur mal kurz vermerken.

Why the "Smart Grid" may be a pipe-dream
by Bob Haavind, Editor-at-large, Photovoltaics World
The media has been full of stories about the coming of the "Smart Grid" for electric power, saving energy while incorporating distributed generators such as solar panels. More than $3B was put in the stimulus bill passed earlier this year to kick-start the transition.
But this Smart Grid vision may turn out to be a dream, suggested Howard Berke, founder and executive chairman of Konarka Technologies, Lowell, MA, at a lively PV America session in Philadelphia.
The US national grid is significantly old -- never having been bombed as were many electric systems in Europe and Asia -- and maintenance has been neglected, Berke explained. It would take decades to reach the Smart Grid vision being bandied about, but if the US spends most of its grid investment on maintenance of the existing infrastructure, other countries, even developing nations, may get there first, he warned.
As occasional widespread blackouts have shown, the electric grid in the US is not foolproof. "It's not dumb, but it could be a lot smarter," suggested Katherine Hamilton, president of the Gridwise Alliance, headquartered in Washington DC. Helping this happen is a major focus of her organization. Whereas in the past the grid grew helter-skelter across different regions, the Gridwise Alliance epitomizes current efforts to get a better coordinated, smoother transition to a smarter, much more energy-efficient system.
This process will take many years, even decades, according to Hamilton, "but a lot will happen in the next five years," she added.
The stimulus bill provides $3.5B for the Smart Grid, including $600M for demonstration projects on a 50-50 shared basis, according to Hamilton, but the various state public utility commissions (PUCs) will need to clear the way for this work to go forward. There is also $100M for workforce development, which is important because the electric utility workforce is aging. "There are no more power engineers," Hamilton noted, because EE students over past decades all favored electronics over power engineering.
The Gridwise Alliance, formed in 2003 in collaboration with the Department of Energy (DoE), has more than 85 members, including giants such as IBM, Google, GE, AT&T, and Cisco, but also many small companies along with universities and even investment companies. Every member, no matter how big or small, has the same voice, Hamilton claims.
"It is a consensus-building coalition, not an association," she emphasized, allowing it to take broad-based, unbiased positions. There are various working groups, such as the Smart Grid Policy Center, which does a lot of work with the states, she added. The coalition provides education and awareness of smart grid issues, and co-sponsors reports and white papers.
Hamilton listed a number of key policy initiatives, such a standards for renewable energy and energy efficiency, responses to climate change, transmission and cyber-security. The coalition prefers various measures to be embedded into broader bills, rather than pushing for special legislation, she noted. The group also helps with regulatory work, such as the FERC smart grid docket.
Climate legislation now making its way through Congress with a carbon cap and trade system will force change in energy markets, Hamilton concluded.
Game-changers
The electric grid is already getting a lot smarter through a wide range of utility initiatives, according to Michael Nix, senior market strategist for PJM Interconnection LLC, a group with 550 member companies stretching from the Mid-Atlantic region to Chicago. PJM's members serve more than 51M customers with a peak electric load of more than 145 MW, he said.
Facilities that have been added to the grid allowing functions such as the automation of distribution and substitution, energy storage, smart metering demand for load management, and market monitoring with SCADA and Phasor measurements. Network adapters allow attachments such as smart chargers or storage aggregators. Nix showed photos of long semi-trailers full of grid-scale storage units that can be hooked to the grid this way.
There will be far more energy storage of various kinds in the future, according to Nix, including flywheels, compressed air (which may come from wind), batteries, and capacitor banks with voltage regulators. The largest source of storage, he said, is still hydro -- water pumped up to holding ponds at night that can be released to drive turbines at times when demand is high. Pennsylvania, for example, has a 2000 MW hydro facility, he said.
"Energy storage will be a game-changer for the Smart Grid," added Hamilton.
Konarka's Berke sees big opportunities for innovative storage technologies, with more portable power to add flexibility to the grid -- but he feels that much innovation may be thwarted because of the fragmented approach to the Smart Grid involving state PUCs. Some regions are so far behind on maintenance that it will seem convenient to use new funds just to fix up the existing plant. And many innovative, promising technologies still require experimentation and investment, and some state PUCs may balk at this, he believes.
"If utilities try to drive new technologies, and the PUCs punish them for it, they could drive the system toward mediocrity," Berke said.
"Obama's got it right on the competitiveness of the US vs. developing nations," he added. If we don't push toward advanced grid capabilities we will fall behind other nations, many of them starting with a nearly clean slate.
As an illustration, Berke cited rising demand for power in New England, enough to call for the equivalent of one new power plant a year, but none are being built. Then he cited press accounts suggesting that $1 trillion might be spent over the next 10 years building new high power transmission lines to carry wind-generated power from the Dakotas to the Northeast. That money could be much better spent on distributed PV solar within the region, he believes, and that distributed generation would lead to a much better balanced power system.
Nix of PJM cited many solar PV projects already being initiated by electric utilities. Some are solar energy "farms," such as a 25MW facility of PS&G, with another 10MW at other sites. The New Jersey Housing Authority is planning 43MW of solar on rooftops, and the Exelon GROWS landfill site in Pennsylvania is the fifth biggest PV facility in the US, he said. Nix also showed how 4KW solar panels are now being hung on electric poles, already providing about 40MW of unmetered power into neighborhoods.
Rising power usage can also be tempered as consumers buy more smart appliances that save energy, he said. In the future homes will have meters that will show price variations during the day, so that users can make informed choices, like running the dishwasher at 2am.
Nix said that PJM is participating in the Mid-Atlantic Grid Interactive Car Consortium (MAGICC) with the U. of Delaware and a consortium including research institutes, other universities, and auto companies as well as electric utilities. The group is preparing for an upsurge in electric cars, which probably would be recharging batteries from 1-3am, and also would need scattered electric charging stations.
"Technology is not the challenge," agreed Berke, who suggested that IP (Internet Protocol) chips could be embedded in everything -- and maybe even everybody. Such implants are already common in pet dogs, he commented. What will be needed are the will, the national policies, investment, and the ability of all elements of the Smart Grid to work smoothly together.
Putting the "D" in DC
Technology allowing DC (direct current) power to be available from wall sockets is one thing he feels will make sense in the future. "Already 40% of the base load is DC," he said, and many more appliances are being made with DC brushless motors. Even further, lighting will be shifting to LEDs in the future, greatly increasing the DC load. Right now AC/DC converters are needed for everything that runs on DC -- he said that he tallied up 128 of them for the electronics and appliances just in his own home.
"This is a huge waste of energy," he pointed out.
An engineer in the session rose to challenge Berke's call for transmitting power as DC rather than AC. Long-distance, high-voltage transmission requires AC, he said, and there are safety factors favoring AC for wall plugs.
Berke countered that there are places in the world with both AC and DC outlets, such as Spain and the Netherlands. It has been shown, he said, that DC can be moved safely in micronetworks, and distributed energy sources like PV panels could directly supply DC power to them.
While the session showed that the electric grid will definitely get smarter, the question is how fast and how widely this will happen, and whether useful innovation with be fostered or thwarted along the way.
by Bob Haavind, Editor-at-large, Photovoltaics World
The media has been full of stories about the coming of the "Smart Grid" for electric power, saving energy while incorporating distributed generators such as solar panels. More than $3B was put in the stimulus bill passed earlier this year to kick-start the transition.
But this Smart Grid vision may turn out to be a dream, suggested Howard Berke, founder and executive chairman of Konarka Technologies, Lowell, MA, at a lively PV America session in Philadelphia.
The US national grid is significantly old -- never having been bombed as were many electric systems in Europe and Asia -- and maintenance has been neglected, Berke explained. It would take decades to reach the Smart Grid vision being bandied about, but if the US spends most of its grid investment on maintenance of the existing infrastructure, other countries, even developing nations, may get there first, he warned.
As occasional widespread blackouts have shown, the electric grid in the US is not foolproof. "It's not dumb, but it could be a lot smarter," suggested Katherine Hamilton, president of the Gridwise Alliance, headquartered in Washington DC. Helping this happen is a major focus of her organization. Whereas in the past the grid grew helter-skelter across different regions, the Gridwise Alliance epitomizes current efforts to get a better coordinated, smoother transition to a smarter, much more energy-efficient system.
This process will take many years, even decades, according to Hamilton, "but a lot will happen in the next five years," she added.
The stimulus bill provides $3.5B for the Smart Grid, including $600M for demonstration projects on a 50-50 shared basis, according to Hamilton, but the various state public utility commissions (PUCs) will need to clear the way for this work to go forward. There is also $100M for workforce development, which is important because the electric utility workforce is aging. "There are no more power engineers," Hamilton noted, because EE students over past decades all favored electronics over power engineering.
The Gridwise Alliance, formed in 2003 in collaboration with the Department of Energy (DoE), has more than 85 members, including giants such as IBM, Google, GE, AT&T, and Cisco, but also many small companies along with universities and even investment companies. Every member, no matter how big or small, has the same voice, Hamilton claims.
"It is a consensus-building coalition, not an association," she emphasized, allowing it to take broad-based, unbiased positions. There are various working groups, such as the Smart Grid Policy Center, which does a lot of work with the states, she added. The coalition provides education and awareness of smart grid issues, and co-sponsors reports and white papers.
Hamilton listed a number of key policy initiatives, such a standards for renewable energy and energy efficiency, responses to climate change, transmission and cyber-security. The coalition prefers various measures to be embedded into broader bills, rather than pushing for special legislation, she noted. The group also helps with regulatory work, such as the FERC smart grid docket.
Climate legislation now making its way through Congress with a carbon cap and trade system will force change in energy markets, Hamilton concluded.
Game-changers
The electric grid is already getting a lot smarter through a wide range of utility initiatives, according to Michael Nix, senior market strategist for PJM Interconnection LLC, a group with 550 member companies stretching from the Mid-Atlantic region to Chicago. PJM's members serve more than 51M customers with a peak electric load of more than 145 MW, he said.
Facilities that have been added to the grid allowing functions such as the automation of distribution and substitution, energy storage, smart metering demand for load management, and market monitoring with SCADA and Phasor measurements. Network adapters allow attachments such as smart chargers or storage aggregators. Nix showed photos of long semi-trailers full of grid-scale storage units that can be hooked to the grid this way.
There will be far more energy storage of various kinds in the future, according to Nix, including flywheels, compressed air (which may come from wind), batteries, and capacitor banks with voltage regulators. The largest source of storage, he said, is still hydro -- water pumped up to holding ponds at night that can be released to drive turbines at times when demand is high. Pennsylvania, for example, has a 2000 MW hydro facility, he said.
"Energy storage will be a game-changer for the Smart Grid," added Hamilton.
Konarka's Berke sees big opportunities for innovative storage technologies, with more portable power to add flexibility to the grid -- but he feels that much innovation may be thwarted because of the fragmented approach to the Smart Grid involving state PUCs. Some regions are so far behind on maintenance that it will seem convenient to use new funds just to fix up the existing plant. And many innovative, promising technologies still require experimentation and investment, and some state PUCs may balk at this, he believes.
"If utilities try to drive new technologies, and the PUCs punish them for it, they could drive the system toward mediocrity," Berke said.
"Obama's got it right on the competitiveness of the US vs. developing nations," he added. If we don't push toward advanced grid capabilities we will fall behind other nations, many of them starting with a nearly clean slate.
As an illustration, Berke cited rising demand for power in New England, enough to call for the equivalent of one new power plant a year, but none are being built. Then he cited press accounts suggesting that $1 trillion might be spent over the next 10 years building new high power transmission lines to carry wind-generated power from the Dakotas to the Northeast. That money could be much better spent on distributed PV solar within the region, he believes, and that distributed generation would lead to a much better balanced power system.
Nix of PJM cited many solar PV projects already being initiated by electric utilities. Some are solar energy "farms," such as a 25MW facility of PS&G, with another 10MW at other sites. The New Jersey Housing Authority is planning 43MW of solar on rooftops, and the Exelon GROWS landfill site in Pennsylvania is the fifth biggest PV facility in the US, he said. Nix also showed how 4KW solar panels are now being hung on electric poles, already providing about 40MW of unmetered power into neighborhoods.
Rising power usage can also be tempered as consumers buy more smart appliances that save energy, he said. In the future homes will have meters that will show price variations during the day, so that users can make informed choices, like running the dishwasher at 2am.
Nix said that PJM is participating in the Mid-Atlantic Grid Interactive Car Consortium (MAGICC) with the U. of Delaware and a consortium including research institutes, other universities, and auto companies as well as electric utilities. The group is preparing for an upsurge in electric cars, which probably would be recharging batteries from 1-3am, and also would need scattered electric charging stations.
"Technology is not the challenge," agreed Berke, who suggested that IP (Internet Protocol) chips could be embedded in everything -- and maybe even everybody. Such implants are already common in pet dogs, he commented. What will be needed are the will, the national policies, investment, and the ability of all elements of the Smart Grid to work smoothly together.
Putting the "D" in DC
Technology allowing DC (direct current) power to be available from wall sockets is one thing he feels will make sense in the future. "Already 40% of the base load is DC," he said, and many more appliances are being made with DC brushless motors. Even further, lighting will be shifting to LEDs in the future, greatly increasing the DC load. Right now AC/DC converters are needed for everything that runs on DC -- he said that he tallied up 128 of them for the electronics and appliances just in his own home.
"This is a huge waste of energy," he pointed out.
An engineer in the session rose to challenge Berke's call for transmitting power as DC rather than AC. Long-distance, high-voltage transmission requires AC, he said, and there are safety factors favoring AC for wall plugs.
Berke countered that there are places in the world with both AC and DC outlets, such as Spain and the Netherlands. It has been shown, he said, that DC can be moved safely in micronetworks, and distributed energy sources like PV panels could directly supply DC power to them.
While the session showed that the electric grid will definitely get smarter, the question is how fast and how widely this will happen, and whether useful innovation with be fostered or thwarted along the way.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 36.828.997 von Scar am 23.03.09 19:57:34Hallo!
Super, dass ich diesen Thread hier gefunden habe. Welche Smart Grid Aktien habt ihr so auf der WL? Ich bin derzeit in Echelon investiert und habe ein Auge auf PowerSecure und PSI geworfen. Bei der PSI AG überlege ich jetzt einzusteigen. Ich hatte zuletzt interessante Gespräche mit RWE Mitarbeitern (nicht die ganz hohe Führungsebene, aber schon etwas höhere Positionen) und dort setzt man voll auf Smart Grid. Darum habe sich RWE ja auch bei PSI eingekauft. Und auch Cisco Systems oder General Electric wollen ja in diesem Markt ein Wörtchen mitreden.
Kurz zu Echelon: Ein Umsatz von knapp 117 Mio. US$ (2008) wird dort derzeit mit einer Market Cap. von knapp 370 Mio. US$ bezahlt, ergo ein KUV von etwas über 3. Bisher schreibt die Firma zwar noch rote Zahlen (EBITDA: -23,66 Mio. US$), aber ich denke die Gewinnschwelle ist nicht mehr so fern. Und mit knapp 88 Mio. US$ Cash ist man gut durchfinanziert. Deshalb habe ich mich bisher für Echelon entschieden, zumal mir deren Technologie gefällt und mich auch der Chart überzeugt hat. Was meint Ihr zu Echelon?
LG Enzo
PS: Mehr Infos zu Echelon gibts auch unter: http://tr.im/utkQ
Super, dass ich diesen Thread hier gefunden habe. Welche Smart Grid Aktien habt ihr so auf der WL? Ich bin derzeit in Echelon investiert und habe ein Auge auf PowerSecure und PSI geworfen. Bei der PSI AG überlege ich jetzt einzusteigen. Ich hatte zuletzt interessante Gespräche mit RWE Mitarbeitern (nicht die ganz hohe Führungsebene, aber schon etwas höhere Positionen) und dort setzt man voll auf Smart Grid. Darum habe sich RWE ja auch bei PSI eingekauft. Und auch Cisco Systems oder General Electric wollen ja in diesem Markt ein Wörtchen mitreden.
Kurz zu Echelon: Ein Umsatz von knapp 117 Mio. US$ (2008) wird dort derzeit mit einer Market Cap. von knapp 370 Mio. US$ bezahlt, ergo ein KUV von etwas über 3. Bisher schreibt die Firma zwar noch rote Zahlen (EBITDA: -23,66 Mio. US$), aber ich denke die Gewinnschwelle ist nicht mehr so fern. Und mit knapp 88 Mio. US$ Cash ist man gut durchfinanziert. Deshalb habe ich mich bisher für Echelon entschieden, zumal mir deren Technologie gefällt und mich auch der Chart überzeugt hat. Was meint Ihr zu Echelon?
LG Enzo
PS: Mehr Infos zu Echelon gibts auch unter: http://tr.im/utkQ
Hallo,
ich bin auf diesen Smart Grid Thread aufmerksam geworden. Leider ist er nicht gerade gut besucht.
Bin selber in Echelon und diversen anderen investiert.
Eigentlich schade das die Aktien der Zukunft die die Internetaktien und die Photovoltaikaktien ablösen werden so wenig besucht bzw. diskutiert werden.
Aber es ist schön mal von anfang an dabei zu sein.
ich bin auf diesen Smart Grid Thread aufmerksam geworden. Leider ist er nicht gerade gut besucht.
Bin selber in Echelon und diversen anderen investiert.
Eigentlich schade das die Aktien der Zukunft die die Internetaktien und die Photovoltaikaktien ablösen werden so wenig besucht bzw. diskutiert werden.
Aber es ist schön mal von anfang an dabei zu sein.

Meine Favoriten sind klar Comverge und Echelon.

aus einem neuen Report von GTM:
1.3.1 Power-oriented (“fast”) energy storage will grow quickly in the near to mid
term but will be constrained in the long term by a modest total market size.
Power-oriented (“fast”) energy storage is poised for strong near- to mid-term growth.
Its most signifi cant component, the frequency regulation market, has recently been
opened up for direct entry by energy storage in some ISO regions of the U.S. with
additional ISOs anticipated. This means that energy storage can secure contracts for
grid frequency regulation on the open market and the owner of the system will get compensated in cash. This capture-able, all cash benefi t stream makes obtaining
compensation for an energy storage system much less complicated than many other
implementations. New highly robust, moderate cost lithium-ion batteries are able to
provide this service cost effectively and are beginning to be deployed successfully in a
few regions of the U.S. and in Chile. This trend is expected to continue and accelerate
with the addition of new renewable resources on the grid and further decreases in the
cost of lithium-ion batteries. Production of fast energy storage in 2009 is estimated at
49 MW and is expected to grow to 479 MW or $500 million in 2015. The total market
size for fast energy storage is estimated at about 7,137 MW total for the U.S. and
about 37,828 MW for the world.
1.3.2 Energy-oriented (load shifting) energy storage has a massive total market
size, however it is only beginning to be ready to be exploited.
Energy-oriented (load shifting) energy storage offers a number of potentially lucrative
opportunities for implementations that strategically combine applications. While
wholesale load shifting is sometimes discussed, it does not create enough value to
be cost effective on its own in most situations right now. There are, however, many
existing strategic load shifting implementations that are or nearly are cost effective.
The challenge with these implementations is that some of the benefi ts are generated
as non-cash benefi ts which can be diffi cult to monetize or the benefi ts come from
bundling different value streams, which are feasible technically but challenging to
accrue to one entity for regulatory reasons. In some parts of the world, like Japan,
where the value created from single applications is higher or utilities are more easily
able to accrue value from the multiple benefi ts generated, sodium sulfur (NaS) load
shifting energy storage has already gained a good foothold and has recently gained
favor in other countries like France and the UAE, though only small pilot installations
exist in the U.S. New fl ow battery technology, particularly zinc-bromide, has recently
become more cost effective than NaS for many implementations and is expected
to grow to surpass NaS installations by 2015. Advanced lead acid batteries are
also expected to show impressive growth due to further cost reduction and plentiful
installed manufacturing capacity able to be repurposed from traditional lead acid
batteries. The currently variable government regulation climate for LS storage is
expected to somewhat limit near-term growth, but more amenable regulation and
mass production cost reduction for LS storage are expected to drive strong mid to
long term growth. In 2009, an estimated 151 MW were produced, but in 2015, 1,066
MW are expected to be produced with revenues of $1,596 million. The total market
size is estimated at 85,000 MW in the U.S. and 450,000 MW in the world.
1.3.3 Government regulation will play a large role in determining the rate of the roll
out of all energy storage.
Government regulation is a critical driver of or inhibitor to energy storage technology
penetrating the market. Recent history and current trends in government regulation
are favorable for energy storage, especially for frequency regulation in the U.S. Recent
political action in favor of renewable power, including energy storage tax incentives
in bill S.1091 recently proposed in the U.S. Congress, is paving the way for a more
favorable environment for LS in the U.S. However, compensation for utilities will also
have to change in order to fully spur progress for LS energy storage, including areas
like allowable inclusions in the rate base, risk compensation and ownership of assets
useful for both T&D and generation. Other countries with differing structures for utility
compensation and greater LS storage penetration, like Japan, France and the UAE,
may offer ideas for how to encourage its penetration in the U.S.
1.3.1 Power-oriented (“fast”) energy storage will grow quickly in the near to mid
term but will be constrained in the long term by a modest total market size.
Power-oriented (“fast”) energy storage is poised for strong near- to mid-term growth.
Its most signifi cant component, the frequency regulation market, has recently been
opened up for direct entry by energy storage in some ISO regions of the U.S. with
additional ISOs anticipated. This means that energy storage can secure contracts for
grid frequency regulation on the open market and the owner of the system will get compensated in cash. This capture-able, all cash benefi t stream makes obtaining
compensation for an energy storage system much less complicated than many other
implementations. New highly robust, moderate cost lithium-ion batteries are able to
provide this service cost effectively and are beginning to be deployed successfully in a
few regions of the U.S. and in Chile. This trend is expected to continue and accelerate
with the addition of new renewable resources on the grid and further decreases in the
cost of lithium-ion batteries. Production of fast energy storage in 2009 is estimated at
49 MW and is expected to grow to 479 MW or $500 million in 2015. The total market
size for fast energy storage is estimated at about 7,137 MW total for the U.S. and
about 37,828 MW for the world.
1.3.2 Energy-oriented (load shifting) energy storage has a massive total market
size, however it is only beginning to be ready to be exploited.
Energy-oriented (load shifting) energy storage offers a number of potentially lucrative
opportunities for implementations that strategically combine applications. While
wholesale load shifting is sometimes discussed, it does not create enough value to
be cost effective on its own in most situations right now. There are, however, many
existing strategic load shifting implementations that are or nearly are cost effective.
The challenge with these implementations is that some of the benefi ts are generated
as non-cash benefi ts which can be diffi cult to monetize or the benefi ts come from
bundling different value streams, which are feasible technically but challenging to
accrue to one entity for regulatory reasons. In some parts of the world, like Japan,
where the value created from single applications is higher or utilities are more easily
able to accrue value from the multiple benefi ts generated, sodium sulfur (NaS) load
shifting energy storage has already gained a good foothold and has recently gained
favor in other countries like France and the UAE, though only small pilot installations
exist in the U.S. New fl ow battery technology, particularly zinc-bromide, has recently
become more cost effective than NaS for many implementations and is expected
to grow to surpass NaS installations by 2015. Advanced lead acid batteries are
also expected to show impressive growth due to further cost reduction and plentiful
installed manufacturing capacity able to be repurposed from traditional lead acid
batteries. The currently variable government regulation climate for LS storage is
expected to somewhat limit near-term growth, but more amenable regulation and
mass production cost reduction for LS storage are expected to drive strong mid to
long term growth. In 2009, an estimated 151 MW were produced, but in 2015, 1,066
MW are expected to be produced with revenues of $1,596 million. The total market
size is estimated at 85,000 MW in the U.S. and 450,000 MW in the world.
1.3.3 Government regulation will play a large role in determining the rate of the roll
out of all energy storage.
Government regulation is a critical driver of or inhibitor to energy storage technology
penetrating the market. Recent history and current trends in government regulation
are favorable for energy storage, especially for frequency regulation in the U.S. Recent
political action in favor of renewable power, including energy storage tax incentives
in bill S.1091 recently proposed in the U.S. Congress, is paving the way for a more
favorable environment for LS in the U.S. However, compensation for utilities will also
have to change in order to fully spur progress for LS energy storage, including areas
like allowable inclusions in the rate base, risk compensation and ownership of assets
useful for both T&D and generation. Other countries with differing structures for utility
compensation and greater LS storage penetration, like Japan, France and the UAE,
may offer ideas for how to encourage its penetration in the U.S.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 37.871.717 von R-BgO am 28.08.09 12:02:39und diese Firmen werden im Report behandelt (die unterstrichenen habe ich im Depot):
6 APPENDICES 92
6.1 Industry Roster – Zinc Bromide Flow Batteries 92
6.1.1 Net Power Technology 92
6.1.2 Premium Power 93
6.1.3 RedFlow 95
6.1.4 ZBB Energy 97
6.2 Industry Roster – Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries 99
6.2.1 Cellenium 99
6.2.2 Cellstrom 100
6.2.3 Prudent Energy [formerly VRB Power Inc. and Sumitomo Electric Industries (SEI)] 101
6.3 Industry Roster – Other Flow Batteries 104
6.3.1 Deeya 104
6.3.2 EnerVault 105
6.3.3 EnStorage
6.3.4 Plurion Systems 107
6.3.5 Primus Power Corporation 108
6.4 Industry Roster – Advanced Lead Acid Batteries 109
6.4.1 Axion Power International/Exide 109
6.4.2 C&D Technologies 111
6.4.3 East Penn/Furukawa 112
6.4.4 Other Advanced Lead Acid Battery Manufacturers 113
6.5 Industry Roster – Sodium Batteries 113
6.5.1 General Electric 113
6.5.2 NGK Insulators 114
6.6 Industry Roster – Lithium-Ion Batteries 117
6.6.1 A123 Systems 117
6.6.2 Altair Nanotechnologies 119
6.6.3 BYD Company Limited 121
6.6.4 Saft 122
6.6.5 Valance 124
6.6.6 Other Lithium-Ion Battery Manufacturers 125
6.7 Industry Roster – Lithium-Air Batteries 125
6.7.1 IBM 125
6.8 Industry Roster – Flywheels 126
6.8.1 Beacon Power 126
6.8.2 Pentadyne 128
6.8.3 Power Tree 129
6.8.4 Other Flywheel Manufacturers
6 APPENDICES 92
6.1 Industry Roster – Zinc Bromide Flow Batteries 92
6.1.1 Net Power Technology 92
6.1.2 Premium Power 93
6.1.3 RedFlow 95
6.1.4 ZBB Energy 97
6.2 Industry Roster – Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries 99
6.2.1 Cellenium 99
6.2.2 Cellstrom 100
6.2.3 Prudent Energy [formerly VRB Power Inc. and Sumitomo Electric Industries (SEI)] 101
6.3 Industry Roster – Other Flow Batteries 104
6.3.1 Deeya 104
6.3.2 EnerVault 105
6.3.3 EnStorage
6.3.4 Plurion Systems 107
6.3.5 Primus Power Corporation 108
6.4 Industry Roster – Advanced Lead Acid Batteries 109
6.4.1 Axion Power International/Exide 109
6.4.2 C&D Technologies 111
6.4.3 East Penn/Furukawa 112
6.4.4 Other Advanced Lead Acid Battery Manufacturers 113
6.5 Industry Roster – Sodium Batteries 113
6.5.1 General Electric 113
6.5.2 NGK Insulators 114
6.6 Industry Roster – Lithium-Ion Batteries 117
6.6.1 A123 Systems 117
6.6.2 Altair Nanotechnologies 119
6.6.3 BYD Company Limited 121
6.6.4 Saft 122
6.6.5 Valance 124
6.6.6 Other Lithium-Ion Battery Manufacturers 125
6.7 Industry Roster – Lithium-Air Batteries 125
6.7.1 IBM 125
6.8 Industry Roster – Flywheels 126
6.8.1 Beacon Power 126
6.8.2 Pentadyne 128
6.8.3 Power Tree 129
6.8.4 Other Flywheel Manufacturers
Alcatel-Lucent Your Smart Grid Partner:
http://www.mthink.com/utilities/alcatel-lucent-0
Programm des E-Energy Jahreskongresses 2009
Elektrizität ist das Rückgrat von Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft. Steigende Nachfrage, die Rohstoffverknappung und der Klimawandel stellen das Energiesystem vor große Herausforderungen.
Es müssen neue Lösungen gefunden werden, die den Anforderungen des Wandels zu liberalisierten Märkten, zu dezentralen und volatilen Erzeugungsstrukturen sowie zur Elektromobilität Rechnung tragen - und ein Höchstmaß an Wirtschaftlichkeit, Versorgungssicherheit und Umweltverträglichkeit sicherstellen. Informations- und Kommunikationstechnologien (IKT) werden dabei eine zentrale Rolle spielen: Mit ihrer Hilfe können intelligente Energiesysteme betrieben werden, in denen viele Erzeugungsanlagen - zunehmend auch solche mit erneuerbaren Energien - mit den Einrichtungen der Stromnetze und den Strom verbrauchenden Endgeräten kommunizieren.
Viele der Initiativen und Aktivitäten in diesem Bereich werden international unter dem Begriff "Smart Grids" zusammengefasst. "Smart" steht in diesem Zusammenhang für die intelligente Nutzung aller zur Verfügung stehenden Ressourcen sowie für die Optimierung und Integration des Gesamtsystems der Elektrizitätsversorgung - von der Gewinnung des Stroms über die Speicherung, den Transport, die Verteilung bis hin zur effizienten Verwendung.
In Deutschland werden die Smart Grid-Aktivitäten unter dem Dach der Förderinitiative "E-Energy - IKTbasiertes Energiesystem der Zukunft" gebündelt, die auf dem IT-Gipfel von der Bundeskanzlerin zum nationalen Leuchtturm-Projekt erklärt wurde. E-Energy - das heißt "Smart Grids - Made in Germany".
Donnerstag, 26. November 2009
14:00 Uhr
Eröffnung des E-Energy Jahreskongresses
Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Technologie
Grußworte seitens der Partnerländer:
- Eidgenössisches Departement für Umwelt, Verkehr, Energie und Kommunikation, Schweiz
- Bundesministeriums für Verkehr, Innovation und Technologie, Österreich
15:00 Uhr
Impulsvortrag
15:30 Uhr
Podiumsgespräch: Schöne neue Welt der IKT- und Energiewirtschaft?
- Dr. Werner Brinker, EWE AG, Vorsitzender des Vorstands
- Prof. Henning Kagermann, acatech - Deutsche
Akademie der Technikwissenschaft e. V., Präsident
- Dr. Holger Krawinkel, Bundesverband Verbraucherzentralen e. V.
- Dr. Jochen Kreusel, Energietechnische Gesellschaft (ETG) im VDE, Vorstand
- Dr. Rudolf Strohmeier, EU Kommission
- Dr. Christian Urbanke, Bundesverband der Deutschen Industrie e. V.
- Alf Henryk Wulf, Alcatel-Lucent-Deutschland AG
http://www.mthink.com/utilities/alcatel-lucent-0
Programm des E-Energy Jahreskongresses 2009
Elektrizität ist das Rückgrat von Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft. Steigende Nachfrage, die Rohstoffverknappung und der Klimawandel stellen das Energiesystem vor große Herausforderungen.
Es müssen neue Lösungen gefunden werden, die den Anforderungen des Wandels zu liberalisierten Märkten, zu dezentralen und volatilen Erzeugungsstrukturen sowie zur Elektromobilität Rechnung tragen - und ein Höchstmaß an Wirtschaftlichkeit, Versorgungssicherheit und Umweltverträglichkeit sicherstellen. Informations- und Kommunikationstechnologien (IKT) werden dabei eine zentrale Rolle spielen: Mit ihrer Hilfe können intelligente Energiesysteme betrieben werden, in denen viele Erzeugungsanlagen - zunehmend auch solche mit erneuerbaren Energien - mit den Einrichtungen der Stromnetze und den Strom verbrauchenden Endgeräten kommunizieren.
Viele der Initiativen und Aktivitäten in diesem Bereich werden international unter dem Begriff "Smart Grids" zusammengefasst. "Smart" steht in diesem Zusammenhang für die intelligente Nutzung aller zur Verfügung stehenden Ressourcen sowie für die Optimierung und Integration des Gesamtsystems der Elektrizitätsversorgung - von der Gewinnung des Stroms über die Speicherung, den Transport, die Verteilung bis hin zur effizienten Verwendung.
In Deutschland werden die Smart Grid-Aktivitäten unter dem Dach der Förderinitiative "E-Energy - IKTbasiertes Energiesystem der Zukunft" gebündelt, die auf dem IT-Gipfel von der Bundeskanzlerin zum nationalen Leuchtturm-Projekt erklärt wurde. E-Energy - das heißt "Smart Grids - Made in Germany".
Donnerstag, 26. November 2009
14:00 Uhr
Eröffnung des E-Energy Jahreskongresses
Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Technologie
Grußworte seitens der Partnerländer:
- Eidgenössisches Departement für Umwelt, Verkehr, Energie und Kommunikation, Schweiz
- Bundesministeriums für Verkehr, Innovation und Technologie, Österreich
15:00 Uhr
Impulsvortrag
15:30 Uhr
Podiumsgespräch: Schöne neue Welt der IKT- und Energiewirtschaft?
- Dr. Werner Brinker, EWE AG, Vorsitzender des Vorstands
- Prof. Henning Kagermann, acatech - Deutsche
Akademie der Technikwissenschaft e. V., Präsident
- Dr. Holger Krawinkel, Bundesverband Verbraucherzentralen e. V.
- Dr. Jochen Kreusel, Energietechnische Gesellschaft (ETG) im VDE, Vorstand
- Dr. Rudolf Strohmeier, EU Kommission
- Dr. Christian Urbanke, Bundesverband der Deutschen Industrie e. V.
- Alf Henryk Wulf, Alcatel-Lucent-Deutschland AG
The Past and Future of Smart Grid 3 comments
by: Greentech Media January 03, 2010 | about: ITRI / GE / PCG / GOOG / MSFT / IBM / CSCO / ORCL / WHR / ENOC / COMV
Greentech Media
By Michael Kanellos
Smart grid may be the most hyped words of 2009 in the green tech space, but that doesn't mean there isn't a lot of hard, cold cash behind the hype. Will 2010 bring a bursting of a smart grid bubble, or a continued unfolding of its promise to provide a framework for renewable energy, efficiency and conservation programs to come? Let these top stories of 2009 be your guide.
1. Government as Market Maker: There's no doubt that smart grid projects wouldn't have seen the success they've seen without a big helping hand from the public sector. In the United States, the $3.9 billion in Department of Energy smart grid stimulus grants given out this fall was widely seen as critical for unlocking private funds largely left on the sidelines amidst an ongoing financial crisis and economic downturn.
But along with the carrots of government grants and incentives are the sticks of mandates to come. The European Union and individual nations have set deadlines for bringing two-way communications and control to their electricity grids.
2. The Rise of the Smart Meter: 2009's smart grid story has largely been one of smart meters - two-way communicating meters that allow utilities to remotely monitor customer energy use and share that information with them. In the United States, stimulus funding was expected to lead to about 18 million smart meters being deployed around the country, adding to the nearly 10 million meters expected to be installed by the end of the year. Worldwide penetration could reach 250 million by 2015, according to some predictions.
That's helped the big five smart meter makers – Itron (ITRI), Landis+Gyr, Elster, Sensus and General Electric (GE) - but it's been even more helpful to the host of startups that offer new technologies to network those smart meters. The most prominent of those include SmartSynch, Trilliant and the big winner so far, Silver Spring Networks.
3. Silver Spring Networks – Smart Grid's First IPO? Silver Spring Networks has been plugging away at standards-based networking for smart meters for close to a decade, but 2009 was its year to shine. With contracts announced this year with utilities including Oklahoma Gas & Electric, Sacramento Municipal Utility District, AEP, Florida Power & Light and others, the Redwood City, Calif.-based startup is on a roll – and with a recent $100 million investment boosting its VC haul to some $275 million to date, it's on a short list of greentech companies expected to announce an IPO in the coming year or so.
4. The Smart Meter Backlash: Smart meters haven't enjoyed wholesale acceptance by utility customers, however. 2009 saw the first inklings of a backlash against the costs imposed on utility customers to roll out the two-way meters, in the form of an uprising by customers of Pacific Gas & Electric in Central California, who complained that their power bills skyrocketed after smart meters were installed in their homes. While PG&E (PCG) denies it's at fault, the resulting lawsuit has put utilities on alert that they'll be asked to give customers a cut of whatever cost reductions they're hoping to achieve for themselves.
5. Home Area Networking – The First Smart Grid Bubble? Smart meters aren't supposed to begin and end as a laborsaving measure for utilities. Almost all the rate cases supporting the cost of installing them point to home area networks to come – communications links between the meters and home devices to monitor, measure and cut down on energy use.
That kind of gadgetry is a natural for startups, and dozens – some of the more prominent include Tendril Networks, Control4, EnergyHub, Onzo, OpenPeak, AlertMe and Energy Inc. – have entered the field. Many have landed utility contracts, though to date only for pilot projects. Two have already been bought this year – Greenbox by smart grid networking company Silver Spring Networks and Lixar by smart grid software company GridPoint.
But at the same time, utilities are struggling with the same questions that have faced energy-smart homes for the decade or more they've been attempted – their cost. Most homeowners aren't willing to spend much money – no more than $100 or so, according to most estimates – on tracking their energy use, but installing real-time controls and communications to a wide range of household electricity loads can cost quite a bit more than that.
6. The Smart Grid Party Crashers: And then, of course, there's the entry of the IT giants to make every startup nervous – or desirous of partnerships that could lead to acquisitions. Both Google (GOOG) and Microsoft (MSFT) have staked their claim to the home energy management market with their own products – and both plan to offer them for free. Cisco (CSCO) has made a major push into the smart grid space on the networking front, and enterprise software giants such as IBM and Oracle (ORCL) are also staking claims.
At the same time, telecommunications companies are making moves to include energy management as part of their home broadband offerings. That's part of a broader effort to offer public wireless networks as an alternative to the predominant model, at least in North America, for utilities to build and operate their own communications networks. Home security and entertainment providers are also adding energy management, with hopes of connecting to utilities in the future.
And that's not to mention the smart appliances being rolled out by General Electric, Whirlpool (WHR) and a host of Asian conglomerates. All these washers, dryers, water heaters, refrigerators and ovens will need to connect with utility and customers communications systems to be effective. Just how all these systems will interconnect remains a big question.
7. The Evolving Demand Response Landscape: While the public's smart grid attention has focused on smart meters and home energy network, the business of curtailing energy use at commercial and industrial sites is already well developed. It's called demand response, and it's spawned the first IPOs in the smart grid space in the form of demand response aggregators Enernoc (ENOC) and Comverge (COMV).
Demand response now accounts for about 41 gigawatts of power use that can be turned down to help utilities manage their peak demand loads today. But the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission projects the potential for peak power reduction could reach 188 gigawatts - and because cutting peak demand eases the need to build new fossil fuel-fired power plants to meet that peak, it's a big target of utilities and government alike.
What's next for demand response? New frontiers include the largely untapped residential market - perhaps enabled by smart meters – as well as new open standards-based demand response technologies that could be more broadly replicated across new smart grid networks.
8. Distribution and Transmission Up Next: Not all smart grid systems are visible to the untrained eye. Upgrading distribution and transmission grids with communications and controls could help utilities squeeze up to 10 percent more efficiency out of their existing generation capacity, according to the Electric Power Research Institute. Those savings can come from preventative maintenance and replacement, shortening outage times, and optimizing grid voltages, among other sources.
At the same time, managing the massive growth in renewable solar, wind and geothermal energy that will be needed to cut the nation's carbon emissions will put new pressures on the grid. Hundreds of billions of dollars will need to be spent on new transmission lines to carry Midwest wind power and Southwest solar power to load centers, according to studies - which opens up new business models for startups.
And at the neighborhood level, distribution grids will need a whole host of new technologies to manage the increase in rooftop solar panels, demand response-enabled homes, and future plug-in hybrid and electric vehicles that will soon place unprecedented new pressures on utilities built on the model of delivering power from central generation stations to millions of customers.
9. Smart Grid 2.0: All of these emerging smart grid technologies will be a lot more useful if they can be linked together. That's the idea for the next surge in the industry – a whole ecosystem of smart architectures, stretching from generations sources and transmission lines to the wireless and wired networks in utility customers' homes and businesses.
GridPoint, one of the more prominent – and well-funded – of the smart grid startups out there, is centered on delivering this kind of integrated offering to utility customers. Its approach has included buying up a host of startups offering vehicle charging, home energy monitoring and industrial and commercial energy management, indicating the breadth of functions it hopes to provide.
What will the smart grid of the future look like? Duke Energy (DUK) CEO Jim Rogers speaks of a utility-managed system that orchestrates smart meters, solar panels, batteries, demand response systems and plug-in vehicle chargers to serve as "virtual power plants" scattered throughout a utility service territory.
But if a utility can orchestrate multiple systems to save money, why can't utility customers? That's the idea behind microgrids, or localized integrated systems that can maximize the same efficiencies to take advantage of the benefits – namely, selling power back to the grid.
10. The Standards Battle: We've saved this one for last, because it's the most complicated issue facing the smart grid industry – and it's developing amidst on-the-ground deployments of technologies both proprietary and open, all of it needing to interoperate with decades-old utility systems. Making the shift to a standards-based architectures for the smart grid is a focus of an ongoing project by the National Institute of Standards and Technology and a host of industry players with their own technologies to champion. Similar processes are unfolding in Europe.
Of course, technologies that have taken an early lead in smart grid deployments today aren't likely to be completely abandoned. At the same time, companies offering open standards-based solutions are sure to press their advantages over more proprietary systems.
by: Greentech Media January 03, 2010 | about: ITRI / GE / PCG / GOOG / MSFT / IBM / CSCO / ORCL / WHR / ENOC / COMV
Greentech Media
By Michael Kanellos
Smart grid may be the most hyped words of 2009 in the green tech space, but that doesn't mean there isn't a lot of hard, cold cash behind the hype. Will 2010 bring a bursting of a smart grid bubble, or a continued unfolding of its promise to provide a framework for renewable energy, efficiency and conservation programs to come? Let these top stories of 2009 be your guide.
1. Government as Market Maker: There's no doubt that smart grid projects wouldn't have seen the success they've seen without a big helping hand from the public sector. In the United States, the $3.9 billion in Department of Energy smart grid stimulus grants given out this fall was widely seen as critical for unlocking private funds largely left on the sidelines amidst an ongoing financial crisis and economic downturn.
But along with the carrots of government grants and incentives are the sticks of mandates to come. The European Union and individual nations have set deadlines for bringing two-way communications and control to their electricity grids.
2. The Rise of the Smart Meter: 2009's smart grid story has largely been one of smart meters - two-way communicating meters that allow utilities to remotely monitor customer energy use and share that information with them. In the United States, stimulus funding was expected to lead to about 18 million smart meters being deployed around the country, adding to the nearly 10 million meters expected to be installed by the end of the year. Worldwide penetration could reach 250 million by 2015, according to some predictions.
That's helped the big five smart meter makers – Itron (ITRI), Landis+Gyr, Elster, Sensus and General Electric (GE) - but it's been even more helpful to the host of startups that offer new technologies to network those smart meters. The most prominent of those include SmartSynch, Trilliant and the big winner so far, Silver Spring Networks.
3. Silver Spring Networks – Smart Grid's First IPO? Silver Spring Networks has been plugging away at standards-based networking for smart meters for close to a decade, but 2009 was its year to shine. With contracts announced this year with utilities including Oklahoma Gas & Electric, Sacramento Municipal Utility District, AEP, Florida Power & Light and others, the Redwood City, Calif.-based startup is on a roll – and with a recent $100 million investment boosting its VC haul to some $275 million to date, it's on a short list of greentech companies expected to announce an IPO in the coming year or so.
4. The Smart Meter Backlash: Smart meters haven't enjoyed wholesale acceptance by utility customers, however. 2009 saw the first inklings of a backlash against the costs imposed on utility customers to roll out the two-way meters, in the form of an uprising by customers of Pacific Gas & Electric in Central California, who complained that their power bills skyrocketed after smart meters were installed in their homes. While PG&E (PCG) denies it's at fault, the resulting lawsuit has put utilities on alert that they'll be asked to give customers a cut of whatever cost reductions they're hoping to achieve for themselves.
5. Home Area Networking – The First Smart Grid Bubble? Smart meters aren't supposed to begin and end as a laborsaving measure for utilities. Almost all the rate cases supporting the cost of installing them point to home area networks to come – communications links between the meters and home devices to monitor, measure and cut down on energy use.
That kind of gadgetry is a natural for startups, and dozens – some of the more prominent include Tendril Networks, Control4, EnergyHub, Onzo, OpenPeak, AlertMe and Energy Inc. – have entered the field. Many have landed utility contracts, though to date only for pilot projects. Two have already been bought this year – Greenbox by smart grid networking company Silver Spring Networks and Lixar by smart grid software company GridPoint.
But at the same time, utilities are struggling with the same questions that have faced energy-smart homes for the decade or more they've been attempted – their cost. Most homeowners aren't willing to spend much money – no more than $100 or so, according to most estimates – on tracking their energy use, but installing real-time controls and communications to a wide range of household electricity loads can cost quite a bit more than that.
6. The Smart Grid Party Crashers: And then, of course, there's the entry of the IT giants to make every startup nervous – or desirous of partnerships that could lead to acquisitions. Both Google (GOOG) and Microsoft (MSFT) have staked their claim to the home energy management market with their own products – and both plan to offer them for free. Cisco (CSCO) has made a major push into the smart grid space on the networking front, and enterprise software giants such as IBM and Oracle (ORCL) are also staking claims.
At the same time, telecommunications companies are making moves to include energy management as part of their home broadband offerings. That's part of a broader effort to offer public wireless networks as an alternative to the predominant model, at least in North America, for utilities to build and operate their own communications networks. Home security and entertainment providers are also adding energy management, with hopes of connecting to utilities in the future.
And that's not to mention the smart appliances being rolled out by General Electric, Whirlpool (WHR) and a host of Asian conglomerates. All these washers, dryers, water heaters, refrigerators and ovens will need to connect with utility and customers communications systems to be effective. Just how all these systems will interconnect remains a big question.
7. The Evolving Demand Response Landscape: While the public's smart grid attention has focused on smart meters and home energy network, the business of curtailing energy use at commercial and industrial sites is already well developed. It's called demand response, and it's spawned the first IPOs in the smart grid space in the form of demand response aggregators Enernoc (ENOC) and Comverge (COMV).
Demand response now accounts for about 41 gigawatts of power use that can be turned down to help utilities manage their peak demand loads today. But the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission projects the potential for peak power reduction could reach 188 gigawatts - and because cutting peak demand eases the need to build new fossil fuel-fired power plants to meet that peak, it's a big target of utilities and government alike.
What's next for demand response? New frontiers include the largely untapped residential market - perhaps enabled by smart meters – as well as new open standards-based demand response technologies that could be more broadly replicated across new smart grid networks.
8. Distribution and Transmission Up Next: Not all smart grid systems are visible to the untrained eye. Upgrading distribution and transmission grids with communications and controls could help utilities squeeze up to 10 percent more efficiency out of their existing generation capacity, according to the Electric Power Research Institute. Those savings can come from preventative maintenance and replacement, shortening outage times, and optimizing grid voltages, among other sources.
At the same time, managing the massive growth in renewable solar, wind and geothermal energy that will be needed to cut the nation's carbon emissions will put new pressures on the grid. Hundreds of billions of dollars will need to be spent on new transmission lines to carry Midwest wind power and Southwest solar power to load centers, according to studies - which opens up new business models for startups.
And at the neighborhood level, distribution grids will need a whole host of new technologies to manage the increase in rooftop solar panels, demand response-enabled homes, and future plug-in hybrid and electric vehicles that will soon place unprecedented new pressures on utilities built on the model of delivering power from central generation stations to millions of customers.
9. Smart Grid 2.0: All of these emerging smart grid technologies will be a lot more useful if they can be linked together. That's the idea for the next surge in the industry – a whole ecosystem of smart architectures, stretching from generations sources and transmission lines to the wireless and wired networks in utility customers' homes and businesses.
GridPoint, one of the more prominent – and well-funded – of the smart grid startups out there, is centered on delivering this kind of integrated offering to utility customers. Its approach has included buying up a host of startups offering vehicle charging, home energy monitoring and industrial and commercial energy management, indicating the breadth of functions it hopes to provide.
What will the smart grid of the future look like? Duke Energy (DUK) CEO Jim Rogers speaks of a utility-managed system that orchestrates smart meters, solar panels, batteries, demand response systems and plug-in vehicle chargers to serve as "virtual power plants" scattered throughout a utility service territory.
But if a utility can orchestrate multiple systems to save money, why can't utility customers? That's the idea behind microgrids, or localized integrated systems that can maximize the same efficiencies to take advantage of the benefits – namely, selling power back to the grid.
10. The Standards Battle: We've saved this one for last, because it's the most complicated issue facing the smart grid industry – and it's developing amidst on-the-ground deployments of technologies both proprietary and open, all of it needing to interoperate with decades-old utility systems. Making the shift to a standards-based architectures for the smart grid is a focus of an ongoing project by the National Institute of Standards and Technology and a host of industry players with their own technologies to champion. Similar processes are unfolding in Europe.
Of course, technologies that have taken an early lead in smart grid deployments today aren't likely to be completely abandoned. At the same time, companies offering open standards-based solutions are sure to press their advantages over more proprietary systems.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 38.662.265 von R-BgO am 04.01.10 17:59:55http://seekingalpha.com/article/180624-the-past-and-future-o…
Lithium-ion Batteries Are Still Not Ready for Prime Time 41 comments
by: John Petersen February 05, 2010 | about: ENS / XIDE / CHP / ZBB / AXPW.OB / AONE / HEV / ALTI / VLNC
John Petersen
Last month the DOE released the 2009 Annual Progress Report for its Energy Storage Research and Development Vehicle Technologies Program. Like the 2008 Annual Progress Report I discussed in a February 2009 article titled DOE Reports That Lithium-ion Batteries Are Not Ready For Prime Time, this new report is a relatively upbeat assessment of lithium-ion battery research and development that once again provides a stark reality check for investors in energy storage stocks. In Section III of the Report, which focuses primarily on meat and potatoes issues like R&D objectives, technical barriers, technical targets and recent accomplishments; the DOE summarized the objectives and technical barriers as follows:
Objectives
* By 2010, develop an electric drive train energy storage device with a 15-year life at 300 Wh with a discharge power of 25 kW for 18 seconds and a cost of $20/kw.
* By 2014, develop a PHEV battery that enables a 40 mile all-electric range and costs $3,400.
Technical Barriers
* Cost – The current cost of Li-based batteries (the most promising chemistry) is approximately a factor of three-five too high on a kWh basis for PHEVs and approximately a factor of two too high on a kW basis for HEVs. The main cost drivers being addressed are the high costs of raw materials and materials processing, cell and module packaging, and manufacturing.
* Performance – The performance advancements required include the need for much higher energy densities to meet the volume and weight requirements, especially for the 40 mile PHEV system, and to reduce the number of cells in the battery (thus reducing system cost).
* Abuse Tolerance – Many Li batteries are not intrinsically tolerant to abusive conditions such as a short circuit (including an internal short circuit), overcharge, over-discharge, crush, or exposure to fire and / or other high temperature environments. The use of Li chemistry in the larger [PHEV] batteries increases the urgency to address these issues.
* Life – The ability to attain a 15-year life with 300,000 HEV cycles or 5,000 EV cycles is unproven and is anticipated to be difficult.
The recent accomplishments section includes about 85 pages of discussion on 25 pending research, development, analysis and testing projects that are nowhere near complete. It's clear from the Report that the DOE is coordinating a massively complex and expensive drive to improve lithium-ion batteries to a point where they will be cost-effective in transportation applications. It's equally clear that the effort has a long way to go before we're able to accurately assess the likelihood that all or any of the pending R&D projects will result in innovations that can survive the transition from the laboratory bench to the factory floor. The R&D is critically important, but favorable results are not guaranteed, costs are likely to exceed budgets by a wide margin and timing is anybody's guess. The only certainties are it won't be soon and it won't be cheap.
When I started writing this blog, my central thesis was that energy storage is the beating heart of cleantech and is destined to become a major investment theme that will endure for decades. Storage is an essential, enabling technology for wind and solar power, an efficient smart grid and emerging transportation applications. It's also a difficult industry that's constrained by laws of chemistry, requires massive volumes of commodity raw materials and can only be described as capital intensive heavy manufacturing. That means we can reasonably expect steady incremental progress over a the long-term.
However, the game changing 'Moore's Law' type advances we've come to expect from information and communications technology are simply not going to happen in energy storage. To borrow a concept from John Mauldin, my favorite Seeking Alpha contributor, energy storage is a 'muddle through' industry that will progress in baby steps that take years, instead of quantum leaps that happen overnight.
When you cut through the happy talk and issue advocacy, energy storage is all about minimizing waste and making inherently variable energy sources more reliable. If waste is cheaper than storage, waste will be the rational choice for over 95% of the population who believe the green in their wallet is more important than the green in their cocktail party conversation. Given the nature of the industry, the law of economic gravity will prevail and the cheapest solution that can do the work will earn the lion's share of the market. The future of energy storage is bright, but it's going to be a long hard slog through the swamp and I can comfortably guarantee that we'll never see teenagers on Sunset Boulevard popping the hood to show off and compare their battery packs.
One of the most difficult parts of blogging on the energy storage sector is explaining that when it comes to investing, entry price and timing are the only things that matter. My favorite example is one everybody knows. I've been a Macintosh user since 1988 and had countless arguments over the years about the technical superiority and ease of use of the Mac OS. The contrary argument, of course, was that products from Apple (AAPL) were too expensive compared to budget priced products that used Microsoft's (MSFT) operating system. Over the last few years Apple products have surged to the forefront as they pared prices to more competitive levels and continued their tradition of technical excellence. The following chart from Yahoo! Finance shows the 25 year comparative stock market performance of the two companies.
As a computer user, I've always insisted on owning Apple. As an investor, the better path would have been to own Microsoft for the first 19 years and then shift to Apple for the last six.
In the long-term, I expect every company that brings a cost-effective energy storage product to market to have more business than it can handle. For the next five to ten years, I expect the biggest gains to accrue in companies like Enersys (ENS), Exide Technologies (XIDE), C&D Technologies (CHP), ZBB Energy (ZBB), and Axion Power (AXPW.OB), that make objectively cheap products today to satisfy immediate needs.
When, and if, advanced battery developers like A123 Systems (AONE), Ener1 (HEV), Altair Nanotechnologies (ALTI) and Valence Technologies (VLNC) succeed in their individual and collective efforts to make objectively expensive products affordable, portfolio adjustments to reflect the new realities will be essential. But if Apple vs. Microsoft teaches anything, it's that cheap beats cool until cool becomes cheap. Promises don't matter. Price tags do.
Last year I said that I'm a simple-minded creature and believe that little things like costs and benefits matter. When the brand new annual progress report from the DOE concludes that:
* Lithium-ion batteries will not be cost-effective in HEVs unless somebody finds a way to slash costs by 50%; and
* Lithium-ion batteries will not be cost-effective in PHEVs unless somebody finds a way to slash costs by 67% to 80%;
I believe them. When I combine the DOE's conclusions with a recent opinion from the National Research Council that the DOE's price objectives "beyond 2012 are extremely aggressive and are unlikely to be reached by the target date or even for a significant time beyond" cruel reality seems obvious: lithium-ion batteries are still not ready for prime time and the plug-in vehicle frenzy is leading investors and the public down a garden path that can only end in disaster like most technology du jour schemes that are conceived in the halls of government and then sold to the public as the next big thing, including:
25 years ago Methanol
15 years ago Electric Vehicles
10 years ago HEVs and Electric Vehicles
5 years ago Hydrogen Fuel Cells
3 years ago Ethanol and Biofuels
Today PHEVs and Electric Vehicles
2012 Here Be Dragons
Will Rogers said , "There are three kinds of men. The one that learns by reading. The few who learn by observation. The rest of them have to pee on the electric fence for themselves." Albert Einstein reportedly defined insanity as doing the same thing over and over again and expecting different results. When will investors learn that technical hype originating from government with a chorus of support from heavily subsidized companies rarely works out well?
Disclosure: Author is a former director of Axion Power International (AXPW.OB) and owns a substantial long position in its stock. He also owns small long positions in Exide Technologies (XIDE), C&D Technologies (CHP) and ZBB Energy (ZBB).
by: John Petersen February 05, 2010 | about: ENS / XIDE / CHP / ZBB / AXPW.OB / AONE / HEV / ALTI / VLNC
John Petersen
Last month the DOE released the 2009 Annual Progress Report for its Energy Storage Research and Development Vehicle Technologies Program. Like the 2008 Annual Progress Report I discussed in a February 2009 article titled DOE Reports That Lithium-ion Batteries Are Not Ready For Prime Time, this new report is a relatively upbeat assessment of lithium-ion battery research and development that once again provides a stark reality check for investors in energy storage stocks. In Section III of the Report, which focuses primarily on meat and potatoes issues like R&D objectives, technical barriers, technical targets and recent accomplishments; the DOE summarized the objectives and technical barriers as follows:
Objectives
* By 2010, develop an electric drive train energy storage device with a 15-year life at 300 Wh with a discharge power of 25 kW for 18 seconds and a cost of $20/kw.
* By 2014, develop a PHEV battery that enables a 40 mile all-electric range and costs $3,400.
Technical Barriers
* Cost – The current cost of Li-based batteries (the most promising chemistry) is approximately a factor of three-five too high on a kWh basis for PHEVs and approximately a factor of two too high on a kW basis for HEVs. The main cost drivers being addressed are the high costs of raw materials and materials processing, cell and module packaging, and manufacturing.
* Performance – The performance advancements required include the need for much higher energy densities to meet the volume and weight requirements, especially for the 40 mile PHEV system, and to reduce the number of cells in the battery (thus reducing system cost).
* Abuse Tolerance – Many Li batteries are not intrinsically tolerant to abusive conditions such as a short circuit (including an internal short circuit), overcharge, over-discharge, crush, or exposure to fire and / or other high temperature environments. The use of Li chemistry in the larger [PHEV] batteries increases the urgency to address these issues.
* Life – The ability to attain a 15-year life with 300,000 HEV cycles or 5,000 EV cycles is unproven and is anticipated to be difficult.
The recent accomplishments section includes about 85 pages of discussion on 25 pending research, development, analysis and testing projects that are nowhere near complete. It's clear from the Report that the DOE is coordinating a massively complex and expensive drive to improve lithium-ion batteries to a point where they will be cost-effective in transportation applications. It's equally clear that the effort has a long way to go before we're able to accurately assess the likelihood that all or any of the pending R&D projects will result in innovations that can survive the transition from the laboratory bench to the factory floor. The R&D is critically important, but favorable results are not guaranteed, costs are likely to exceed budgets by a wide margin and timing is anybody's guess. The only certainties are it won't be soon and it won't be cheap.
When I started writing this blog, my central thesis was that energy storage is the beating heart of cleantech and is destined to become a major investment theme that will endure for decades. Storage is an essential, enabling technology for wind and solar power, an efficient smart grid and emerging transportation applications. It's also a difficult industry that's constrained by laws of chemistry, requires massive volumes of commodity raw materials and can only be described as capital intensive heavy manufacturing. That means we can reasonably expect steady incremental progress over a the long-term.
However, the game changing 'Moore's Law' type advances we've come to expect from information and communications technology are simply not going to happen in energy storage. To borrow a concept from John Mauldin, my favorite Seeking Alpha contributor, energy storage is a 'muddle through' industry that will progress in baby steps that take years, instead of quantum leaps that happen overnight.
When you cut through the happy talk and issue advocacy, energy storage is all about minimizing waste and making inherently variable energy sources more reliable. If waste is cheaper than storage, waste will be the rational choice for over 95% of the population who believe the green in their wallet is more important than the green in their cocktail party conversation. Given the nature of the industry, the law of economic gravity will prevail and the cheapest solution that can do the work will earn the lion's share of the market. The future of energy storage is bright, but it's going to be a long hard slog through the swamp and I can comfortably guarantee that we'll never see teenagers on Sunset Boulevard popping the hood to show off and compare their battery packs.
One of the most difficult parts of blogging on the energy storage sector is explaining that when it comes to investing, entry price and timing are the only things that matter. My favorite example is one everybody knows. I've been a Macintosh user since 1988 and had countless arguments over the years about the technical superiority and ease of use of the Mac OS. The contrary argument, of course, was that products from Apple (AAPL) were too expensive compared to budget priced products that used Microsoft's (MSFT) operating system. Over the last few years Apple products have surged to the forefront as they pared prices to more competitive levels and continued their tradition of technical excellence. The following chart from Yahoo! Finance shows the 25 year comparative stock market performance of the two companies.
As a computer user, I've always insisted on owning Apple. As an investor, the better path would have been to own Microsoft for the first 19 years and then shift to Apple for the last six.
In the long-term, I expect every company that brings a cost-effective energy storage product to market to have more business than it can handle. For the next five to ten years, I expect the biggest gains to accrue in companies like Enersys (ENS), Exide Technologies (XIDE), C&D Technologies (CHP), ZBB Energy (ZBB), and Axion Power (AXPW.OB), that make objectively cheap products today to satisfy immediate needs.
When, and if, advanced battery developers like A123 Systems (AONE), Ener1 (HEV), Altair Nanotechnologies (ALTI) and Valence Technologies (VLNC) succeed in their individual and collective efforts to make objectively expensive products affordable, portfolio adjustments to reflect the new realities will be essential. But if Apple vs. Microsoft teaches anything, it's that cheap beats cool until cool becomes cheap. Promises don't matter. Price tags do.
Last year I said that I'm a simple-minded creature and believe that little things like costs and benefits matter. When the brand new annual progress report from the DOE concludes that:
* Lithium-ion batteries will not be cost-effective in HEVs unless somebody finds a way to slash costs by 50%; and
* Lithium-ion batteries will not be cost-effective in PHEVs unless somebody finds a way to slash costs by 67% to 80%;
I believe them. When I combine the DOE's conclusions with a recent opinion from the National Research Council that the DOE's price objectives "beyond 2012 are extremely aggressive and are unlikely to be reached by the target date or even for a significant time beyond" cruel reality seems obvious: lithium-ion batteries are still not ready for prime time and the plug-in vehicle frenzy is leading investors and the public down a garden path that can only end in disaster like most technology du jour schemes that are conceived in the halls of government and then sold to the public as the next big thing, including:
25 years ago Methanol
15 years ago Electric Vehicles
10 years ago HEVs and Electric Vehicles
5 years ago Hydrogen Fuel Cells
3 years ago Ethanol and Biofuels
Today PHEVs and Electric Vehicles
2012 Here Be Dragons
Will Rogers said , "There are three kinds of men. The one that learns by reading. The few who learn by observation. The rest of them have to pee on the electric fence for themselves." Albert Einstein reportedly defined insanity as doing the same thing over and over again and expecting different results. When will investors learn that technical hype originating from government with a chorus of support from heavily subsidized companies rarely works out well?
Disclosure: Author is a former director of Axion Power International (AXPW.OB) and owns a substantial long position in its stock. He also owns small long positions in Exide Technologies (XIDE), C&D Technologies (CHP) and ZBB Energy (ZBB).
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 38.896.415 von R-BgO am 06.02.10 14:47:11http://seekingalpha.com/article/186910-lithium-ion-batteries…
Posted on 19. April 2010 by Keith Redfern, GE Energy
Renewables and Grid Integration Needs Smarter Thinking
Gearing up the grid for renewables integration.
London, UK [Renewable Energy World Magazine]
You would be hard pressed to name an industry or technology that's gone virtually unchanged since the 19th Century and yet which is still thriving today. But that is the story of the electricity transmission grid.
Growing energy demand and increasing global temperatures are a double challenge. With today’s energy infrastructure, the only way to meet this increasing demand is to boost the use of carbon-producing power generation – a roadmap to disaster.
Concerns about the environment have utilities companies and legislators looking towards clean energy alternatives. Members of the European Union have agreed to increase renewable energy generation by 20% and reduce carbon emissions by 20% by 2020, but today’s infrastructure is unable to maximize the benefits of renewable resources. Wind and solar resources are tacked onto the grid without being integrated with other generation or optimized as a reliable first-tier energy source. Grid congestion can act as a barrier to full utilization and renewable variability can cause reliability challenges at relatively high levels of penetration.
The solution is a smarter grid infrastructure which can improve the future of both energy demand and energy generation. Smart grid technologies hold the potential to do just that, creating efficiencies and lowering electricity consumption, while at the same time making it easier to connect renewable energy sources into the power grid.
Solutions Already Exist for a Better Grid
The good news is that the technologies needed to create this smarter grid and make wind, solar and biomass energies a greater part of the generation mix already exist. These technologies are capable of fully integrating renewable generation into the grid efficiently and reliably, through demand response programs, Energy and Distribution Management Systems (EMS and DMS) and energy storage technology.
National Grid, one of the world’s major utilities, serves over 16 million households in the UK and the US. The company sees renewable energy sources as a large part of meeting the formidable challenge ahead. We will draw an ever-increasing proportion of our energy needs from cleaner, renewable sources, much of which will be sourced locally, according to Steve Holliday, National Grid’s CEO. National Grid is just one example of what we will need to see around the world with renewable energy in the generation mix. From funding considerations to regulatory reform, we need government support to be firmly behind the move to renewable energy.
Putting Smart Grid Technology to Work
But for renewable generated power to fill the need outlined by the EU, the smart grid technologies at our disposal must be applied. Renewable energy is very different from the ways we generate power now. We need to update our infrastructure to accommodate the differences and capitalize on the advantages. Inventors have created the solutions, we need to employ them.
Traditionally, electricity has flowed one way; from a power station to a customer. However, as more renewable energy is generated by alternative sources, power will be entering the network from multiple locations, including the distribution network, otherwise known as distributed generation.
The current grid was not designed with multi-directional power flows in mind. Smart grid technologies will enable the optimization and use of high percentages of renewable power and prepare the grid to integrate widespread distributed generation.
Renewable energy has two distinct profiles for entering the grid: distributed installations and large-scale generation plants. Smart grid technologies exist to handle both scenarios.
Distributed generation can be located throughout the grid, with deployment of small-scale installations of wind turbines or rooftop solar. To integrate this power into the grid effectively, utilities need to update their DMS software to accommodate the two-way power flow. With the potential of these smaller-scale deployments of renewable generation being located throughout the grid — even at as small a scale as individual household wind turbines — grid network management needs to be much smarter than it was in the past. Utilities throughout the world are installing smart grid DMS systems to integrate this energy and use it to replace fossil fuel generated power. For example, 13 of the 14 energy distribution companies in the UK already use a GE DMS system designed to handle distributed generation and capitalize on renewable resources located virtually anywhere along the grid.
Large-scale renewable generation such as wind farms and concentrated solar installations are capable of delivering large amounts of energy from a centralized location, similar to traditional generation but with some challenging differences. As the government encourages the growth of these renewable energy plants, smart grid technologies are needed to improve the high-voltage transmission from the plants to neighbourhood distribution grids. Energy Management Systems in a smart grid scenario have the facility to monitor the capacity on lines and maximize the efficiency of transmission. Since renewable sources are not capable of constant, predictable output, a smart EMS system can optimize the power transmitted. This maximizes capacity, reduces the need for additional transmission lines and reduces wasted power.
Constant Power from a Variable Resource
Renewable power is not constant, but smart grid technologies can help to even out the spikes in power availability from renewable resources. For instance, GE smart grid integrated forecasting technologies introduced at large wind plants in Hawaii help predict the amount of renewable power which will be available.
Integrating that information with energy management and distribution systems enables utilities to free up the capacity needed on power lines when generation will be high. It also tells them when other generation sources will be needed to fill in the gaps. Smart grid renewable prediction also tells utilities when there may be more renewable potential than is needed or than the available power lines can accommodate, preventing unnecessary production and congestion on the lines.
Two-way power flow, sophisticated controls and grid automation technologies can help bring wind, solar and other alternative energy solutions safely into the distribution grid and move it where it’s needed when it’s needed.
Smart grid technologies can also help change the way we look at power storage. Today we generate power to meet real time needs; we need more power, we turn on more turbines. Smart grid storage technologies can help maximize renewable energy capacity by allowing us to generate and store renewable power whenever the resource is readily available — whether there is demand on the line or not. Battery banks and controls can hold renewable overcapacity and release it into the grid as it is needed.
The goal of increasing the efficiency of our grid is also very achievable with smart grid technologies, particularly as an awful lot of the energy put into the power grid is wasted.
That shouldn’t be a surprise because the grid was actually designed to need overcapacity or waste to operate. The lights go on when you flip the switch because there is more than enough power on the lines. Smart grid solutions can introduce better, two-way communication within the grid. That means utilities have a better idea what the real demand for power is, so they can produce and deliver an amount of energy that more closely mirrors that actual demand, reducing power losses and waste.
With a smarter grid, utilities will be able to control power more effectively to be more efficient, squeezing as much performance as possible out of the existing grid, allowing costly infrastructure upgrades to be deferred longer and stretching the effectiveness of fuel supplies.
With new demand response technology, utilities will be able to explore how reducing a consumer’s energy ‘load’ or demand might help the utility to manage variations in renewable energy production. For example, consumers may ‘opt-in’ to utility programmes which automatically adjust high energy consuming devices, such as water heaters, during periods of peak demand and higher prices.
Smarter Grid Moves Beyond Buildings
How does a wind-powered car sound? A solar scooter? With smart grid technologies they really are possible, because the smart grid makes Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) practical realities.
Cars being introduced today can travel the average daily commute of most people on a single battery charge and smart grid technologies can make that charging a snap. Dynamic pricing and automated charging stations will charge the cars overnight, when the demand and costs of electricity are lower. And, with a higher concentration of renewable energy in the mix, it will be as though wind energy is powering our automobiles. Wind power is also strongest at night, so we can put the clean and green power that’s being generated directly into our cars and onto our cleaner roads.
All of this new technology means more jobs. For example, in the UK, the government’s new 2008 Planning Act will make it easier to plan, approve and fund the big projects that are needed to modernize the grid. And that modernization will mean jobs. The UK Energy and Utilities Skills Sector Council has conducted research which suggests there will be a need for an additional 9000 highly skilled workers in the industry in the next five years.
Shared Ideas and a Common Vision Needed
The smart grid can literally change our world. We already see how technologies exist to incorporate more renewable energy into the power mix that runs our economy and powers our everyday lives. The technologies for change already exist. They are being used every day in utilities around the world. Many of the technologies are already being used, but we need more. We need to work together to incorporate these technologies throughout our infrastructure. We need to change policies and regulations to make it worthwhile for utilities and consumers to embrace new ways of doing business.
For example, many of the UK’s energy policies and regulations were created to address the needs and realities of outmoded operating models. We need to do more to move our regulation and our focus to deploying solutions today. Technology companies, utilities, academia and government need to work together to create a new roadmap to smart grid success. It needs to be an open, dynamic vision that includes open systems and shared platforms, so that innovations and new solutions can come from anyone and everyone.
Finally, we need to view the smart grid as the holistic, end-to-end energy solution that it is. Integrating renewable generation is but one element of a truly successful smart grid. Using the world of smart grid technologies can raise the efficiency, increase the reliability, decrease the waste and dramatically shrink energy’s carbon footprint.
Keith Redfearn is the EMEA & India regional general manager for Transmission & Distribution, GE Energy. Email: neil.gazeley@ge.com
Renewables and Grid Integration Needs Smarter Thinking
Gearing up the grid for renewables integration.
London, UK [Renewable Energy World Magazine]
You would be hard pressed to name an industry or technology that's gone virtually unchanged since the 19th Century and yet which is still thriving today. But that is the story of the electricity transmission grid.
Growing energy demand and increasing global temperatures are a double challenge. With today’s energy infrastructure, the only way to meet this increasing demand is to boost the use of carbon-producing power generation – a roadmap to disaster.
Concerns about the environment have utilities companies and legislators looking towards clean energy alternatives. Members of the European Union have agreed to increase renewable energy generation by 20% and reduce carbon emissions by 20% by 2020, but today’s infrastructure is unable to maximize the benefits of renewable resources. Wind and solar resources are tacked onto the grid without being integrated with other generation or optimized as a reliable first-tier energy source. Grid congestion can act as a barrier to full utilization and renewable variability can cause reliability challenges at relatively high levels of penetration.
The solution is a smarter grid infrastructure which can improve the future of both energy demand and energy generation. Smart grid technologies hold the potential to do just that, creating efficiencies and lowering electricity consumption, while at the same time making it easier to connect renewable energy sources into the power grid.
Solutions Already Exist for a Better Grid
The good news is that the technologies needed to create this smarter grid and make wind, solar and biomass energies a greater part of the generation mix already exist. These technologies are capable of fully integrating renewable generation into the grid efficiently and reliably, through demand response programs, Energy and Distribution Management Systems (EMS and DMS) and energy storage technology.
National Grid, one of the world’s major utilities, serves over 16 million households in the UK and the US. The company sees renewable energy sources as a large part of meeting the formidable challenge ahead. We will draw an ever-increasing proportion of our energy needs from cleaner, renewable sources, much of which will be sourced locally, according to Steve Holliday, National Grid’s CEO. National Grid is just one example of what we will need to see around the world with renewable energy in the generation mix. From funding considerations to regulatory reform, we need government support to be firmly behind the move to renewable energy.
Putting Smart Grid Technology to Work
But for renewable generated power to fill the need outlined by the EU, the smart grid technologies at our disposal must be applied. Renewable energy is very different from the ways we generate power now. We need to update our infrastructure to accommodate the differences and capitalize on the advantages. Inventors have created the solutions, we need to employ them.
Traditionally, electricity has flowed one way; from a power station to a customer. However, as more renewable energy is generated by alternative sources, power will be entering the network from multiple locations, including the distribution network, otherwise known as distributed generation.
The current grid was not designed with multi-directional power flows in mind. Smart grid technologies will enable the optimization and use of high percentages of renewable power and prepare the grid to integrate widespread distributed generation.
Renewable energy has two distinct profiles for entering the grid: distributed installations and large-scale generation plants. Smart grid technologies exist to handle both scenarios.
Distributed generation can be located throughout the grid, with deployment of small-scale installations of wind turbines or rooftop solar. To integrate this power into the grid effectively, utilities need to update their DMS software to accommodate the two-way power flow. With the potential of these smaller-scale deployments of renewable generation being located throughout the grid — even at as small a scale as individual household wind turbines — grid network management needs to be much smarter than it was in the past. Utilities throughout the world are installing smart grid DMS systems to integrate this energy and use it to replace fossil fuel generated power. For example, 13 of the 14 energy distribution companies in the UK already use a GE DMS system designed to handle distributed generation and capitalize on renewable resources located virtually anywhere along the grid.
Large-scale renewable generation such as wind farms and concentrated solar installations are capable of delivering large amounts of energy from a centralized location, similar to traditional generation but with some challenging differences. As the government encourages the growth of these renewable energy plants, smart grid technologies are needed to improve the high-voltage transmission from the plants to neighbourhood distribution grids. Energy Management Systems in a smart grid scenario have the facility to monitor the capacity on lines and maximize the efficiency of transmission. Since renewable sources are not capable of constant, predictable output, a smart EMS system can optimize the power transmitted. This maximizes capacity, reduces the need for additional transmission lines and reduces wasted power.
Constant Power from a Variable Resource
Renewable power is not constant, but smart grid technologies can help to even out the spikes in power availability from renewable resources. For instance, GE smart grid integrated forecasting technologies introduced at large wind plants in Hawaii help predict the amount of renewable power which will be available.
Integrating that information with energy management and distribution systems enables utilities to free up the capacity needed on power lines when generation will be high. It also tells them when other generation sources will be needed to fill in the gaps. Smart grid renewable prediction also tells utilities when there may be more renewable potential than is needed or than the available power lines can accommodate, preventing unnecessary production and congestion on the lines.
Two-way power flow, sophisticated controls and grid automation technologies can help bring wind, solar and other alternative energy solutions safely into the distribution grid and move it where it’s needed when it’s needed.
Smart grid technologies can also help change the way we look at power storage. Today we generate power to meet real time needs; we need more power, we turn on more turbines. Smart grid storage technologies can help maximize renewable energy capacity by allowing us to generate and store renewable power whenever the resource is readily available — whether there is demand on the line or not. Battery banks and controls can hold renewable overcapacity and release it into the grid as it is needed.
The goal of increasing the efficiency of our grid is also very achievable with smart grid technologies, particularly as an awful lot of the energy put into the power grid is wasted.
That shouldn’t be a surprise because the grid was actually designed to need overcapacity or waste to operate. The lights go on when you flip the switch because there is more than enough power on the lines. Smart grid solutions can introduce better, two-way communication within the grid. That means utilities have a better idea what the real demand for power is, so they can produce and deliver an amount of energy that more closely mirrors that actual demand, reducing power losses and waste.
With a smarter grid, utilities will be able to control power more effectively to be more efficient, squeezing as much performance as possible out of the existing grid, allowing costly infrastructure upgrades to be deferred longer and stretching the effectiveness of fuel supplies.
With new demand response technology, utilities will be able to explore how reducing a consumer’s energy ‘load’ or demand might help the utility to manage variations in renewable energy production. For example, consumers may ‘opt-in’ to utility programmes which automatically adjust high energy consuming devices, such as water heaters, during periods of peak demand and higher prices.
Smarter Grid Moves Beyond Buildings
How does a wind-powered car sound? A solar scooter? With smart grid technologies they really are possible, because the smart grid makes Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) practical realities.
Cars being introduced today can travel the average daily commute of most people on a single battery charge and smart grid technologies can make that charging a snap. Dynamic pricing and automated charging stations will charge the cars overnight, when the demand and costs of electricity are lower. And, with a higher concentration of renewable energy in the mix, it will be as though wind energy is powering our automobiles. Wind power is also strongest at night, so we can put the clean and green power that’s being generated directly into our cars and onto our cleaner roads.
All of this new technology means more jobs. For example, in the UK, the government’s new 2008 Planning Act will make it easier to plan, approve and fund the big projects that are needed to modernize the grid. And that modernization will mean jobs. The UK Energy and Utilities Skills Sector Council has conducted research which suggests there will be a need for an additional 9000 highly skilled workers in the industry in the next five years.
Shared Ideas and a Common Vision Needed
The smart grid can literally change our world. We already see how technologies exist to incorporate more renewable energy into the power mix that runs our economy and powers our everyday lives. The technologies for change already exist. They are being used every day in utilities around the world. Many of the technologies are already being used, but we need more. We need to work together to incorporate these technologies throughout our infrastructure. We need to change policies and regulations to make it worthwhile for utilities and consumers to embrace new ways of doing business.
For example, many of the UK’s energy policies and regulations were created to address the needs and realities of outmoded operating models. We need to do more to move our regulation and our focus to deploying solutions today. Technology companies, utilities, academia and government need to work together to create a new roadmap to smart grid success. It needs to be an open, dynamic vision that includes open systems and shared platforms, so that innovations and new solutions can come from anyone and everyone.
Finally, we need to view the smart grid as the holistic, end-to-end energy solution that it is. Integrating renewable generation is but one element of a truly successful smart grid. Using the world of smart grid technologies can raise the efficiency, increase the reliability, decrease the waste and dramatically shrink energy’s carbon footprint.
Keith Redfearn is the EMEA & India regional general manager for Transmission & Distribution, GE Energy. Email: neil.gazeley@ge.com
Batteries Are Included in KB Home and BYD's Solar House
[ 2010-3-26]
California's KB Home and China's BYD Co. teamed up to showcase solar homes of the future, complete with batteries to store electricity.
The home of the future – with solar-electric modules on the roof and a lithium-ion battery in the garage – may have a welcome mat out sooner than expected.
The California-based builder KB Home and China's BYD Co., which makes plug-in cars, batteries and solar equipment, have partnered to build modestly priced homes in Lancaster, Calif., that will go a step further than other new solar housing developments by including battery storage of the solar electricity.
Off-grid solar owners for many years have used battery banks to store their generated electricity for later use, but the plan for the KB Home development – smack in the middle of a grid-tied suburban subdivision – could help alter the trajectory for adoption of both solar electricity and plug-in vehicles.
"The energy produced by the solar panels during the peak time is stored in the battery system and can be used later at night for the home," said Bill Wang, business development director for BYD America Corp., at a press conference to announce the partnership in Lancaster, a city about 70 miles north of Los Angeles.
Unlike homemade off-grid battery banks, which have typically used traditional lead-acid batteries, the storage system that KB Home and BYD showed off packages the lithium-ion battery packs in sleek, dark-tinted cabinets with flashing LED lights that continuously display the system's – and perhaps the future homeowner's – status.
The battery packs may store as much as 16 kilowatt-hours of electricity. A typical Southern California household uses about 20 kwh a day. The lithium-ion ferrous phosphate battery packs will be the same type used in plug-in vehicles that BYD expects to roll out in Los Angeles later this year.
Thomas C. DiPrima, executive vice president of KB Home's Southern California division, said the plan is to offer the solar-and-battery combinations first in one model home and four production homes in West Lancaster at no extra cost to the buyers, then to offer the systems as an option in the same subdivision and others. The West Lancaster houses have starting prices that range from about $210,000 to $257,000.
"Our long-term goal is to get to where we can do this nationwide," Mr. DiPrima said. "Our hope and our goal is to make it so affordable that it can be offered in a new home as a standard feature," he added, noting that solar PV is becoming cost-effective as a retrofit for many existing homes. Because the approach is a new one, it could be years before such a system is standard in a new KB home, he said.
Until now, it was thought that battery storage of solar electricity would not even begin to be an option for typical urban and suburban solar owners until years in the future.
Automakers in recent years have been outlining the future potential deployment of used batteries from plug-in cars to store solar electricity. Because automotive battery packs are expected to have typical lifetimes of about seven years and 100,000 miles, and large-scale manufacturing of electrified vehicles is still about two years away, it appeared that widespread use of used batteries in residential garages would not begin until 2018 to 2020.
But the plan described by KB Home and BYD to install new lithium-ion battery packs in garages changes a scenario that was already evolving rapidly. The plan meshes with the accelerating installation of new digital meters at households throughout the nation.
"Smart" meters make it easier for homeowners and utilities to monitor electricity use, and allow for time-of-use pricing, under which electricity costs more at times of peak demand – typically around breakfast and in the afternoon and early evening – and less during off-peak periods.
Solar photovoltaic systems produce electricity only during the daytime, and their early afternoon peak production often coincides with rising air-conditioning loads. The electricity that utilities buy for distribution at such times generally costs much more than does off-peak production. Traditionally, households have paid a predetermined, average price per kwh for electricity. Time-of-use rates permit pricing that more closely reflects real-world usage and generation patterns.
The plan to use new lithium-ion battery packs in residential garages could open up a range of potential opportunities for owners of solar-electric systems and plug-in vehicles. For the first time, they could have significant control over their generation, storage and use of electricity, moving it from a solar array to a car battery, into the home or into a storage battery, depending on their needs and the electricity's price at a particular time.
The battery pack also could pull low-cost electricity off the grid at night for use during higher-priced peak periods, either in the home or in the grid. The system's operation could be programmed with cellphones, PDAs or computers, or could be automated.
Another potential benefit: the end of blackouts. If a power outage occurred on the grid, a homeowner with a digital meter, a solar-and-battery combination, and perhaps a plug-in vehicle, could be unaffected. Grid-tied systems are designed at present to shut down automatically when grid power goes out, but that is likely to change as the technology develops.
If this use of new lithium-ion batteries were to become very popular, it would likely drive down the cost of such batteries for use both in homes and in vehicles more rapidly than expected through economies of scale in manufacturing.
Reducing the cost of solar and battery technologies is a key part of the plan. Using energy more sparingly and efficiently, and saving money for consumers, is the ultimate goal. KB Home plans to study the usage patterns of those who buy the solar-and-battery homes.
"All we'll ask of the homeowners is that they'll share with us their energy bills so we can see what the actual savings are in a home," said Mr. DiPrima.
The city of Lancaster, which has a population of about 145,000 people, is in the Mojave Desert's Antelope Valley, in northern Los Angeles County. The city waived municipal development fees for the homes to be outfitted with solar-and-battery systems, and has fast-tracked the permitting process. The first solar model home is expected to be completed in three or four months.
R. Rex Parris, the mayor of Lancaster, said at the press conference that petroleum is a finite energy source.
"The price of energy is just going to go up and up and up," he said. "If we can reduce the amount of energy we're using and the cost of it, it becomes much more affordable to live for all the hard-working families in the Antelope Valley and everywhere else."
Mr. Parris said the new approach "redefines how Americans are going to use energy in their houses."
BYD became prominent in U.S. investment circles when Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway Inc. bought 10 percent of the company in 2008. It started as a low-cost producer of cellphone batteries, and only recently began manufacturing automobiles, lithium-ion battery packs for plug-in vehicles, and solar equipment. Wang Chuanfu, BYD's chairman, is believed to now be the wealthiest person in China.
Stella Li, senior vice president of BYD, said at the press conference that the goals of the partnership to build the solar-and-battery-equipped homes are to help people "save money and make a cleaner planet."
Mr. DiPrima of KB Home said he expects homeowners to have some reservations about the new technology at first.
"I think the biggest concern will be, 'How difficult will it be for me? Do I have to go throw a switch? Do I have to program a computer?' And the fact that the system does that will probably take some of the fear away," he said.
Unlike some new solar-home developments that are installing tiles that blend in with a roof, KB Home and BYD plan to use stand-off modules of the type commonly added as retrofits to existing buildings. Modules with air space beneath them operate at higher efficiency because of the cooling effect, but are more visible than tiles.
"We are not seeing the aesthetics of solar being a deterrent," Mr. DiPrima said. "In fact, in California we've found that people want to show off their solar panels."
He added that because some people do prefer the look of solar tiles, KB Home works with local officials on the type, style and aesthetics of equipment, as it does with other elements of home designs.
"We're not looking at aesthetics as being a challenge," Mr. DiPrima said. "We've got to make sure that the system is as easy to operate as possible. The less they have to do, the better."
Source: sunpluggers.com
[ 2010-3-26]
California's KB Home and China's BYD Co. teamed up to showcase solar homes of the future, complete with batteries to store electricity.
The home of the future – with solar-electric modules on the roof and a lithium-ion battery in the garage – may have a welcome mat out sooner than expected.
The California-based builder KB Home and China's BYD Co., which makes plug-in cars, batteries and solar equipment, have partnered to build modestly priced homes in Lancaster, Calif., that will go a step further than other new solar housing developments by including battery storage of the solar electricity.
Off-grid solar owners for many years have used battery banks to store their generated electricity for later use, but the plan for the KB Home development – smack in the middle of a grid-tied suburban subdivision – could help alter the trajectory for adoption of both solar electricity and plug-in vehicles.
"The energy produced by the solar panels during the peak time is stored in the battery system and can be used later at night for the home," said Bill Wang, business development director for BYD America Corp., at a press conference to announce the partnership in Lancaster, a city about 70 miles north of Los Angeles.
Unlike homemade off-grid battery banks, which have typically used traditional lead-acid batteries, the storage system that KB Home and BYD showed off packages the lithium-ion battery packs in sleek, dark-tinted cabinets with flashing LED lights that continuously display the system's – and perhaps the future homeowner's – status.
The battery packs may store as much as 16 kilowatt-hours of electricity. A typical Southern California household uses about 20 kwh a day. The lithium-ion ferrous phosphate battery packs will be the same type used in plug-in vehicles that BYD expects to roll out in Los Angeles later this year.
Thomas C. DiPrima, executive vice president of KB Home's Southern California division, said the plan is to offer the solar-and-battery combinations first in one model home and four production homes in West Lancaster at no extra cost to the buyers, then to offer the systems as an option in the same subdivision and others. The West Lancaster houses have starting prices that range from about $210,000 to $257,000.
"Our long-term goal is to get to where we can do this nationwide," Mr. DiPrima said. "Our hope and our goal is to make it so affordable that it can be offered in a new home as a standard feature," he added, noting that solar PV is becoming cost-effective as a retrofit for many existing homes. Because the approach is a new one, it could be years before such a system is standard in a new KB home, he said.
Until now, it was thought that battery storage of solar electricity would not even begin to be an option for typical urban and suburban solar owners until years in the future.
Automakers in recent years have been outlining the future potential deployment of used batteries from plug-in cars to store solar electricity. Because automotive battery packs are expected to have typical lifetimes of about seven years and 100,000 miles, and large-scale manufacturing of electrified vehicles is still about two years away, it appeared that widespread use of used batteries in residential garages would not begin until 2018 to 2020.
But the plan described by KB Home and BYD to install new lithium-ion battery packs in garages changes a scenario that was already evolving rapidly. The plan meshes with the accelerating installation of new digital meters at households throughout the nation.
"Smart" meters make it easier for homeowners and utilities to monitor electricity use, and allow for time-of-use pricing, under which electricity costs more at times of peak demand – typically around breakfast and in the afternoon and early evening – and less during off-peak periods.
Solar photovoltaic systems produce electricity only during the daytime, and their early afternoon peak production often coincides with rising air-conditioning loads. The electricity that utilities buy for distribution at such times generally costs much more than does off-peak production. Traditionally, households have paid a predetermined, average price per kwh for electricity. Time-of-use rates permit pricing that more closely reflects real-world usage and generation patterns.
The plan to use new lithium-ion battery packs in residential garages could open up a range of potential opportunities for owners of solar-electric systems and plug-in vehicles. For the first time, they could have significant control over their generation, storage and use of electricity, moving it from a solar array to a car battery, into the home or into a storage battery, depending on their needs and the electricity's price at a particular time.
The battery pack also could pull low-cost electricity off the grid at night for use during higher-priced peak periods, either in the home or in the grid. The system's operation could be programmed with cellphones, PDAs or computers, or could be automated.
Another potential benefit: the end of blackouts. If a power outage occurred on the grid, a homeowner with a digital meter, a solar-and-battery combination, and perhaps a plug-in vehicle, could be unaffected. Grid-tied systems are designed at present to shut down automatically when grid power goes out, but that is likely to change as the technology develops.
If this use of new lithium-ion batteries were to become very popular, it would likely drive down the cost of such batteries for use both in homes and in vehicles more rapidly than expected through economies of scale in manufacturing.
Reducing the cost of solar and battery technologies is a key part of the plan. Using energy more sparingly and efficiently, and saving money for consumers, is the ultimate goal. KB Home plans to study the usage patterns of those who buy the solar-and-battery homes.
"All we'll ask of the homeowners is that they'll share with us their energy bills so we can see what the actual savings are in a home," said Mr. DiPrima.
The city of Lancaster, which has a population of about 145,000 people, is in the Mojave Desert's Antelope Valley, in northern Los Angeles County. The city waived municipal development fees for the homes to be outfitted with solar-and-battery systems, and has fast-tracked the permitting process. The first solar model home is expected to be completed in three or four months.
R. Rex Parris, the mayor of Lancaster, said at the press conference that petroleum is a finite energy source.
"The price of energy is just going to go up and up and up," he said. "If we can reduce the amount of energy we're using and the cost of it, it becomes much more affordable to live for all the hard-working families in the Antelope Valley and everywhere else."
Mr. Parris said the new approach "redefines how Americans are going to use energy in their houses."
BYD became prominent in U.S. investment circles when Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway Inc. bought 10 percent of the company in 2008. It started as a low-cost producer of cellphone batteries, and only recently began manufacturing automobiles, lithium-ion battery packs for plug-in vehicles, and solar equipment. Wang Chuanfu, BYD's chairman, is believed to now be the wealthiest person in China.
Stella Li, senior vice president of BYD, said at the press conference that the goals of the partnership to build the solar-and-battery-equipped homes are to help people "save money and make a cleaner planet."
Mr. DiPrima of KB Home said he expects homeowners to have some reservations about the new technology at first.
"I think the biggest concern will be, 'How difficult will it be for me? Do I have to go throw a switch? Do I have to program a computer?' And the fact that the system does that will probably take some of the fear away," he said.
Unlike some new solar-home developments that are installing tiles that blend in with a roof, KB Home and BYD plan to use stand-off modules of the type commonly added as retrofits to existing buildings. Modules with air space beneath them operate at higher efficiency because of the cooling effect, but are more visible than tiles.
"We are not seeing the aesthetics of solar being a deterrent," Mr. DiPrima said. "In fact, in California we've found that people want to show off their solar panels."
He added that because some people do prefer the look of solar tiles, KB Home works with local officials on the type, style and aesthetics of equipment, as it does with other elements of home designs.
"We're not looking at aesthetics as being a challenge," Mr. DiPrima said. "We've got to make sure that the system is as easy to operate as possible. The less they have to do, the better."
Source: sunpluggers.com
Mark Boslet: August 3, 2010
Lithium Battery Prices on Slow Decline
Chinese manufacturing advantage seen disappearing
Car makers are becoming increasingly comfortable with the capabilities of the lithium batteries they once considered risky and unproven.
But they worry it will still be years before price declines permit electric vehicles to compete effectively with gasoline-powered models without subsidies. Several vehicle designers at the Plug-In 2010 conference said prices could fall 50 percent to 75 percent -- but only over the next five to 10 years.
Lithium-ion battery prices today are generally said to be between $500 and $1,000 a kilowatt-hour. Consider then an average price of $750. They have declined over the past couple years as stimulus money allocated worldwide lifted production volumes.
Clearly there are different opinions about the pace of future declines. But several observations from the conference suggest:
* Prices could drop to between $350 and $400 a kilowatt-hour in five years, according to a projection from Ron Iacobelli, chief technology officer at Azure Dynamics, a supplier of drive technology for commercial electric and hybrid vehicles.
* Forecasts -- or at least hopes -- see price declines to $250 by 2020 (even as energy density improves 30 percent to 50 percent). Asked if the target is conceivable, Ford's Director of Global Electrification Nancy Gioia says: "That's what everyone is shooting for."
* At prices below $300 a kilowatt-hour, car makers see an electric car competing effectively with gasoline vehicles without subsidies.
Perhaps most surprising is that the Chinese cost advantage seems to be disappearing as lithium-ion battery production expands in the United States and elsewhere.
Eighteen months ago, Chinese manufacturers touted costs that were significantly lower. This was in part because some manufacturers didn't incorporate warranties. Other producers sold close to 100 percent of their production, even if some of it did not live up to quality standards.
Since then, costs have risen slightly and are comparable -- or between $500 and $1,000 a kilowatt-hour, says Haresh Kamath, a project manager at the Electric Power Research Institute. The reason is that American manufacturers increased production volumes and lowered costs even while improving manufacturing processes, so discards -- which previously could account for 25 percent of volume -- fell.
At the same time, Chinese companies spent money to improve quality standards in order to match the yields at American-owned factories. They also began to offer warranties.
Lithium Battery Prices on Slow Decline
Chinese manufacturing advantage seen disappearing
Car makers are becoming increasingly comfortable with the capabilities of the lithium batteries they once considered risky and unproven.
But they worry it will still be years before price declines permit electric vehicles to compete effectively with gasoline-powered models without subsidies. Several vehicle designers at the Plug-In 2010 conference said prices could fall 50 percent to 75 percent -- but only over the next five to 10 years.
Lithium-ion battery prices today are generally said to be between $500 and $1,000 a kilowatt-hour. Consider then an average price of $750. They have declined over the past couple years as stimulus money allocated worldwide lifted production volumes.
Clearly there are different opinions about the pace of future declines. But several observations from the conference suggest:
* Prices could drop to between $350 and $400 a kilowatt-hour in five years, according to a projection from Ron Iacobelli, chief technology officer at Azure Dynamics, a supplier of drive technology for commercial electric and hybrid vehicles.
* Forecasts -- or at least hopes -- see price declines to $250 by 2020 (even as energy density improves 30 percent to 50 percent). Asked if the target is conceivable, Ford's Director of Global Electrification Nancy Gioia says: "That's what everyone is shooting for."
* At prices below $300 a kilowatt-hour, car makers see an electric car competing effectively with gasoline vehicles without subsidies.
Perhaps most surprising is that the Chinese cost advantage seems to be disappearing as lithium-ion battery production expands in the United States and elsewhere.
Eighteen months ago, Chinese manufacturers touted costs that were significantly lower. This was in part because some manufacturers didn't incorporate warranties. Other producers sold close to 100 percent of their production, even if some of it did not live up to quality standards.
Since then, costs have risen slightly and are comparable -- or between $500 and $1,000 a kilowatt-hour, says Haresh Kamath, a project manager at the Electric Power Research Institute. The reason is that American manufacturers increased production volumes and lowered costs even while improving manufacturing processes, so discards -- which previously could account for 25 percent of volume -- fell.
At the same time, Chinese companies spent money to improve quality standards in order to match the yields at American-owned factories. They also began to offer warranties.
Herman K. Trabish: August 6, 2010
Xcel Shows it Can Catch the Wind in a Big Battery
Utility’s test results prove wind power and solar power can work better with a battery.
Xcel Energy has taken a big step toward the pot of gold at the end of the battery storage of renewable energy rainbow with the successful testing of a battery big enough to store wind power-generated electricity for 500 homes.
"This is critical technology," Forbes Black, a battery technology and energy storage systems engineer, said of Xcel's work. "We're going to have to figure out ways to store energy for when renewables are not generating and this sounds like a really good step in that direction."
Xcel is testing a sodium sulfur (NaS) battery at an 11-megawatt (MW) wind farm near Luverne, Minnesota. The 80-ton battery made by NGK Insulators Ltd. of Japan is a constellation of twenty 50-kilowatt modules the size of two semi trailers. It stores 7.2 megawatt-hours of electricity in total and can instantly absorb or generate one megawatt of power.
The sodium sulfur battery, Black observed, is likely both simple and inexpensive. The key, he said, "is storing the most kilowatt-hours per dollar that you possibly can. You need big cheap batteries."
"My doubts," he added, "are scale-related. I am not sure any battery technology right now can be used for grid-scale energy storage. There is a huge expense related to that."
Frank Novachek, Xcel Energy's Director of Corporate Planning and the manager of the wind-to-battery storage project, explained how the preliminary results of the field test that began in October 2008 unequivocally prove the technical capability of the batteries to store wind. They also confirm Black's doubts.
"We don't know what the right battery price is," Novachek said about the use of battery storage for shifting wind energy from off-peak availability (when electricity is least expensive) to peak demand availability (when electricity is most expensive). "But we do know it's too high for looking at the time-shifting aspects alone."
But time shifting is only one of battery storage's many uses. Deferring the need for a transmission/distribution system upgrade is a much more cost-effective application, according to Novachek. Renewable capacity is going to waste and being left uninstalled in resource-rich places around the U.S. because new transmission is so expensive and red-tape-intensive. But, in West Virginia, AEP, Novachek said, has relieved a distribution bottleneck sufficiently to have deferred the need for new wires through the use of a one-megawatt sodium sulfur battery.
Battery storage is also cost-effective when it is used to ease wind's variability. "You use the battery to slow down any changes in the output of the wind farm," Novachek explained. A small amount of instantly available capacity allows more time for secondary generation sources to ramp. "If the wind picks up really quickly, the battery would start charging," he said. "If the wind drops off, you use the battery to discharge to the grid."
There are other ways grid operators can use battery storage to integrate wind and solar more efficiently into the transmission system. One is a crucial but very technical use of battery storage that has to do with balancing voltage. Another is the precise mixing of battery-stored electricity into minute-by-minute grid supply fluctuations.
Xcel and its partners at the University of Minnesota have only just begun to understand the ideal ratio of battery storage capability to total project capacity needed for effective ramp rate control. "It's somewhere between one and five megawatts for this wind farm," Novachek said of the ratio derived from the eleven-megawatt Minnesota wind farm field test. "We were only able to test one- and five-megawatt capacities. I think it's probably closer to one. I don't think you need half the size of the wind farm."
The right ratio also depends on what the project and grid operators want the storage to accomplish.
"In Japan," Novachek explained, "NGK -- the people who provided our sodium sulfur battery -- have a facility where they have a 30-megawatt battery tied to a 50-megawatt wind farm."
The Japanese transmission system does not integrate wind and other variable renewables like the U.S. system will. "The island's grid system will only accept power if it's guaranteed at a constant output," Novachek said. "So they charge the batteries at night and then they use the batteries for a constant output during the day. As the wind goes down and up, the batteries go up and down to make sure the sum of their output is constant."
In the U.S., as long as there is a mix of fossil, nuclear and renewable energies being integrated, grid operators will be more concerned with controlling the rate at which the electricity supply changes from one source to another. "If you can control the rate of change to where the overall system can respond," Novachek said, "that will facilitate wind integration."
The most sophisticated uses of battery storage will come, Novachek contends, when wind and the other renewables are "somewhere greater than 30 percent" of the power on the grid. That allows for the several years Novachek foresees as still necessary to study the technology, understand its parameters and bring down the costs about which Black was rightly concerned.
"The functionality is there to do the things we need to have done for both solar and wind variability," Novachek said. "The big issues out there now are the technical issues associated with getting the cost down." He isn't certain when that can happen. "Every situation is going to have its own price point."
Xcel Shows it Can Catch the Wind in a Big Battery
Utility’s test results prove wind power and solar power can work better with a battery.
Xcel Energy has taken a big step toward the pot of gold at the end of the battery storage of renewable energy rainbow with the successful testing of a battery big enough to store wind power-generated electricity for 500 homes.
"This is critical technology," Forbes Black, a battery technology and energy storage systems engineer, said of Xcel's work. "We're going to have to figure out ways to store energy for when renewables are not generating and this sounds like a really good step in that direction."
Xcel is testing a sodium sulfur (NaS) battery at an 11-megawatt (MW) wind farm near Luverne, Minnesota. The 80-ton battery made by NGK Insulators Ltd. of Japan is a constellation of twenty 50-kilowatt modules the size of two semi trailers. It stores 7.2 megawatt-hours of electricity in total and can instantly absorb or generate one megawatt of power.
The sodium sulfur battery, Black observed, is likely both simple and inexpensive. The key, he said, "is storing the most kilowatt-hours per dollar that you possibly can. You need big cheap batteries."
"My doubts," he added, "are scale-related. I am not sure any battery technology right now can be used for grid-scale energy storage. There is a huge expense related to that."
Frank Novachek, Xcel Energy's Director of Corporate Planning and the manager of the wind-to-battery storage project, explained how the preliminary results of the field test that began in October 2008 unequivocally prove the technical capability of the batteries to store wind. They also confirm Black's doubts.
"We don't know what the right battery price is," Novachek said about the use of battery storage for shifting wind energy from off-peak availability (when electricity is least expensive) to peak demand availability (when electricity is most expensive). "But we do know it's too high for looking at the time-shifting aspects alone."
But time shifting is only one of battery storage's many uses. Deferring the need for a transmission/distribution system upgrade is a much more cost-effective application, according to Novachek. Renewable capacity is going to waste and being left uninstalled in resource-rich places around the U.S. because new transmission is so expensive and red-tape-intensive. But, in West Virginia, AEP, Novachek said, has relieved a distribution bottleneck sufficiently to have deferred the need for new wires through the use of a one-megawatt sodium sulfur battery.
Battery storage is also cost-effective when it is used to ease wind's variability. "You use the battery to slow down any changes in the output of the wind farm," Novachek explained. A small amount of instantly available capacity allows more time for secondary generation sources to ramp. "If the wind picks up really quickly, the battery would start charging," he said. "If the wind drops off, you use the battery to discharge to the grid."
There are other ways grid operators can use battery storage to integrate wind and solar more efficiently into the transmission system. One is a crucial but very technical use of battery storage that has to do with balancing voltage. Another is the precise mixing of battery-stored electricity into minute-by-minute grid supply fluctuations.
Xcel and its partners at the University of Minnesota have only just begun to understand the ideal ratio of battery storage capability to total project capacity needed for effective ramp rate control. "It's somewhere between one and five megawatts for this wind farm," Novachek said of the ratio derived from the eleven-megawatt Minnesota wind farm field test. "We were only able to test one- and five-megawatt capacities. I think it's probably closer to one. I don't think you need half the size of the wind farm."
The right ratio also depends on what the project and grid operators want the storage to accomplish.
"In Japan," Novachek explained, "NGK -- the people who provided our sodium sulfur battery -- have a facility where they have a 30-megawatt battery tied to a 50-megawatt wind farm."
The Japanese transmission system does not integrate wind and other variable renewables like the U.S. system will. "The island's grid system will only accept power if it's guaranteed at a constant output," Novachek said. "So they charge the batteries at night and then they use the batteries for a constant output during the day. As the wind goes down and up, the batteries go up and down to make sure the sum of their output is constant."
In the U.S., as long as there is a mix of fossil, nuclear and renewable energies being integrated, grid operators will be more concerned with controlling the rate at which the electricity supply changes from one source to another. "If you can control the rate of change to where the overall system can respond," Novachek said, "that will facilitate wind integration."
The most sophisticated uses of battery storage will come, Novachek contends, when wind and the other renewables are "somewhere greater than 30 percent" of the power on the grid. That allows for the several years Novachek foresees as still necessary to study the technology, understand its parameters and bring down the costs about which Black was rightly concerned.
"The functionality is there to do the things we need to have done for both solar and wind variability," Novachek said. "The big issues out there now are the technical issues associated with getting the cost down." He isn't certain when that can happen. "Every situation is going to have its own price point."
Aus ienem GTM-Artikel vom 27.5.:
When it comes to lithium-based battery chemistries, there is always talk of a lithium shortage or the U.S. being beholden to China or Bolivia for lithium the same way we are beholden to OPEC for oil. In Almgren's view, "Even in the most aggressive growth scenario -- lithium supplies will not be a problem. It's the more exotic materials like cobalt, nickel and manganese that might be a problem." Access to NMP, a key ingredient in the solvent-based process, might also become a challenge. Simbol Mining is a startup focused on developing lower-cost lithium and extracting other elements from geothermal brines.
"Lithium-ion is getting to megawatt scale," according to Dan Rastler of the Electric Power Research Institute, citing a 1-megawatt, 15-minute Li-ion system. He adds, "There are as many different Li-ion chemistries as there are California wines." There are currently early field trials by Altair Nano and A123 using Li-ion at utility scale.
According to Rastler, "We need to get below $300 per kilowatt-hour installed, all in." He said that the current cost of Li-ion ranges from $400 per kilowatt-hour to $1,200 per kilowatt-hour.
Haresh Kamath of EPRI's Technology Innovation Group said, "Storage is a great idea -- except for the cost." Kamath expects the cost of large-format lithium-ion (for electric vehicles and utility-scale storage) to drop to $250 per kilowatt-hour.
China's BYD is building utility-scale battery-based grid storage from their LiFe batteries. They are deploying 4-megawatt energy storage batteries for ancillary services and energy arbitrage. According to a spokesperson, the battery cost was in the $500-per-kilowatt-hour range, which is within striking distance of many experts' competitive target of $250 per kilowatt-hour.
When it comes to lithium-based battery chemistries, there is always talk of a lithium shortage or the U.S. being beholden to China or Bolivia for lithium the same way we are beholden to OPEC for oil. In Almgren's view, "Even in the most aggressive growth scenario -- lithium supplies will not be a problem. It's the more exotic materials like cobalt, nickel and manganese that might be a problem." Access to NMP, a key ingredient in the solvent-based process, might also become a challenge. Simbol Mining is a startup focused on developing lower-cost lithium and extracting other elements from geothermal brines.
"Lithium-ion is getting to megawatt scale," according to Dan Rastler of the Electric Power Research Institute, citing a 1-megawatt, 15-minute Li-ion system. He adds, "There are as many different Li-ion chemistries as there are California wines." There are currently early field trials by Altair Nano and A123 using Li-ion at utility scale.
According to Rastler, "We need to get below $300 per kilowatt-hour installed, all in." He said that the current cost of Li-ion ranges from $400 per kilowatt-hour to $1,200 per kilowatt-hour.
Haresh Kamath of EPRI's Technology Innovation Group said, "Storage is a great idea -- except for the cost." Kamath expects the cost of large-format lithium-ion (for electric vehicles and utility-scale storage) to drop to $250 per kilowatt-hour.
China's BYD is building utility-scale battery-based grid storage from their LiFe batteries. They are deploying 4-megawatt energy storage batteries for ancillary services and energy arbitrage. According to a spokesperson, the battery cost was in the $500-per-kilowatt-hour range, which is within striking distance of many experts' competitive target of $250 per kilowatt-hour.
PSI ist wenigstens profitabel. Habe auf PSI in diesem Bereich gesetzt.
By Nilima Choudhury - 24 February 2012, 13:02In News, Power Generation
Boston Consulting and Pike Research estimate 30% increase in use of battery technologies
Market research firms Boston Consulting and Pike Research, have estimated a growth of more than US$10 billion over the next five years for the stationary energy storage market. An increased use of advanced battery technologies and new smart-grid technologies to enable the wide-scale use of wind and solar energy has could lead to as much as a 30% increase.
This has been facilitated by the latest round of funding grant awards from the US Department of Energy’s American Recovery and Reinvestment Act 2009 Storage Demonstration program. This and enabled companies like EnerVault to complete its first installation. The company’s 1MWh system will be installed with partner Raytheon Ktech at a solar installation near Turlock, California, US.
EnerVault has announced the completion of a US$15.5 million Series B financing, bringing total funding to date to US$24.5 million. The company's investors include Mitsui Global Investment, Total Energy Ventures, 3M, TEL Venture, Commercial Energy of California, Oceanshore Ventures and US Invest. The investor funds compliment the company's grant awards totalling $5.5 million from the US DOE, California Energy Commission and New York State Energy Research and Development Authority. EnerVault is developing energy storage systems based on a novel redox flow battery technology.
"Redox flow batteries are creating a new paradigm for grid-scale energy storage," said Richard See, investment partner at MGI. "Because you scale the power independently of energy storage capacity, you can tailor the system to the needs of the application. EnerVault's approach expands upon the fundamental configuring and sizing benefits of flow batteries to yield the best approach for utility-scale electricity. The more energy needed, the lower the costs, so it's ideally suited for a number of situations where more than an hour or two of storage is needed."
"There is a high level of interest in our systems for addressing the stationary energy storage market," commented EnerVault CEO and co-founder Dr. Craig R. Horne. "Utilizing our patented Engineered Cascade technology, we are able to develop large-scale energy storage systems needed in a variety of applications with an unmatched combination of cost-effectiveness, safety and reliability."
Boston Consulting and Pike Research estimate 30% increase in use of battery technologies
Market research firms Boston Consulting and Pike Research, have estimated a growth of more than US$10 billion over the next five years for the stationary energy storage market. An increased use of advanced battery technologies and new smart-grid technologies to enable the wide-scale use of wind and solar energy has could lead to as much as a 30% increase.
This has been facilitated by the latest round of funding grant awards from the US Department of Energy’s American Recovery and Reinvestment Act 2009 Storage Demonstration program. This and enabled companies like EnerVault to complete its first installation. The company’s 1MWh system will be installed with partner Raytheon Ktech at a solar installation near Turlock, California, US.
EnerVault has announced the completion of a US$15.5 million Series B financing, bringing total funding to date to US$24.5 million. The company's investors include Mitsui Global Investment, Total Energy Ventures, 3M, TEL Venture, Commercial Energy of California, Oceanshore Ventures and US Invest. The investor funds compliment the company's grant awards totalling $5.5 million from the US DOE, California Energy Commission and New York State Energy Research and Development Authority. EnerVault is developing energy storage systems based on a novel redox flow battery technology.
"Redox flow batteries are creating a new paradigm for grid-scale energy storage," said Richard See, investment partner at MGI. "Because you scale the power independently of energy storage capacity, you can tailor the system to the needs of the application. EnerVault's approach expands upon the fundamental configuring and sizing benefits of flow batteries to yield the best approach for utility-scale electricity. The more energy needed, the lower the costs, so it's ideally suited for a number of situations where more than an hour or two of storage is needed."
"There is a high level of interest in our systems for addressing the stationary energy storage market," commented EnerVault CEO and co-founder Dr. Craig R. Horne. "Utilizing our patented Engineered Cascade technology, we are able to develop large-scale energy storage systems needed in a variety of applications with an unmatched combination of cost-effectiveness, safety and reliability."
http://www.mcphy.com/en/news/releases-554.php
Grenoble, France – July 23, 2012 – McPhy Energy, a leading developer and manufacturer of solid state hydrogen storage, today announced that the Company as part of a consortium of 7 partners has successfully kicked off the INGRID project, a major R&D and demonstration project with an overall budget of 23.9M Euros. The project will be granted with a financial contribution of 13.8M Euro by the European Commission within the Seventh Framework Programme for European Research and Innovation and will take four years to complete.
Consortium members include Engineering Ingegneria Informatica, the largest privately owned Italian ICT technology provider and coordinator of this project, Agenzia per la tecnologia e l’Innovazione (ARTI, Puglia, Italy), which represents the operational arm of Puglia regional authority for the innovation and technology transfer, Enel Distribuzione, Italy’s largest electricity distribution company, Hydrogenics (Belgium), the leading provider of hydrogen generators, the French McPhy Energy SA a leader in innovative technologies for solid and safe hydrogen storage, and the research institutions Ricerca sul Sistema Energetico (RSE, Italy), leader in research projects in the field of power generation, transmission and distribution and TECNALIA (Spain).
The core innovation of the INGRID project will consist of combining solid-state high-density hydrogen storage systems and electrolysis with advanced ICT technologies for smart distribution grids monitoring and control in a scenario of high penetration of renewable energy sources in order to balance power supply and demand.
The consortium will design, build, deploy and operate a 39 MWh energy storage facility using McPhy hydrogen-based solid state storage and Hydrogenics electrolysis technology and fuel cell power systems in the Puglia region in Italy, where over 3.500 MW of solar, wind, and biomass are already installed. The hydrogen energy storage installation, with more than 1 ton of safely stored hydrogen (the largest ever built), including a novel fast responding 1.2 MW hydrogen generator, will provide effective and smart balancing support for the local grid managed by Enel Distribuzione. Several potential value streams for the generated carbon-neutral hydrogen will be investigated.
All consortium partners are delighted to be part of this important energy storage project which further substantiates the enabling position of hydrogen technologies for renewable energy integration. The importance that the EU places on hydrogen technologies, that hold the key to solving utility-scale energy storage issues of today and tomorrow, is gratifying for the companies involved. The technologies at the core of INGRID Project are well placed and proven to enable greater renewable power generation around the globe.
Grenoble, France – July 23, 2012 – McPhy Energy, a leading developer and manufacturer of solid state hydrogen storage, today announced that the Company as part of a consortium of 7 partners has successfully kicked off the INGRID project, a major R&D and demonstration project with an overall budget of 23.9M Euros. The project will be granted with a financial contribution of 13.8M Euro by the European Commission within the Seventh Framework Programme for European Research and Innovation and will take four years to complete.
Consortium members include Engineering Ingegneria Informatica, the largest privately owned Italian ICT technology provider and coordinator of this project, Agenzia per la tecnologia e l’Innovazione (ARTI, Puglia, Italy), which represents the operational arm of Puglia regional authority for the innovation and technology transfer, Enel Distribuzione, Italy’s largest electricity distribution company, Hydrogenics (Belgium), the leading provider of hydrogen generators, the French McPhy Energy SA a leader in innovative technologies for solid and safe hydrogen storage, and the research institutions Ricerca sul Sistema Energetico (RSE, Italy), leader in research projects in the field of power generation, transmission and distribution and TECNALIA (Spain).
The core innovation of the INGRID project will consist of combining solid-state high-density hydrogen storage systems and electrolysis with advanced ICT technologies for smart distribution grids monitoring and control in a scenario of high penetration of renewable energy sources in order to balance power supply and demand.
The consortium will design, build, deploy and operate a 39 MWh energy storage facility using McPhy hydrogen-based solid state storage and Hydrogenics electrolysis technology and fuel cell power systems in the Puglia region in Italy, where over 3.500 MW of solar, wind, and biomass are already installed. The hydrogen energy storage installation, with more than 1 ton of safely stored hydrogen (the largest ever built), including a novel fast responding 1.2 MW hydrogen generator, will provide effective and smart balancing support for the local grid managed by Enel Distribuzione. Several potential value streams for the generated carbon-neutral hydrogen will be investigated.
All consortium partners are delighted to be part of this important energy storage project which further substantiates the enabling position of hydrogen technologies for renewable energy integration. The importance that the EU places on hydrogen technologies, that hold the key to solving utility-scale energy storage issues of today and tomorrow, is gratifying for the companies involved. The technologies at the core of INGRID Project are well placed and proven to enable greater renewable power generation around the globe.
Digitimes Research: Battery technologies regain focus as energy storage demand rises
Enoki Chen, DIGITIMES Research, Taipei [Monday 13 May 2013]
Demand for energy storage continues to rise and lithium-ion batteries are a common choice. However, due to prices, safety and energy storage, many substitutes such as lithium-sulfur and sodium-sulfur batteries have been surfacing. In addition, US-based GF has been promoting sodium-nickel halide batteries.
Firms have been focusing on the previous generation of battery technologies such as flow and liquid metal batteries due to increasing demand for energy storage for the electricity grid, according to Digitimes Research. In the past, these types of batteries were not suitable to install into mobile devices and automobiles due to characteristics such as size and the fact that the batteries cannot be shaken. However, these batteries are suitable energy storage methods for fixed installations.
Despite the regained popularity, battery technologies still face competition from low price natural gas. Hence, it is more likely for the battery technologies to develop in regions where prices of natural gas are higher.
Enoki Chen, DIGITIMES Research, Taipei [Monday 13 May 2013]
Demand for energy storage continues to rise and lithium-ion batteries are a common choice. However, due to prices, safety and energy storage, many substitutes such as lithium-sulfur and sodium-sulfur batteries have been surfacing. In addition, US-based GF has been promoting sodium-nickel halide batteries.
Firms have been focusing on the previous generation of battery technologies such as flow and liquid metal batteries due to increasing demand for energy storage for the electricity grid, according to Digitimes Research. In the past, these types of batteries were not suitable to install into mobile devices and automobiles due to characteristics such as size and the fact that the batteries cannot be shaken. However, these batteries are suitable energy storage methods for fixed installations.
Despite the regained popularity, battery technologies still face competition from low price natural gas. Hence, it is more likely for the battery technologies to develop in regions where prices of natural gas are higher.
Eos Raises $15M for Zinc-Air Grid Batteries
A Series B round with investors including Fisher Brothers and NRG Energy
JEFF ST. JOHN: MAY 20, 2013
Eos Energy Storage, the zinc-air battery startup targeting a super-low $160 per kilowatt-hour for grid-scale energy storage, has raised a $15 million Series B round from a syndicate of twenty-one strategic and financial investors, including Fisher Brothers and a big potential strategic partner, NRG Energy.
New York-based Eos has previously raised about $12 million from investors, though it hasn’t disclosed much about its investors before Tuesday’s funding announcement. The startup was originally bootstrapped by founders Michael Oster and Steven Amendola, and has spent the past five years bringing their technology through R&D and lab trials to more recent field tests.
Eos is working with hometown utility Consolidated Edison and five other unnamed partners to test small-scale versions of its battery chemistry and supporting grid interconnections. The company’s goal is a 1-megawatt, 6-megawatt-hour cargo container-sized battery called the Eos Aurora, set to be released in 2014 with characteristics that include long life, fairly high efficiency and a super-low cost of $140 per kilowatt-hour -- a fraction of the price of competing flow batteries, lithium-ion and advanced lead acid batteries on the market.
Eos represents the first energy storage investment for NRG, but the Princeton, N.J.-based energy giant is deeply involved in wind and solar power, plug-in vehicle charging and other green endeavors. “Eos’ technology is of strategic interest to NRG as we seek to enhance the value of our generation assets and evaluate novel energy storage business opportunities,” Denise Wilson, NRG executive vice president and head of its New Businesses unit, said in Tuesday’s release.
Fisher Brothers is a privately owned New York City-based real estate firm which also owns Plaza Construction, a contractor with experience building urban power plants and renewable energy projects. It’s also a co-sponsor with Morgan Stanley of the City Investment Fund, as well as a founding partner of Convergent Energy + Power, an energy storage asset development company with a pipeline of projects in New York, California and elsewhere.
Here’s our previous coverage on Eos.
The company claims its batteries can achieve 75 percent round-trip efficiency, along with a 10,000-cycle, or 30-year, lifetime. That compares favorably to the lifespan of other batteries on the market, and matches the round-trip efficiencies of flow batteries now on the market, though not those of the latest lithium-ion battery chemistries now in deployment on the grid.
But it’s the low price Eos is offering that has utilities and competitors most interested. Eos is targeting a total system cost of $1,000 per kilowatt, or $160 per kilowatt-hour of energy storage for its six-hour system, according to Philippe Bouchard, Manager of Business Development at the firm. Today’s flow batteries are being priced anywhere from $400 to $600 per kilowatt-hour, but at lower efficiencies. Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, while offering certain power delivery strengths that Eos doesn’t match, cost $800 to $1,000 per kilowatt-hour and up, he said -- although some Chinese Li-ion manufacturers are targeting $500 per kilowatt-hour.
Part of what makes it so cheap is its use of zinc, Bouchard noted. Zinc is much cheaper than lithium, at approximately $2 a kilogram, with global reserves of 1.9 billion tons and 30 million tons a year in production. That’s made zinc air-based battery chemistries popular, and indeed, many are on the market today -- but almost all in non-rechargeable formats. Getting them to recharge is much tougher, for various complex technical reasons having to do with the way air affects the anodes and cathodes of the batteries.
Eos says it has fixed those cycling issues by using what’s essentially salt water as an aqueous electrolyte in its battery cells, with the ability to amend or refill the system with more liquid as needed, he said. That’s gotten it to 6,000 cycles in lab tests, way beyond other zinc-air-based rechargeable batteries, and on a par with lithium-ion batteries, giving the startup optimism that it will reach its 10,000-cycle goal for its commercial-scale units, he said.
Eos isn’t the only startup promising groundbreaking advances in batteries, of course. On the rechargeable zinc-air front, contenders include Revolt Technology and PowerAir, PowerGenix and Taiwan’s APET. On the more esoteric front, venture investors like Vinod Khosla believe that batteries for the grid will involve new chemistries like Pellion's magnesium ion. Kleiner Perkins is betting on sodium-ion batteries from Aquion, and Kleiner Perkins and Khosla Ventures have also invested in battery startup QuantumScape.
Eos is just in the early stages of real-world testing, Bouchard stressed. The ConEd project won’t actually get underway until 2014, and while Eos expects to unveil other utility partners in the coming months, those projects will also be running on similar timeframes.
That may seem to put it behind competing energy storage vendors like NGK, A123 or Xtreme Power, which collectively have installed hundreds of megawatts of grid batteries to date. At the same time, Eos is taking a slow and steady approach that befits an as-yet-unproven technology, Bouchard said.
“We’ve built this fully transparent relationship with major utilities that are themselves going to be trendsetters for the industry,” he said. “They know exactly what we’re doing -- we’ve given them an in-depth perspective on the technology and how it operates, so there are no surprises.”
At the same time, Eos is still perfecting various parts of its grid-ready storage system, including developing a new generation of its current battery management software (BMS), which monitors the state of each liquid-filled cell within the battery arrays that Eos stacks together for power and energy data, as well as safety, he said. But unlike lithium-ion, which must be carefully managed to avoid thermal runaway, Eos’ aqueous-based, electrolyte-filled cells power themselves down in high-temperature extremes, presenting no fire hazard, he said.
As for what ConEd plans to use Eos’ first battery for, the partners are still looking into various options, Bouchard said. But the utility certainly has a lot of challenges in keeping its mostly underground, highly stressed metropolitan grid balanced, both in terms of delivering power to certain congested corridors during peak demand times and in keeping power quality stable amidst new intermittent generation sources like rooftop solar, he said.
Indeed, ConEd is also working on a broad range of energy storage projects as part of its $181 million in smart grid stimulus grants, including an $18 million project with Brooklyn-based Green Charge Networks to install batteries at 7-Eleven stores and airport EV charging stations to help balance end-use power for grid purposes. With 2012 grid upgrade plans that added up to $1.2 billion (PDF), the utility certainly has a lot of opportunities to look for places where batteries could help it avoid replacing or augmenting the 86 percent of its 130,000 miles of power lines that lie underground, for instance.
The grant Eos and ConEd are using for their pilot is also just part of millions of dollars in energy storage grants given out by the New York State Energy and Research Development Authority (NYSERDA). The state agency has backed everything from flywheel maker Beacon Power’s 20-megawatt energy storage facility in upstate New York (the company went bankrupt, but the facility is still providing frequency regulation to the grid), to startups like Eos and Albany, N.Y.-based BESS Technologies in more recent grants.
A Series B round with investors including Fisher Brothers and NRG Energy
JEFF ST. JOHN: MAY 20, 2013
Eos Energy Storage, the zinc-air battery startup targeting a super-low $160 per kilowatt-hour for grid-scale energy storage, has raised a $15 million Series B round from a syndicate of twenty-one strategic and financial investors, including Fisher Brothers and a big potential strategic partner, NRG Energy.
New York-based Eos has previously raised about $12 million from investors, though it hasn’t disclosed much about its investors before Tuesday’s funding announcement. The startup was originally bootstrapped by founders Michael Oster and Steven Amendola, and has spent the past five years bringing their technology through R&D and lab trials to more recent field tests.
Eos is working with hometown utility Consolidated Edison and five other unnamed partners to test small-scale versions of its battery chemistry and supporting grid interconnections. The company’s goal is a 1-megawatt, 6-megawatt-hour cargo container-sized battery called the Eos Aurora, set to be released in 2014 with characteristics that include long life, fairly high efficiency and a super-low cost of $140 per kilowatt-hour -- a fraction of the price of competing flow batteries, lithium-ion and advanced lead acid batteries on the market.
Eos represents the first energy storage investment for NRG, but the Princeton, N.J.-based energy giant is deeply involved in wind and solar power, plug-in vehicle charging and other green endeavors. “Eos’ technology is of strategic interest to NRG as we seek to enhance the value of our generation assets and evaluate novel energy storage business opportunities,” Denise Wilson, NRG executive vice president and head of its New Businesses unit, said in Tuesday’s release.
Fisher Brothers is a privately owned New York City-based real estate firm which also owns Plaza Construction, a contractor with experience building urban power plants and renewable energy projects. It’s also a co-sponsor with Morgan Stanley of the City Investment Fund, as well as a founding partner of Convergent Energy + Power, an energy storage asset development company with a pipeline of projects in New York, California and elsewhere.
Here’s our previous coverage on Eos.
The company claims its batteries can achieve 75 percent round-trip efficiency, along with a 10,000-cycle, or 30-year, lifetime. That compares favorably to the lifespan of other batteries on the market, and matches the round-trip efficiencies of flow batteries now on the market, though not those of the latest lithium-ion battery chemistries now in deployment on the grid.
But it’s the low price Eos is offering that has utilities and competitors most interested. Eos is targeting a total system cost of $1,000 per kilowatt, or $160 per kilowatt-hour of energy storage for its six-hour system, according to Philippe Bouchard, Manager of Business Development at the firm. Today’s flow batteries are being priced anywhere from $400 to $600 per kilowatt-hour, but at lower efficiencies. Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, while offering certain power delivery strengths that Eos doesn’t match, cost $800 to $1,000 per kilowatt-hour and up, he said -- although some Chinese Li-ion manufacturers are targeting $500 per kilowatt-hour.
Part of what makes it so cheap is its use of zinc, Bouchard noted. Zinc is much cheaper than lithium, at approximately $2 a kilogram, with global reserves of 1.9 billion tons and 30 million tons a year in production. That’s made zinc air-based battery chemistries popular, and indeed, many are on the market today -- but almost all in non-rechargeable formats. Getting them to recharge is much tougher, for various complex technical reasons having to do with the way air affects the anodes and cathodes of the batteries.
Eos says it has fixed those cycling issues by using what’s essentially salt water as an aqueous electrolyte in its battery cells, with the ability to amend or refill the system with more liquid as needed, he said. That’s gotten it to 6,000 cycles in lab tests, way beyond other zinc-air-based rechargeable batteries, and on a par with lithium-ion batteries, giving the startup optimism that it will reach its 10,000-cycle goal for its commercial-scale units, he said.
Eos isn’t the only startup promising groundbreaking advances in batteries, of course. On the rechargeable zinc-air front, contenders include Revolt Technology and PowerAir, PowerGenix and Taiwan’s APET. On the more esoteric front, venture investors like Vinod Khosla believe that batteries for the grid will involve new chemistries like Pellion's magnesium ion. Kleiner Perkins is betting on sodium-ion batteries from Aquion, and Kleiner Perkins and Khosla Ventures have also invested in battery startup QuantumScape.
Eos is just in the early stages of real-world testing, Bouchard stressed. The ConEd project won’t actually get underway until 2014, and while Eos expects to unveil other utility partners in the coming months, those projects will also be running on similar timeframes.
That may seem to put it behind competing energy storage vendors like NGK, A123 or Xtreme Power, which collectively have installed hundreds of megawatts of grid batteries to date. At the same time, Eos is taking a slow and steady approach that befits an as-yet-unproven technology, Bouchard said.
“We’ve built this fully transparent relationship with major utilities that are themselves going to be trendsetters for the industry,” he said. “They know exactly what we’re doing -- we’ve given them an in-depth perspective on the technology and how it operates, so there are no surprises.”
At the same time, Eos is still perfecting various parts of its grid-ready storage system, including developing a new generation of its current battery management software (BMS), which monitors the state of each liquid-filled cell within the battery arrays that Eos stacks together for power and energy data, as well as safety, he said. But unlike lithium-ion, which must be carefully managed to avoid thermal runaway, Eos’ aqueous-based, electrolyte-filled cells power themselves down in high-temperature extremes, presenting no fire hazard, he said.
As for what ConEd plans to use Eos’ first battery for, the partners are still looking into various options, Bouchard said. But the utility certainly has a lot of challenges in keeping its mostly underground, highly stressed metropolitan grid balanced, both in terms of delivering power to certain congested corridors during peak demand times and in keeping power quality stable amidst new intermittent generation sources like rooftop solar, he said.
Indeed, ConEd is also working on a broad range of energy storage projects as part of its $181 million in smart grid stimulus grants, including an $18 million project with Brooklyn-based Green Charge Networks to install batteries at 7-Eleven stores and airport EV charging stations to help balance end-use power for grid purposes. With 2012 grid upgrade plans that added up to $1.2 billion (PDF), the utility certainly has a lot of opportunities to look for places where batteries could help it avoid replacing or augmenting the 86 percent of its 130,000 miles of power lines that lie underground, for instance.
The grant Eos and ConEd are using for their pilot is also just part of millions of dollars in energy storage grants given out by the New York State Energy and Research Development Authority (NYSERDA). The state agency has backed everything from flywheel maker Beacon Power’s 20-megawatt energy storage facility in upstate New York (the company went bankrupt, but the facility is still providing frequency regulation to the grid), to startups like Eos and Albany, N.Y.-based BESS Technologies in more recent grants.
Data centers likely to adopt more Li batteries, say Taiwan makers
Aaron Lee, Taipei; Adam Hwang, DIGITIMES [Wednesday 5 February 2014]
While more than 80% of UPS (uninterruptible power supply) systems in cloud computing data centers are equipped with lead-acid batteries, use of lithium (Li) batteries is expected to increase, according to sources with Taiwan-based battery makers.
Lead-acid batteries are popular choices for data center UPS systems due to their relatively low costs, which are only 20-30% of the costs for Li batteries per watt-hour, according to the Taiwan government-sponsored Industrial Economics & Knowledge Center (IEK).
However, there has been a growing interest in adopting Li batteries, which compared with lead-acid batteries, offer better performance, longer service life, smaller form factors, and more eco-friendly manufacturing processes, the sources said.
Taiwan-based ODM Quanta Computer exhibited Quanta QCT Battery Backup System (BBS), a module consisting of four sets of Li battery packs for 3-minute emergency power supply for data centers, at Facebook's 2014 Open Compute Project Summit in San Jose during January 28-29, the sources indicated. Designs similar to BBS are expected to be increasingly adopted, the sources noted, adding UPS system suppliers have offered Li batteries as an alternative to lead-acid batteries.
Taiwan-based Simplo Technology and Dynapak International Technology in 2013 began small-volume supply of Li battery modules for Delta Electronics and Lite-On Technology, two Taiwan-based makers of UPS devices used in cloud computing data centers, the sources added.
Aaron Lee, Taipei; Adam Hwang, DIGITIMES [Wednesday 5 February 2014]
While more than 80% of UPS (uninterruptible power supply) systems in cloud computing data centers are equipped with lead-acid batteries, use of lithium (Li) batteries is expected to increase, according to sources with Taiwan-based battery makers.
Lead-acid batteries are popular choices for data center UPS systems due to their relatively low costs, which are only 20-30% of the costs for Li batteries per watt-hour, according to the Taiwan government-sponsored Industrial Economics & Knowledge Center (IEK).
However, there has been a growing interest in adopting Li batteries, which compared with lead-acid batteries, offer better performance, longer service life, smaller form factors, and more eco-friendly manufacturing processes, the sources said.
Taiwan-based ODM Quanta Computer exhibited Quanta QCT Battery Backup System (BBS), a module consisting of four sets of Li battery packs for 3-minute emergency power supply for data centers, at Facebook's 2014 Open Compute Project Summit in San Jose during January 28-29, the sources indicated. Designs similar to BBS are expected to be increasingly adopted, the sources noted, adding UPS system suppliers have offered Li batteries as an alternative to lead-acid batteries.
Taiwan-based Simplo Technology and Dynapak International Technology in 2013 began small-volume supply of Li battery modules for Delta Electronics and Lite-On Technology, two Taiwan-based makers of UPS devices used in cloud computing data centers, the sources added.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 43.413.691 von R-BgO am 23.07.12 12:34:09Gehen nun an die Börse
Thread: McPhy - französischer Wasserstoff-Speicher-Hersteller
Thread: McPhy - französischer Wasserstoff-Speicher-Hersteller
welche insbes. stationären Speicherkonzepte seht ihr mittelfristig vorne ? gibt es konkurrenzfähige Ansätze in China ?
ohne Wertung einige Links
http://www.focus.de/finanzen/news/wirtschaftsticker/wichtige…
http://enervault.com/enervault-turlock-dedication/
Ein Update der Fraunhofer-Gesellschaften zum Thema stationäre Energiespeicher ist m.W. für ende 2014 geplant.
http://www.isi.fraunhofer.de/isi-de/t/projekte/at-lib-2015-r…
Ich finde bemerkenswert, dass TSLAs geplante Speicherfabrik bei manchen Fachleuten zumindest als möglicher game changer gesehen wird
ohne Wertung einige Links
http://www.focus.de/finanzen/news/wirtschaftsticker/wichtige…
http://enervault.com/enervault-turlock-dedication/
Ein Update der Fraunhofer-Gesellschaften zum Thema stationäre Energiespeicher ist m.W. für ende 2014 geplant.
http://www.isi.fraunhofer.de/isi-de/t/projekte/at-lib-2015-r…
Ich finde bemerkenswert, dass TSLAs geplante Speicherfabrik bei manchen Fachleuten zumindest als möglicher game changer gesehen wird
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 47.814.116 von SmartCap am 18.09.14 14:45:24was denkst Du, wohin sie mit den Kosten pro kWh kommen werden?
traue ich mir im moment überhaupt kein urteil zu, sammle derzeit nur infos ...
in der pv dominieren offensichtlich die chinesen. mich würde interessieren ob so etwas in der speichertech auch denkbar ist, oder eher illusorisch ...
17.09.2014 15:19 -
Der erste virtuelle Großspeicher geht im Oktober in Betrieb. Bisher sind Tausende von dezentralen Einzelspeichern zusammengeschlossen. Die Betreiber profitieren vom kostenlosen Netzstrom.
Der erste virtuelle Großspeicher geht ab Ende Oktober dieses Jahres in Betrieb. Das teilt der Speicherhersteller Deutsche Energieversorgung. Die Leipziger haben das Projekt Econamic Grid ins Leben gerufen. Es basiert darauf, dass die Besitzer der einzelnen dezentralen Speicher kostenlos Strom aus dem Regelleistungsmarkt beziehen und verbrauchen. Insgesamt geht die Deutsche Energieversorgung davon aus, dass jeder Speicher etwa 800 Kilowattstunden überflüssigen Netzstrom bekommt. Gleichzeitig wird der Strom auch in Wärmeenergie umgewandelt, wodurch der Haushalt bis zu 2.500 Kilowattstunden Heizenergie ebenso zum Nulltarif verbrauchen kann. Durch die Einspeicherung des überschüssigen Stroms wird das Netz spürbar entlastet. Diese Entlastung wird wiederum von den Netzbetreibern vergütet, so dass die Deutsche Energieversorgung auch in der Lage ist, den Strom kostenlos zur Verfügung zu stellen.
In der Anfangsphase ist das Projekt Econamic Grid auf 5.000 Teilnehmer begrenzt. Bisher sind bereits über 2.500 Speicher in den virtuellen Großspeicher zusammengeschlossen. Besitzer eines Speichers der Deutschen Energieversorgung (Senec) können sich auch nach dem Start im Oktober noch registrieren. „Etwa im März oder April 2015 werden alle freien Plätze für Econamic Grid vergeben sein“, schätzt Mathias Hammer, Geschäftsführer der Deutschen Energieversorgung.
Kostenloser Strom zum Heizen
Das Projekt ermöglicht dem Haushalt vor allem in den Wintermonaten den Bezug von kostenfreiem Strom und kostenfreier Wärmeenergie. Gerade von Oktober bis März sorgen Stromüberschüsse durch Windenergieanlagen für eine häufige Überbelastung der Netze. Der virtuelle Großspeicher sorgt dann für Netzentlastung und lädt die angeschlossenen Akkus mit dem überschüssigen Netzstrom auf. „Durch Econamic Grid müssen unsere Kunden im Winter deutlich weniger Strom aus dem Netz beziehen“, sagt Mathias Hammer.
Wirtschaftlichkeit des Speichers verbessern
Der Bezug von überschüssigem Strom wirkt sich nicht nur positiv auf die Netzstabilität aus, sondern verbessert auch die Wirtschaftlichkeit des Speichers. „Eine Photovoltaikanlage amortisiert sich mit unserem Speicher im Schnitt nach zehn Jahren“, rechnet Mathias Hammer vor. Durch Econamic Grid sei die Anschaffung einer Photovoltaikanlage mit dem Senec-Speicher wirtschaftlicher, als eine Anlage ohne Speicher, betont er. (su)
Der erste virtuelle Großspeicher geht im Oktober in Betrieb. Bisher sind Tausende von dezentralen Einzelspeichern zusammengeschlossen. Die Betreiber profitieren vom kostenlosen Netzstrom.
Der erste virtuelle Großspeicher geht ab Ende Oktober dieses Jahres in Betrieb. Das teilt der Speicherhersteller Deutsche Energieversorgung. Die Leipziger haben das Projekt Econamic Grid ins Leben gerufen. Es basiert darauf, dass die Besitzer der einzelnen dezentralen Speicher kostenlos Strom aus dem Regelleistungsmarkt beziehen und verbrauchen. Insgesamt geht die Deutsche Energieversorgung davon aus, dass jeder Speicher etwa 800 Kilowattstunden überflüssigen Netzstrom bekommt. Gleichzeitig wird der Strom auch in Wärmeenergie umgewandelt, wodurch der Haushalt bis zu 2.500 Kilowattstunden Heizenergie ebenso zum Nulltarif verbrauchen kann. Durch die Einspeicherung des überschüssigen Stroms wird das Netz spürbar entlastet. Diese Entlastung wird wiederum von den Netzbetreibern vergütet, so dass die Deutsche Energieversorgung auch in der Lage ist, den Strom kostenlos zur Verfügung zu stellen.
In der Anfangsphase ist das Projekt Econamic Grid auf 5.000 Teilnehmer begrenzt. Bisher sind bereits über 2.500 Speicher in den virtuellen Großspeicher zusammengeschlossen. Besitzer eines Speichers der Deutschen Energieversorgung (Senec) können sich auch nach dem Start im Oktober noch registrieren. „Etwa im März oder April 2015 werden alle freien Plätze für Econamic Grid vergeben sein“, schätzt Mathias Hammer, Geschäftsführer der Deutschen Energieversorgung.
Kostenloser Strom zum Heizen
Das Projekt ermöglicht dem Haushalt vor allem in den Wintermonaten den Bezug von kostenfreiem Strom und kostenfreier Wärmeenergie. Gerade von Oktober bis März sorgen Stromüberschüsse durch Windenergieanlagen für eine häufige Überbelastung der Netze. Der virtuelle Großspeicher sorgt dann für Netzentlastung und lädt die angeschlossenen Akkus mit dem überschüssigen Netzstrom auf. „Durch Econamic Grid müssen unsere Kunden im Winter deutlich weniger Strom aus dem Netz beziehen“, sagt Mathias Hammer.
Wirtschaftlichkeit des Speichers verbessern
Der Bezug von überschüssigem Strom wirkt sich nicht nur positiv auf die Netzstabilität aus, sondern verbessert auch die Wirtschaftlichkeit des Speichers. „Eine Photovoltaikanlage amortisiert sich mit unserem Speicher im Schnitt nach zehn Jahren“, rechnet Mathias Hammer vor. Durch Econamic Grid sei die Anschaffung einer Photovoltaikanlage mit dem Senec-Speicher wirtschaftlicher, als eine Anlage ohne Speicher, betont er. (su)
16.09.2014 14:23 -
Der Schweriner Energieversorger Wemag hat den ersten Großspeicher in Betrieb genommen. In Zukunft soll der Stromspeicher das Netz stabilisieren und Regelenergie liefern. Damit lässt sich durchaus Geld verdienen.
Der Schweriner Energieversorger Wemag betreibt seit heute seinen Fünf-Megawatt-Stromspeicher kommerziell. Nach nur zwölf Monaten Bauzeit haben die Berliner Speicherspezialisten von Younicos das System jetzt schlüsselfertig übergeben. Künftig wollen die Schweriner Geld mit ihm verdienen. Der vollautomatische Lithium-Ionen-Speicher wird eigenständig kurzfristige Schwankungen der Netzfrequenz ausgleichen und in den übrigen Zeiten Regelenergie liefern.
Mit dem Speicher Geld verdienen
Im Inneren des etwa turnhallengroßen Gebäudes speichern 25.600 Lithium-Manganoxid-Zellen Strom innerhalb von Millisekunden. Zelllieferant Samsung SDI garantiert die Leistung des Batteriekraftwerks für mindestens 20 Jahre. Fünf, jeweils vier Tonnen schwere Mittelspannungstransformatoren verbinden das Kraftwerk sowohl mit dem regionalen Verteilnetz als auch mit dem nahegelegenen 380-Kilovolt-Höchstspannungsnetz. Damit soll es möglich werden, die fluktuierende Einspeisung von Solar- und Windstrom auszugleichen. Ist mehr Strom im Netz vorhanden als verbraucht wird, fließt er in die Batterie. Diese wird dann entladen, wenn die Sonne nicht scheint und gleichzeitig Windflaute herrscht. „Bislang wird unser Stromnetz größtenteils von inflexiblen Kohlekraftwerken stabilisiert, die dafür aber ein Vielfaches der tatsächlich benötigten Ausgleichsleistung produzieren müssen und die Netze demzufolge mit Strom aus fossilen Energieträgern blockieren“, erklärt Clemens Triebel, Technischer Vorstand von Younicos, die Notwendigkeit solcher Speicher. „Dadurch wird ungewollt Energie aus Wind und Sonne abgeregelt. Diesen volkswirtschaftlichen Schaden vermeidet unser Batteriepark, weil er sich deutlich schneller und genauer steuern lässt als ein thermisches Kraftwerk.“ Innerhalb von Sekundenbruchteilen kann der Speicher seinen Strom ins Netz einspeisen. Der Vorteil: Er tut das konkret nur in den Zeiten, wenn der Strom auch gebraucht wird. Die restliche Zeit übernehmen die Photovoltaik- und Windkraftanlagen die Versorgung. Insgesamt ersetzt der Fünf-Megawatt-Speicher das Regelpotenzial einer konventionellen mit der zehnfachen Leistung. „Zukünftig soll die Batterie darüber hinaus andere Systemdienstleistungen wie Schwarzstartfähigkeit oder Blindleistung bereitstellen“, erklärt Thomas Pätzold, Technischer Vorstand der Wemag. „Sie bietet also weitere lukrative wirtschaftliche Perspektiven.“
Speicher nicht überflüssig
Zwar haben Wissenschaftler in einer Studie im Auftrag von Agora Energiewende herausgefunden, dass die Integration der erneuerbaren Energien auch ohne Speicher gelingen kann. Doch überflüssig sind sie deshalb nicht. „Aus Sicht der Wissenschaft ist klar, dass Batteriekraftwerke technisch besonders gut zur Systemstabilität beitragen können“, betont Michael Sterner, Professor für Energiespeicher an der Ostbayerischen Technischen Hochschule Regensburg, während der feierlichen Übergabe des Speichers. Sterner ist einer der Mitautoren der Agora-Studie. „Bei den derzeit stark fallenden Batteriepreisen wirkt ihr Einsatz kostensenkend und ist damit gesamtwirtschaftlich sinnvoll. In der von mir geleiteten Speicherstudie für die Agora Energiewende, die gestern veröffentlicht wurde, haben wir empfohlen, bestehende Märkte und neue Märkte für Flexibilität technologieoffen zu gestalten und damit den Speichern durch Abbau von Hemmnissen eine faire Chance zu geben“, stellt Sterner klar.
Neues Zeitalter der Energieversorgung
Auch für die Wemag fängt jetzt ein neues Zeitalter der Energieversorgung an. „Die Wemag zeigt, dass sich intelligente Kurzzeitspeicher schon heute aus betriebswirtschaftlicher und volkswirtschaftlicher Sicht lohnen. Wir sind stolz darauf, die Entwicklung der Speichertechnologien zentral mitzugestalten“, freut sich Ewald Woste, Aufsichtsratsvorsitzender des Schweriner Energieversorgers. „Im Netzgebiet der Wemag werden bereits mehr als 80 Prozent der verbrauchten Strommengen aus Wind und Sonne produziert. Damit sind wir Vorreiter bei den Erneuerbaren“, sein Technikchef Thomas Pätzold. „Aus dieser Position heraus begreifen wir es als unsere gesellschaftliche Aufgabe, innovative und effiziente Lösungen für die Energiewende an den Markt zu bringen. Unser Batteriespeicher ist hier doppelt wegweisend: Er ist die technisch beste Lösung, um die naturbedingten Schwankungen aus regenerativer Einspeisung auszugleichen und ist zudem wirtschaftlich sehr attraktiv.“
Für die Photovoltaik ist der Speicher die Chance, endlich die Debatten um ihre Integration ins Stromnetz zu beenden. „Die Photovoltaik kann mithilfe von Stromspeichern wichtige Systemdienstleistungen übernehmen, die bislang nur Kohle- und Atomkraftwerken zugeschrieben wurden“, betont Jörg Mayer, Geschäftsführer des Bundesverbandes Solarwirtschaft. „Solarstromspeicher tragen zur Netzstabilität bei und reduzieren Einspeise- und Lastspitzen. Und oft sind Speicher eine kostengünstige Alternative zum Netzausbau, gerade dann, wenn der Netzausbau nicht im erwarteten Umfang kommt. Das Energiewendeland Deutschland braucht intelligente Solarbatterien. Sie werden mit einem Mehr an Ökostrom immer wichtiger“, erklärt Mayer. (Sven Ullrich)
Der Schweriner Energieversorger Wemag hat den ersten Großspeicher in Betrieb genommen. In Zukunft soll der Stromspeicher das Netz stabilisieren und Regelenergie liefern. Damit lässt sich durchaus Geld verdienen.
Der Schweriner Energieversorger Wemag betreibt seit heute seinen Fünf-Megawatt-Stromspeicher kommerziell. Nach nur zwölf Monaten Bauzeit haben die Berliner Speicherspezialisten von Younicos das System jetzt schlüsselfertig übergeben. Künftig wollen die Schweriner Geld mit ihm verdienen. Der vollautomatische Lithium-Ionen-Speicher wird eigenständig kurzfristige Schwankungen der Netzfrequenz ausgleichen und in den übrigen Zeiten Regelenergie liefern.
Mit dem Speicher Geld verdienen
Im Inneren des etwa turnhallengroßen Gebäudes speichern 25.600 Lithium-Manganoxid-Zellen Strom innerhalb von Millisekunden. Zelllieferant Samsung SDI garantiert die Leistung des Batteriekraftwerks für mindestens 20 Jahre. Fünf, jeweils vier Tonnen schwere Mittelspannungstransformatoren verbinden das Kraftwerk sowohl mit dem regionalen Verteilnetz als auch mit dem nahegelegenen 380-Kilovolt-Höchstspannungsnetz. Damit soll es möglich werden, die fluktuierende Einspeisung von Solar- und Windstrom auszugleichen. Ist mehr Strom im Netz vorhanden als verbraucht wird, fließt er in die Batterie. Diese wird dann entladen, wenn die Sonne nicht scheint und gleichzeitig Windflaute herrscht. „Bislang wird unser Stromnetz größtenteils von inflexiblen Kohlekraftwerken stabilisiert, die dafür aber ein Vielfaches der tatsächlich benötigten Ausgleichsleistung produzieren müssen und die Netze demzufolge mit Strom aus fossilen Energieträgern blockieren“, erklärt Clemens Triebel, Technischer Vorstand von Younicos, die Notwendigkeit solcher Speicher. „Dadurch wird ungewollt Energie aus Wind und Sonne abgeregelt. Diesen volkswirtschaftlichen Schaden vermeidet unser Batteriepark, weil er sich deutlich schneller und genauer steuern lässt als ein thermisches Kraftwerk.“ Innerhalb von Sekundenbruchteilen kann der Speicher seinen Strom ins Netz einspeisen. Der Vorteil: Er tut das konkret nur in den Zeiten, wenn der Strom auch gebraucht wird. Die restliche Zeit übernehmen die Photovoltaik- und Windkraftanlagen die Versorgung. Insgesamt ersetzt der Fünf-Megawatt-Speicher das Regelpotenzial einer konventionellen mit der zehnfachen Leistung. „Zukünftig soll die Batterie darüber hinaus andere Systemdienstleistungen wie Schwarzstartfähigkeit oder Blindleistung bereitstellen“, erklärt Thomas Pätzold, Technischer Vorstand der Wemag. „Sie bietet also weitere lukrative wirtschaftliche Perspektiven.“
Speicher nicht überflüssig
Zwar haben Wissenschaftler in einer Studie im Auftrag von Agora Energiewende herausgefunden, dass die Integration der erneuerbaren Energien auch ohne Speicher gelingen kann. Doch überflüssig sind sie deshalb nicht. „Aus Sicht der Wissenschaft ist klar, dass Batteriekraftwerke technisch besonders gut zur Systemstabilität beitragen können“, betont Michael Sterner, Professor für Energiespeicher an der Ostbayerischen Technischen Hochschule Regensburg, während der feierlichen Übergabe des Speichers. Sterner ist einer der Mitautoren der Agora-Studie. „Bei den derzeit stark fallenden Batteriepreisen wirkt ihr Einsatz kostensenkend und ist damit gesamtwirtschaftlich sinnvoll. In der von mir geleiteten Speicherstudie für die Agora Energiewende, die gestern veröffentlicht wurde, haben wir empfohlen, bestehende Märkte und neue Märkte für Flexibilität technologieoffen zu gestalten und damit den Speichern durch Abbau von Hemmnissen eine faire Chance zu geben“, stellt Sterner klar.
Neues Zeitalter der Energieversorgung
Auch für die Wemag fängt jetzt ein neues Zeitalter der Energieversorgung an. „Die Wemag zeigt, dass sich intelligente Kurzzeitspeicher schon heute aus betriebswirtschaftlicher und volkswirtschaftlicher Sicht lohnen. Wir sind stolz darauf, die Entwicklung der Speichertechnologien zentral mitzugestalten“, freut sich Ewald Woste, Aufsichtsratsvorsitzender des Schweriner Energieversorgers. „Im Netzgebiet der Wemag werden bereits mehr als 80 Prozent der verbrauchten Strommengen aus Wind und Sonne produziert. Damit sind wir Vorreiter bei den Erneuerbaren“, sein Technikchef Thomas Pätzold. „Aus dieser Position heraus begreifen wir es als unsere gesellschaftliche Aufgabe, innovative und effiziente Lösungen für die Energiewende an den Markt zu bringen. Unser Batteriespeicher ist hier doppelt wegweisend: Er ist die technisch beste Lösung, um die naturbedingten Schwankungen aus regenerativer Einspeisung auszugleichen und ist zudem wirtschaftlich sehr attraktiv.“
Für die Photovoltaik ist der Speicher die Chance, endlich die Debatten um ihre Integration ins Stromnetz zu beenden. „Die Photovoltaik kann mithilfe von Stromspeichern wichtige Systemdienstleistungen übernehmen, die bislang nur Kohle- und Atomkraftwerken zugeschrieben wurden“, betont Jörg Mayer, Geschäftsführer des Bundesverbandes Solarwirtschaft. „Solarstromspeicher tragen zur Netzstabilität bei und reduzieren Einspeise- und Lastspitzen. Und oft sind Speicher eine kostengünstige Alternative zum Netzausbau, gerade dann, wenn der Netzausbau nicht im erwarteten Umfang kommt. Das Energiewendeland Deutschland braucht intelligente Solarbatterien. Sie werden mit einem Mehr an Ökostrom immer wichtiger“, erklärt Mayer. (Sven Ullrich)
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 47.815.271 von SmartCap am 18.09.14 16:17:01illusorisch wohl nicht, aber der Tech-Gehalt dürfte deutlich höher sein und damit die Hürde für einen vergleichbaren Durchmarsch
Energy Storage Will Soon Replace Simple Cycle Combustion Turbine Peaker Plants
Chet Lyons, Principal, Energy Strategies Group November 05, 2014 | 2 Comments
Power grids need extra generating capacity to work properly. For example, about 20 percent of New York State’s generation fleet runs less than 250 hours a year. Because they don’t run much, “peaker plants” are by design the cheapest and least efficient fossil generators. When they do run they cost a lot to operate and produce more air pollution than other types of fossil generation. Wouldn’t it be great if we had a cost-effective and environmentally sustainable substitute for dirty fossil-based peakers?
As has happened with solar PV, the costs for multi-hour energy storage are about to undergo a steep decline over the next 2 to 3 years. This cost trend will disrupt the economic rationale for gas-fired simple cycle combustion turbines (CTs) in favor of flexible zero emissions energy storage. This will be especially true for storage assets owned and operated by vertical utilities and distributed near utility substations.
Simple cycle gas-fired CTs have been a workhorse utility asset for adding new peaker capacity for decades. But times and technologies change, and the power grid’s long love affair with gas-fired CTs is about to be challenged by multi-hour energy storage. Flow batteries that utilize a liquid electrolyte are especially cost-effective because the energy they store can be easily and inexpensively increased just by adding more electrolyte.
CTs cost from $670 per installed kilowatt to more than twice that much for CT’s located in urban areas. But the economics of peaking capacity must also reflect the benefits side of the cost/benefit equation. Distributed storage assets can deliver both regional (transmission) and local (distribution) level energy balancing services using the same storage asset. This means the locational value and capacity use factor for distributed storage can be significantly higher compared to CTs operated on a central station basis.
These points are discussed in Energy Strategies Group’s white paper, “Guide to Procurement of Flexible Peaking Capacity: Energy Storage of Combustion Turbines.” As noted in the paper, Capex for a 4-hour storage peaker is projected to be $1,390 by 2017, or $348 per (installed) kilowatt-hour of capacity. Factoring in the added value of locating storage on the distribution grid and ownership and operation by a vertical utility, 4-hour energy storage will win over CTs at the high end of the CT cost range by 2017.
By 2018 the cost of ViZn Energy’s 4-hour storage solution, which was selected by Energy Strategies Group as a proxy for the lowest cost multi-hour storage solutions currently being commercialized, is projected to be $974 per kW, nearly identical to that of a conventional simple cycle peaker. For a 4-hour storage resource – that translates to $244 per (installed) kilowatt-hour of capacity. Given the added benefits of installing storage in the distribution network, by 2018 storage will be a winner against the mid-range cost for a simple cycle CT and clearly disruptive compared to higher cost simple cycle CTs.
The disruptive potential of energy storage as a substitute for simple cycle CTs has been recognized. For example, Arizona Public Service (APS) and the Residential Utility Consumer Office (RUCO) recently filed a proposed settlement which, if approved, would require that at least 10% of any new peaker capacity now being planned as simple cycle combustion turbines would instead need to be energy storage — as long as the storage meets the cost effectiveness and reliability criteria of any CTs being proposed.
When selecting new peaking capacity, utility planners can choose between assets that better fit the emerging distributed grid architecture or the older and disappearing centralized approach to grid design. The choices we make today should be consistent with current and long-term cost-performance trends in fossil-based generation, solar PV and energy storage.
Lower cost solar PV and its rising penetration in all market segments will have a profoundly disruptive effect on utility operations and the utility cost-of-service business model. This has already started to happen. Storage offers a way for utilities to replace lost revenues premised on margins from kilowatt-hour energy sales by placing energy storage into the rate based and earning low-risk regulated returns.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 48.238.246 von R-BgO am 06.11.14 09:08:09die Links am besten direkt über die Quelle ansehen: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2014/11…
schade, dass sie keine absoluten Zahlen nennen:
18.11.2014 14:28 -Batteriespeicher für Solarstrom in Ein- und Mehrfamilienhäusern werden immer günstiger. 2015 könnte das so weitergehen. Das zeigt eine aktuelle Befragung unter Solarteuren in Deutschland.
Die Preisentwicklung von Energiespeichern im häuslichen Bereich in Deutschland zeigt auch im vierten Quartal 2014 eine fallende Tendenz. So erreichen sowohl die Netto-Einkaufspreise für Blei- als auch für Lithiumspeicher das niedrigste Niveau seit Jahresbeginn. Das ergibt eine aktuelle Befragung des Bonner Markt- und Meinungsforschers EuPD Research unter Installateursbetrieben in Deutschland, die mehr als 150 Kilowatt Photovoltaikleistung pro Jahr verkaufen.
Die Entwicklung des entsprechenden Preisindexes verdeutlicht das: Der Nettopreis für bleibasierte Photovoltaikstromspeicher beträgt im laufenden Quartal nur noch 52 Prozent im Vergleich zum dritten Quartal 2013. Auch der Preis für Lithiumsysteme reduzierte sich in diesem Zeitraum deutlich. „Die von uns festgestellten Preissenkungen im Segment der Stromspeicher für Wohngebäude belegen weiterhin die Dynamik im deutschen Markt“, kommentiert Thomas Olbrecht. „ Sie setzen ein positives Signal für ein weiteres Marktwachstum im kommenden Jahr 2015“, sagt Olbrecht. Er leitet die Marktforschungsabteilung bei EuPD Research.
Deutschland gilt derzeit als stark wachsender Markt für Energiespeicher im häuslichen Bereich. Die Kombination aus einem privaten Aufdachsegment für Photovoltaikanlagen, sinkender Einspeisevergütungen und gestiegener Haushaltsstrompreise in den vergangenen Jahren, bieten die Voraussetzungen für weiteres Wachstum, urteilten die Marktforscher. (nhp)
von Renewable Energy World
Energy StorageIn September, Philip Hiersemenzel, spokesman for the energy company Younicos stated that Germany could be using 60 percent renewable energy if the right technology were in place. 2 GW of battery storage, with one hour of backup capacity, could replace 25 thermal power plants that are currently used for frequency regulation, he said. Hiersemenzel pegged the cost at €3 billion to build this infrastructure. Startling as this announcement seems, the U.S. is not as far behind as people think.
ROY L. HALES, Contributor
The U.S. is surging ahead in terms of adopting battery storage. In 2013-2014, U.S. companies installed, or were in the process of installing more than 300 MW of energy storage capacity. The largest is Southern California Edison’s Tehachapi Energy Storage Project. It is a 8-MW system capable of supplying 32 megawatt-hours of electricity to the grid.
“One of the shots that was heard around the world was AB 2514, which is a California mandate for the minimum amount of energy storage the utilities have to install by 2020. That minimum allocated across the three major IOUs in California — Southern California Edison (SCE), Pacific Gas & Electric (PG&E) and San Diego Gas and Electric (SDG&E) — totals 1.325 gigawatts,” according to John Jung, CEO of the energy storage software, services & systems company GreenSmith.
GreenSmith is battery agnostic. It develops the software used in battery storage facilities. By the end of this year, it will have integrated a dozen battery storage units to the grid. That represents 23 MW of installed capacity deployed in four states.
“We are seeing major procurement —RFPs, RFOs and RFIs — happening in places like Hawaii, Ontario (Canada), the North East of the United States and Texas,” said Jung.
Adding Renewables to the Aging US Infrastructure
The aging U.S. infrastructure is a problem when it comes to grid stability. Many of the distribution feeders are nearing the end of their expected useful life. They are fairly weak and not equipped to handle a large influx of intermittent energy.
“A Southern California utility that we’ve delivered five different projects for, including about 6 MWh of grid stability and deferral applications this year, has reported in excess of 35 percent grid penetration of PV alone,” Jung said.
A lot of GreenSmith’s applications are 3-5 hours in length, which gives utilities more control over when electrons hit the grid.
“We’ve got what you call ‘peak shaving’ that allows you to take those electrons generated by renewable (and other intermittent) resources and store them until the peak hours when they are needed,” said Jung. “The issue is really about smoothing out the intermittency so that it mitigates the effect on distribution feeders.”
Jung said the U.S. usually uses only about half of its electrical generation capacity. The peak times only amount to 2 or 3 percent of the year. Very expensive equipment is being purchased to meet that peak demand and it is not used very often.
Instead of simply replacing the old grid with a new one, U.S. utilities should ask questions like: Where will we get the most value for our investments? What value do we place on getting a more resilient, more reliable grid? How important is it to have a grid that utilizes more renewable resources? Do we want to lengthen the life of existing resources?
Jung added, “We think all of these things can be done better. Not by spending another dollar on hardware equipment, but by spending another 10 cents on software and algorithms.”
Battery Storage for Ramp-up Speed
Like the US-based GreenSmith, Germany-based Younicos’ real contribution is software. Its battery plant focuses on 15-minute applications, the maximum allowed under “regulations/market design.”
“Batteries use all of their power (positive and negative) and because they are much faster and much more precise, our 5-MW unit replaces 50 MW of conventional generation capacity that would be AT THE VERY least required for the same /- 5 MW,” said Hiersemenzel, emphatically. Landis D. Kannberg, Manager of Energy Storage and Renewable Integration at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, agrees that batteries have a superior ramp rate.
“A coal-freed power plant might have (if modified for such) a ramp rate of 5 percent/minute,” he said. “Batteries can literally go to 100 percent (and in some cases higher for short periods of time) of rated power, in seconds. Flywheels also have extremely fast response.”
“Energy storage is by far one of the fastest resources, capable of handling the increase or decrease of the required frequency almost instantaneously,” echoed Jung.
Their weakness is duration. They become energy limited if forced to carry loads over an extended time. Utilities use a progression of plants for providing spinning reserve, primary and secondary reserves.
Younicos’ solution replaces a large number of those first line plants with battery packs.
Hiersemenzel explained, “To be able to adjust their power just a little up and down, these plants have to run at something like 70 percent of capacity. In fact a typical coal fired power plant runs at 90 percent in order to adjust 2 percent up and down. The remainder of the power thus produced has to be absorbed by the grid and thus blocks space for renewable generation. In Germany we have about 25 gigawatts of such so-called “must-run” capacity. With an average load of 60 and a low of 45 GW that means that in times of low load everything above 20 GW of renewable generation has to be powered down or exported.”
It is not economically feasible to insert more than 75 percent of renewable content into the grid, using battery packs. Younico’s goal is 60 percent annually. This means some conventional plants will have to remain online until a new technology is developed.
Kannberg is not convinced that it is necessary for Germany to replace quite so many conventional plants.
“If you rule out conventional generation (which will by definition be what happens at very high penetration of wind and solar) then all you have is storage (assuming load reduction is not an option). At very high penetration of renewables, the relative expense for any technology becomes high because of the very low capacity factor (you don’t want to use it, but it has to be there in case you need it). Biofuels may become an acceptable carbon-neutral fuel for thermal power production for limited use. Another aspect of the future potential approaches for enabling very high renewables is the use of vehicular storage (e.g. EV’s), which should become a viable grid resource in the future, under the right conditions.”
Can the US Build a Green Grid?
Regardless of whether Younicos’ solution works in Germany, or not, it is not applicable to the U.S.
“We couldn’t do that right now because we are not generating enough renewable energy to store, even if we had the storage available,” said Allan Hoffman, a former senior executive with the U.S. Department of Energy.
Hoffman believes the U.S. will eventually use 80 percent renewable energy, and referred to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s Renewable Electricity Futures Study:
“Renewable electricity generation from technologies that are commercially available today, in combination with a more flexible electric system, is more than adequate to supply 80 percent of total U.S. electricity generation in 2050 while meeting electricity demand on an hourly basis in every region of the country.”
Jung has seen projections that call for anywhere between 50 percent and 100 percent renewable content.
“There’s an interplay around what assumptions you are making about what investments you are making into the grid infrastructure,” said Jung. “Without those, even targets like 33 percent renewable content in California appear challenging.”
Kannberg said 80 percent “is technically feasible. Costs are non-trivial, perhaps under all scenarios, but particularly if we want to get there quickly. Perhaps the largest barriers, at least in the U.S., are institutional. Having the collective will and enduring commitment to achieving such a goal, that is the biggest challenge.”
“What we lack is a national energy policy,” Hoffman said. “That’s going to create an environment in which people will be willing to invest and know that 10 to 20 years down the road they can count on a rate of return. Nobody in their right mind, whether they are liberal or conservative or anything, is going to put up that kind of money unless they know it is safe and they are going to get a return on their investment.”
Roy L. Hales is a Canadian freelance writer who writes for a variety of renewable energy publications. Roy an environmental news website and radio program called the ECOreport.
Belectric startet Stromspeicher am Solarpark Alt Daber
26.11.2014 11:43 Als erster Solarpark in Europa erbringt Alt Daber zusammen mit einem Speicher, der zwei Megawattstunden Kapazität besitzt, Regelenergie in der Hochspannungsebene. Der Solarpark wird somit zu einem Hybridspeicher, der von Vattenfall am Strommarkt vermarktet werden soll.
Der Projektierer Belectric aus Kolitzheim hat heute einen Stromspeicher an das Solarkraftwerk Alt Daber in Brandenburg angeschlossen. Damit ist es laut Vattenfall das erste Solarkraftwerk Europas, das Regelenergie in der Hochspannungsebene analog zu konventionellen Großkraftwerken erbringen kann. Das Unternehmen 50 Hertz ist für die Höchstspannungsleitungen in Ostdeutschland zuständig, nachdem Vattenfall sein Höchstspannungsnetz verkauft hat. Solarkraftwerke müssen zukünftig Funktionen der Netzsteuerung übernehmen. „In Verbindung mit einem Speicher leisten sie einen wichtigen Beitrag, die Energieversorgung und Netzstabilität an die Erfordernisse der Energiewende anzupassen“, erklärt Bernhard Beck, Geschäftsführer bei Belectric.
Der Blei-Säure-Speicher mit einer Kapazität von zwei Megawattstunden und zwei Megawatt Leistung ist für den Einsatz in erneuerbaren und konventionellen Kraftwerken vorgesehen. Mit dem Speicher wird die Leistungsbereitstellung der Kraftwerke flexibler und das Stromnetz aktiv stabilisiert. Durch die lange Lebensdauer und niedrige Zyklenkosten der Speichereinheit setze Belectric einen Meilenstein bei der kosteneffizienten Erbringung von Systemdienstleistungen, teilt das Unternehmen mit. Der Speicher sei leicht zu transportieren und werde in Serie für Energieversorger hergestellt.
Erbringung von Primärregelleistung
Verbunden mit der Speichereinheit werden Solar- und Windparks zu Hybridkraftwerken, indem volatile Energieträger Systemverantwortung übernehmen und zum Fluktuationsausgleich beitragen. Die sogennaten must-run-Kapazitäten konventioneller Kraftwerke können gesenkt und durch so ausgestattete Ökostromkraftwerke ersetzt werden.
Zudem können dezentrale Energiesysteme gerade in Verbindung mit Speichern den Ausbaubedarf der Übertragungs- und Verteilnetze reduzieren. Und damit die Kosten der Energiewende senken. „Speicher werden ein wesentlicher Baustein der Energiewende sein und unterstützen unseren Anspruch eine perfekte Marktintegration der Erneuerbaren sicher zu stellen“, sagt Alfred Hoffmann, Manager bei Vattenfall. Der Stromspeicher wird zudem von Vattenfall am Primärregelleistungsmarkt vermarktet. (Niels H. Petersen)
Marktdisruptives Potential: Paradigmenwechsel in der Batteriespeichertechnik?
20.11.2014 von Hagen LangWarum er glaubt, dass die neue Batteriesteuerungs-Elektronik »Pacadu« das Zeug dazu hat, den Speicherweltmarkt umzukrempeln, erklärt im Gespräch Dipl. Ing. Wolfram Walter, Geschäftsführer der ASD Automatic Storage Device GmbH aus Umkirch.
Wolfram Walter, Geschäftsführer der ASD Automatic Storage Device GmbH: »Ich glaube nicht, dass in fünf Jahren noch Speicher mit reihengeschalteten Zellen hergestellt werden. Pacadu ist ein Paradigmenwechsel.«
Markt&Technik: Herr Walter, woran liegt es, dass bislang niemand auf die Idee kam, die Konstruktionsprinzipien von Batteriespeichern grundlegend zu überdenken?
Wolfram Walter: Das liegt am eingeschlagenen Technologiepfad. Seit über 100 Jahren schalten wir Batterien in Reihe. Das hat allerdings einige »Nebenwirkungen« beim Aufbau. Ich muss als Speicherdesigner alle Zellen vom gleichen Hersteller nehmen, alle müssen die gleiche Kapazität haben, den gleichen Innenwiderstand, den gleichen Ladezustand, den gleichen Gesundheitszustand, müssen idealerweise aus der gleichen Produktionscharge stammen und idealerweise auch noch selektiert sein. Nur dann habe ich eine Chance, einen Speicher zu bauen, der optimal funktioniert.
Trotzdem wird die Zelle, die zuerst geladen ist, dem System sagen: »Ich bin voll, bitte mit dem Laden aufhören, sonst gehe ich kaputt«. Alle anderen Zellen könnten noch weiter laden. Die Zelle, die zuerst leer ist, wird wiederum dem System sagen: »Ich bin leer, bitte höre auf zu entladen, sonst gehe ich kaputt.« Alle anderen Zellen haben noch Ladung und könnten sie abgeben, werden aber daran gehindert. Das ist in allen Speichersystem weltweit heute so. Und wenn in Zukunft eine Zelle des Speichers kaputt geht, verschlechtert sich die gerade geschilderte Situation zusätzlich, weil diese Zelle mit anderem Innenwiderstand, anderer Kapazität und anderem Gesundheitszustand die Funktion des Blocks insgesamt beeinträchtigt und zur Kompromittierung des ganzen Systems führt.
Wenn eine Zelle in einem System nur noch 40 Prozent Kapazität besitzt, hat das Gesamtsystem insgesamt nur noch 40 Prozent Kapazität. Stirbt eine Zelle des Verbundes, fällt das Gesamtsystem aus. Das sind die Themen, die uns Speicherhersteller heute beschäftigen. Sie limitieren die Freiheit im Speicherdesign.
Was gab den Anstoß zu ihrer Neuentwicklung?
Meine Bauchschmerzen bei der angedeuteten Problematik. Zum einen wurde mir klar, dass die angesprochenen Probleme eine Folge der Reihenschaltung sind. Das Reihenschaltungskonzept hat man seit 100 Jahren nicht mehr grundsätzlich überdacht. Der Batteriehersteller denkt bis zu seinem Plus- und Minuspol, der Systemintegrator schreibt an seinen Eingang »Hier erwarte ich z.B. 48 Volt DC«. Um das, was dazwischen passiert, hat sich niemand richtig gekümmert. Zum Zweiten ermöglicht die rapide Entwicklung der digitalen Bauelemente überhaupt erst seit einigen Jahren den technischen Lösungsweg, den wir verfolgen. Früher wäre das nicht möglich gewesen. Die Zeit war jetzt reif.

Wie werden die Zellen von ihrem »Pacadu« angesteuert?
Jede Zelle bekommt ihr eigenes Pacadu, es ist nicht nur eine Ladeelektronik. Pacadu bedeutet »Parallel Automatic Charge and Discharge Unit« und kann Laden und Entladen. Mit ihm brauchen wir keine Wechselrichter mehr, keine Schaltelemente, keine Shunts und haben deutlich weniger Aufwand in der Verkabelung. Jede Zelle wird perfekt bedient. Wenn Sie eine Zelle mit nur noch 10 Prozent Kapazität haben, wird sie diese 10 Prozent optimal zum Gesamtsystem beisteuern, ohne, dass das die besseren Zellen des Batteriesystems stört. Das Kriterium für einen Zellentausch wird künftig nur noch sein, ob ich den zur Verfügung stehenden Platz lieber für eine bessere Zelle nutzen möchte.
Welche Bauteile stecken im Pacadu und wie kommunizieren Pacadus miteinander?
Dazu möchte ich momentan noch nichts sagen. Wir haben neun Patente angemeldet, aber wollen nicht gleich alle Konkurrenten auf die Spur setzen. Ein Patent wird nach 18 Monaten offengelegt und alle können nachlesen, wie es geht. Jedes Pacadu verfügt über einen Prozessor, der über einen Bus mit einem Zentralrechner verbunden ist, der wiederum die Steuerung übernimmt. Insgesamt brauchen wir 50 Prozent weniger Elektronik als früher. Für eine PV-Anlage brauchen Sie künftig auch keine Wechselrichter mehr, sie schließen die PV direkt ans Pacadu an, von wo aus der Gleichstrom direkt in die Batterie und der Wechselstrom direkt ins Netz kann.
Dann müssten die Systeme ja insgesamt billiger werden.
Nach unseren Berechnungen ist es mit Pacadu möglich, in Verbindung mit einer PV-Anlage und einer Lithium-Eisen-Phosphat-4-Zelle Strom für etwa 18 Cent/kWh und in Verbindung mit einer Lithium-Titanat-Oxyd-Zelle sogar für 12,5 Cent/kWh bereitzustellen. Mit Pacadus werden Speicher künftig eine Kapitalrendite erwirtschaften. Sie werden »bankable«, eine staatliche Speicherförderung braucht niemand mehr. Derzeit wird an der Universität Offenburg eine Diplomarbeit erstellt, die wissenschaftlich seriös belegt, dass diese Speicher Geld verdienen.
Wie geht es jetzt weiter, was sind Ihre nächsten Schritte?
Als Speicherhersteller ASD Automatic Storage Device GmbH arbeiten wir an der Umstellung unserer Produktion vom gegenwärtigen Modell »Future ON« auf den neuen »Hybridspeicher«. Wenn im zweiten Quartal 2015 Pacadu wie geplant in Serie geht, werden wir den Speicher mit Pacadu anbieten. Ob wir Pacadu lizensieren werden, steht noch nicht fest. Ich glaube nicht, dass in fünf Jahren noch Speicher mit reihengeschalteten Zellen hergestellt werden. Pacadu ist ein Paradigmenwechsel.
Quelle: http://www.energie-und-technik.de/energiespeicher/artikel/11…
weltweite Übersicht zu pumped water storage

Quelle: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/blog/post/2015/01/di…
von der Solarpraxis:
http://www.solarpraxis.de/unternehmen/newspresse/newsdetail/…Die Preise für Lithium-Ionen-Akkus können bis 2030 um 60 Prozent sinken, wenn die globale Produktionskapazität dieses Batterietyps im gleichen Zeitraum um rund 30 Prozent pro Jahr wächst. In Elektroautos würde damit der Preis für eine gespeicherte Kilowattstunde Strom von heute über 20 Eurocent auf rund 5 Eurocent abnehmen. Das ist ein Ergebnis einer neuen Untersuchung, die auf dem 15. Forum Solarpraxis in Berlin vorgestellt wird. Die Untersuchung des langjährigen Präsidenten der EPIA (European PV Industry Association) und CEO Winfried Hoffmann basiert auf einer neu erstellten Preis-Erfahrungs-Kurve für Lithium-Ionen-Akkus. Das Forum Solarpraxis gehört mit über 600 Teilnehmern zu den führenden Solarkonferenzen Deutschlands und findet am 27. und 28. November 2014 im Hilton Hotel Berlin statt.
...
Winfried Hoffmann kommentiert die Folgen sinkender Preise für Stromspeicher: „Die Treibstoffkosten eines sparsamen Mittelklasse-Autos liegen bei ungefähr 6 Euro pro 100 km. In einem Elektroauto mit einem Verbrauch von 12 kWh pro 100 km sind Sie bereits heute 25 Prozent günstiger unterwegs, wenn man von selbst produziertem Solarstrom und heutigen Speicherkosten ausgeht. Die stark sinkenden Speicherpreise werden also völlig neue Perspektiven besonders für Erneuerbare Energien wie Photovoltaik und Windenergie eröffnen. Nicht nur dass die Preise für Strom aus Wind und Sonne kontinuierlich sinken, auch ihre natürlichen Schwankungen lassen sich dann wesentlich kostengünstiger ausgleichen.“
Karl-Heinz Remmers vom Veranstalter Solarpraxis AG geht davon aus, dass die Preise sogar noch schneller sinken werden als bisher angenommen: „Je mehr Akkus produziert werden, desto stärker sinkt ihr Preis. Die Elektromobilität ist dafür der stärkste Treiber: Während die Nachfrage nach Elektroautos in Europa noch relativ verhalten ist, steht der chinesische Markt vor einem rasanten Wachstum. Die chinesische Regierung fördert Elektroautos mit bis zu 12.000 Euro, im Jahr 2020 sollen schon fünf Millionen Fahrzeuge mit alternativen Antrieben auf Chinas Straßen unterwegs sein. Das wird dem Batteriemarkt enormen Schub verleihen.“
Energy Storage for the Grid is Expected to Reach $15.6 Billion in Annual Revenue by 2024
September 18, 2014Technology vendors are moving down the supply chain to supply deployment solutions, report concludes
A new report from Navigant Research analyzes the global market for utility-scale energy storage for both bulk and ancillary service applications.
Developing energy storage that is viable for grid applications has been a goal of vendors and grid operators for a number of years. Recently a number of factors have begun to converge to bring that goal close to fruition. Click to tweet: According to a new report from Navigant Research, worldwide revenue from energy storage for the grid and ancillary services is expected to grow from $675 million annually in 2014 to $15.6 billion in 2024.
“The grid-scale energy storage market continues to develop in a piecemeal fashion, but there are signals that it is poised for significant expansion in the coming years,” says Anissa Dehamna, senior research analyst with Navigant Research. “In particular, after several years of faltering growth, lithium ion batteries are emerging as the breakout technology in this sector.”
Still, the market challenges are significant for energy storage to be deployed widely on the grid. The industry needs more systems integrators and financing models to succeed, according to the report, as there is more value in providing solutions at the end of the supply chain (such as systems integration, including power conversion systems and inverters) than in the core technologies. As a result, technology vendors have been moving down the supply chain to filling in this void, the report concludes.
The report, “Energy Storage for the Grid and Ancillary Services,” analyzes the global market for utility-scale energy storage for both bulk an ancillary service applications. Specifically, the markets analyzed in this report are: grid asset optimization, wind integration, solar integration, arbitrage, T&D upgrade deferral, frequency regulation, voltage support, spinning reserve, electric supply reserve capacity, and load following. The report provides an analysis of the market issues, opportunities, and market challenges, associated with utility scale storage. Global market forecasts for power capacity, energy capacity, and revenue, broken out by both segment and region, extend through 2024. The report also examines the key technologies related to utility-scale energy storage, as well as the competitive landscape. An Executive Summary of the report is available for free download on the Navigant Research website.
=> das wären 36,9% p.a.
Bloomber-Artikel über Batterie-start-ups
u.a. scheint Bill Gates bei einigen dabei zu sein...http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2015/04…
Names to be checked:
http://www.ambri.com/
http://www.aquionenergy.com/
http://seeo.com/
Vielleicht findet ja doch irgendeiner bald mal den heiligen Gral...
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 49.747.107 von R-BgO am 09.05.15 16:13:58Unsinn!
Es sind:
$3.000 für 7 kWh
$3.500 für 10 kWh
Es sind:
$3.000 für 7 kWh
$3.500 für 10 kWh
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 49.577.189 von R-BgO am 16.04.15 11:21:21http://alevo.com/
Preispunkt
Weckruf für die Speicherbranche.
Niels Hendrik Petersen
3.06.2015 12:02 -
Paukenschlag zur Intersolar: Beim neuen Speichersystem von Solarwatt wachsen Solargenerator und Batterien zusammen. Das System läuft wie die Photovoltaik über die Stringanschlüsse des Wechselrichters. Auf diese Weise lässt sich MyReserve bei jeder beliebigen Anlage problemlos nachrüsten. Und die Preise sind kaum zu schlagen.
Lange wurde gemunkelt, welche neuen Stromspeicher Solarwatt in München zeigen wird. Vor zwei Jahren waren die Sachsen mit der Sonnenbatterie gestartet, hatten sich im vergangenen Jahr jedoch aus dieser Kooperation verabschiedet. Nun ist die Katze aus dem Sack: Gestern stellte Solarwatt am Unternehmenssitz in Dresden die technischen und ökonomischen Details des neuen Speichersystems MyReserve vor. Auf der Intersolar wird MyReserve am Stand 510 in Halle B1 ausgestellt und erläutert.
Solarstrings und Speicher werden eins
Um es vorwegzunehmen: So konsequent wurde die Einheit von Photovoltaik und Stromspeicher bisher nirgends gedacht und praktiziert. MyReserve bietet in der Basisvariante eine Speicherkapazität von 4,4 Kilowattstunden, aus Lithium-NMC-Zellen eines renommierten Herstellers aus Südkorea.
Mit zusätzlichen Batteriemodulen zu je 2,2 Kilowattstunden lässt sich das System auf elf Kilowattstunden erweitern. Der Batteriespeicher kann vollständig entladen werden, das wird über schonende Ladekurven erreicht. Die Zellen verfügen über keramische Separatoren, sind also sehr sicher. Sie werden auch in Automobilen eingesetzt, der Hersteller ist als Zulieferer zertifiziert.
Der Clou an der Sache: Die Batterie wird zusammen mit der Photovoltaikanlage an den MPP-Tracker des Wechselrichters angeschlossen. „Der Speicher gaukelt dem Wechselrichter eine Solaranlage vor“, erläutert Detlef Neuhaus, Chef von Solarwatt.
Andere Anbieter schließen ihre DC-Speicher an den Zwischenkreis des Wechselrichters an. Solarwatt braucht diesen Umweg nicht, weil der Speicher die MPP-Kurve der Solaranlage nicht verändert. Der Wechselrichter bekommt nicht mit, ob er Strom aus den Solarmodulen oder den Batteriemodulen bezieht. Die Gesamteffizienz (Roundtrip) liegt bei 93 Prozent (Batterie: 99,2 Prozent).
Nur 5.499 Euro brutto
Versuche am Institut für Technologie in Karlsruhe (KIT) haben dieses Regime bestätigt. Der Wechselrichter unterscheidet faktisch nicht mehr zwischen Speicher und Solarstrings. Das hat den Vorteil, dass sich die neuen Speicher an jedem beliebigen Wechselrichter nachrüsten lassen, ohne Batteriewechselrichter, ohne Eingriff in die Leistungselektronik oder die Kommunikation der Stringwechselrichter.
Das System ist streng auf DC ausgelegt, die DC-Steller sind in die Speichersteuerung integriert. Kombiniert mit dem Energiemanager von Solarwatt kann der MyReserve auch Netzfunktionen übernehmen. Der Energiemanager benötigt einen Sensor am Hauszähler, um die Schnittstelle zum Netz zu überwachen (zwei Sensorleitungen plus einmal 230 Volt für die Elektronik).
Wirklich sportlich sind die Preise, die Solarwatt aufruft: Der neue Speicher kostet in der Basisausführung nur 5.499 Euro. So zumindest lautet die unverbindliche Preisempfehlung für die Endkunden, brutto wohlgemerkt. Netto sind es um 4.600 Euro. Hinzu kommen die Montagekosten durch die Elektrofachkraft.
Sehr einfache Montage
Die allerdings nicht allzu hoch ausfallen dürften. Denn auch bei der Installation punktet der Speicher mit simplen, einfachen Ideen. Zwei Dübel arretieren ein Wandblech, in das der Speicher komplett im Gehäuse nur noch eingehängt werden muss. Das Gehäuse mit der Batteriesteuerung wiegt nur 28 Kilogramm, das kann ein Mann allein ohne Schwierigkeiten bewerkstelligen. Jedes Batterierack wiegt nur 25 Kilogramm.
Die beiden in Stahlgehäusen verpackten Zellblöcke werden mit Hilfe eines handlichen Montagebügels eingehängt, DC-Stecker rein und fertig. Der Anschluss der Photovoltaikanlage erfolgt über Klemmen, der DC-Ausgang wird zum Wechselrichter geführt – wie bislang die Solaranlage. Dann ist das System komplett und betriebsbereit – in weniger als einer halben Stunde. Displays gibt es nicht, der Betriebszustand wird über LED signalisiert.
Leicht erweiterbar
Um den Speicher auf elf Kilowattstunden zu erweitern, wird lediglich ein baugleiches Gehäuse daneben gehängt, das drei Batteriemodule zu je 2,2 Kilowattstunden aufnehmen kann. Die Steuerung läuft über das Basisgerät und den Energiemanager, wenn gewünscht. Das System wird ab der Intersolar in München lieferbar sein. Außer den asiatischen Zellen kommen alle Komponenten aus Deutschland, sie wurden nach Vorgaben von Solarwatt spezifiziert. Die Endmontage und die Gerätetests erfolgen in Dresden.
Derzeit befinden sich etliche Geräte in der Felderprobung, unter anderem in Karlsruhe. Das System erfüllt die DIN EN 62619 und ist für den Transport gemäß Richtlinie UN 38.3 zertifiziert. Es erfüllt alle Vorgaben des Leitfadens zu Batteriespeichern, die der BSW-Solar im vergangenen Jahr unter anderem mit Wissenschaftlern des KIT und anderen Partnern veröffentlicht hat. Die Prüfungen beim TÜV Rheinland und Cetecom hat MyReserve erfolgreich absolviert. Die letzten Prüfungen zur elektromagnetischen Verträglichkeit (EMV) stehen kurz vor dem Abschluss.
Ein lukratives Komplettpaket
Bisher werden Stromspeicher meist als ergänzende Zusatzkomponente verkauft, das gilt in der Nachrüstung von Bestandsanlagen auch für MyReserve. Doch Solarwatt geht einen Schritt weiter: Der Speicher (Basisvariante) wird mit einer Solaranlage (3,12 Kilowatt aus Glas-Glas-Modulen) und Wechselrichter ab der Messe in München für 8.999 Euro angeboten. Auch der Energiemanager mit Sensor ist im Paket enthalten.
Das ist ein unverbindlicher Nettopreis für den Endkunden. „Daraus resultieren Stromkosten von 0,23 Eurocent je Kilowattstunde“, rechnet Detlef Neuhaus vor. „Wir haben die Amortisationszeit mit rund zehn Jahren angesetzt, bei einem Autarkiegrad von 55 Prozent.“ Das bedeutet, dass Stromerzeugung durch Photovoltaik und Stromspeicherung zusammen nur noch 23 Cent kosten, in der oben beschriebenen Paketkonfiguration.
Mit offenen Karten spielen
So etwas war bislang nur mit Bleibatterien möglich. Nicht eingerechnet sind zusätzliche Vorteile durch die Förderung im KfW-Speicherprogramm, die der Kunde in Anspruch nehmen kann. „Wir sind ganz bewusst von sehr konservativen Annahmen ausgegangen, um mit offenen Karten zu spielen“, erläutert Neuhaus. „Was nützt es, den Leuten 10.000 Ladezyklen vorzurechnen? Auch wenn eine gute Lithiumbatterie rechnerisch diese Zyklen durchhält, so wird sie nach spätestens 15 Jahren das Ende ihrer chemischen Festigkeit erreichen.“ Ein Solarspeicher braucht im Jahr zwischen 230 und 270 Ladezyklen.
Der Dresdener Anbieter gibt auf die Speicherbatterie eine Garantie von zehn Jahren. Auf die Glas-Glas-Module werden 30 Jahren garantiert, sowohl bei der Leistung als auch auf das Produkt. Für den Wechselrichter, der von einem bekannten Zulieferer aus dem Allgäu kommt, gibt Solarwatt gleichfalls zehn Jahre Garantie. Damit decken die Fristen die gesamte Amortisationszeit des Pakets ab.
Der neue Speicher aus Dresden dürfte die Branche beflügeln, so viel steht fest. Es wird spannend sein, welche Innovationen die Konkurrenz in München präsentiert. Denn Fakt ist: Die Preise fallen schneller als erwartet, auch bei kleinen Heimspeichern. Für die Installateure und ihre Kunden öffnen sich völlig neue Möglichkeiten. Willkommen zur Speichershow in München: „Reine“ Photovoltaik war gestern. Jetzt liefert der Solargenerator sogar nachts noch Strom. (Heiko Schwarzburger)
ViZn macht Zink-Eisen Flow-Batterien
ViZn Turns to Jabil to Meet Growing Demand for Flow BatteriesJune 4, 2015
By Andrew Burger, Correspondent
Energy storage startup ViZn, developer of advanced zinc-iron flow battery technology, is scaling up the size and scope of its operations as it works to meet growing demand from a variety of customers both in the U.S. and abroad. It entered into a strategic manufacturing and supply chain management agreement with Jabil Circuit, a leading global provider of such services.
ViZn is seeing demand for its zinc-iron flow batteries growing across a range of applications and end-users, from microgrids, commercial and industrial companies to military applications and utility-scale systems, said CEO Ron Van Dell.
“We have over 20-MW of demand to serve right now. The next two to three quarters will be a very fast ramp-up period for us,” Van Dell said. Management expects orders to continue growing through 2016. It's looking to begin scaling up manufacturing at Jabil's principal facility in St. Petersburg, FL in this year's third quarter, expand capacity in Q4, and then ramp up even more substantially in Q1 2016.
Scaling Up Via a Strategic Manufacturing Partnership
In searching for a strategic contract manufacturing partner, ViZn was looking for an organization that not only was able to scale up production of its zinc-iron flow batteries in short order, but had financial strength and a strong multinational reputation.
What sealed the deal for ViZn was Jabil's previous experience working with startups looking to evolve from a technology development company into fully formed multinational business organization, Van Dell explained. Set for an initial term of five years, leveraging Jabil Circuit's strengths and expertise in specialized manufacturing and supply chain management will enable ViZn to grow and mature much more rapidly than would otherwise be the case.
Jabil has 90 sites across 24 countries, which will help ViZn meet demand for its zinc-iron flow batteries, as well as develop its customer service and maintenance capabilities, Van Dell noted.
Bright Prospects for Solar-Plus-Storage Solutions
A ViZn zinc-iron flow battery system integrated with a solar PV system is up and running at Randolph-Macon College in Virginia as part of a Dominion Power installation.
ViZn sees bright prospects for the combination of solar and battery storage in the well-developed energy markets of the U.S. and Europe where renewable energy deployment is high and grid integration is a priority. Demand for solar-plus-storage is growing even faster in developing countries where electricity is unreliable and/or prohibitively expensive, or not available at all.
Typically “flow batteries tend to be energy- [as opposed to power-] centric; they're not ideally suited to meet peak power demand,” Van Dell explained. ViZn has resolved that issue, as well as fast switching between polarities. “These have been tough challenges, but ones ViZn has been able to solve. That's essentially what our IP [intellectual property] is all about.”
Addressing costs, Van Dell said ViZn's zinc-iron flow batteries today come in at $400-$500 per kWh. Management is confident that will drop below $200 per kWh over the next two to three years. “We feel pretty good about how we're positioned,” Van Dell said.
While lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery storage is the dominant growth driver in the fledgling market for advanced energy storage solutions, Van Dell sees this changing in the near-term.
Van Dell believes there are a number of reasons, both economic and non-economic, why Li-ion batteries don't make sense when it comes to mid-tier and utility-grade stationary applications. “We think it's kind of flawed logic to think that magically the right storage technology for mobile transport purposes like EVs turns out to be the optimal storage technology for large stationary apps.”
While touting Li-ion technology as a stationary battery storage solution “may be convenient if you're looking to create demand for a huge factory, the real world will tell us that the applications and attributes of advanced battery storage systems are so distinct as to argue strongly against such broad-based adoption.”
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 49.577.189 von R-BgO am 16.04.15 11:21:21
Fortschreibung watchlist
Zitat von R-BgO: u.a. scheint Bill Gates bei einigen dabei zu sein...
http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/rea/news/article/2015/04…
Names to be checked:
http://www.ambri.com/
http://www.aquionenergy.com/
http://seeo.com/
www.imergy.com
www.alevo.com
www.solarwatt.de
www.viznenergy.com
www.younicos.com
http://www.teslamotors.com/de_DE/powerwall
Vielleicht findet ja doch irgendeiner bald mal den heiligen Gral...
Flow-Batteries
EnerVault ist pleite: https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/Flow-Battery-St…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 49.998.948 von R-BgO am 18.06.15 10:20:31
RedFlow,
Sumitomo,
ZBB Energy,
Prudent Energy,
Gildemeister,
UniEnergy,
Primus Power,
Imergy,
EnStorage and
ITN."
in der Quelle stehen ein paar weitere Player
"Despite that claim, vanadium seems to be the predominant chemistry in the crowded flow-battery field, which includesRedFlow,
Sumitomo,
ZBB Energy,
Prudent Energy,
Gildemeister,
UniEnergy,
Primus Power,
Imergy,
EnStorage and
ITN."
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 49.998.948 von R-BgO am 18.06.15 10:20:31
Flow-Batteries - noch einer
http://www.greenenergystorage.eu/en/ weitere Lead-Liste
http://www.navigantresearch.com/research/community-residenti…4. Key Industry Players
4.1 Core Technology
4.1.1 Aquion Energy
4.1.2 FIAMM SoNick
4.1.3 GILDEMEISTER energy solutions
4.1.4 Kokam Co., Ltd.
4.1.5 Kyocera
4.1.6 LG Chem
4.1.7 Panasonic
4.1.8 RedFlow Technologies
4.1.9 Samsung SDI
4.2 Software and Integration
4.2.1 CODA Energy
4.2.2 E3/DC
4.2.3 Green Charge Networks
4.2.4 Greensmith Energy Management Systems
4.2.5 Ideal Power
4.2.6 Moixa Energy Holdings
4.2.7 S&C Electric Company
4.2.8 Stem
update Batteriehersteller
Li-IonThread: Presse: Panasonic will Solarzellen-Produktion in Europa schließen - Tesla-Lieferant
Thread: GS Yuasa - macht JV mit Bosch - JV will Leistungsdichte verdoppeln
Thread: LG Chem(ical) - verwässert durch Chemie
Thread: Sekisui Chemical :Technischer Durchbruch bei Lithium-Akkus für Elektroautos - dlrowralos Liebling
Thread: Nicht billig aber klasse - SAFT GROUPE S.A. ACTIONS NOMINATIVES EO 1 - manche verdienen sogar Geld mit Li-Ion
Thread: ELectrovaya - Li-Ionen-Batterien - nicht nur Elon hat WILDE Träume
Thread: Leclanché - Schweizer Li-Ionen Produzent - dto.
Thread: Homeowners Can Save Energy and Prevent Unexpected Repairs With New Johnson Controls Smart Thermostat - verwässert durch Auto & Haustechnik
Thread: BYD CO LTD - mit Zukunft ?
andere Batterie-/oder Energiespeicher-Player
Thread: NGK Insulators - NaS Batteriehersteller - Flow-Batterien aus Japan
Thread: Einstieg Enersys - Weltmarktführer Pb-Zn
Thread: McPhy - französischer Wasserstoff-Speicher-Hersteller - Wasserstoffspeicher
Thread: ITM Power - Elektrolyse und Brennstoffzelle
Thread: Axion Power - neue WKN nach reverse split - PbC
Thread: ZBB Energy
Thread: Active Power - UPS
Thread: Redflow - The Holy Grail?
vorbörsliche
http://www.ambri.com/
http://www.aquionenergy.com/
http://seeo.com/
www.imergy.com
www.alevo.com
www.solarwatt.de
www.viznenergy.com
www.younicos.com
http://www.pdenergy.com/
http://www.uetechnologies.com/
http://www.primuspower.com/
http://www.enstorageinc.com/
http://www.itnes.com/news-ARPA-E_VRB.html
http://24-m.com/
for the record:
Tesla CTO: Bulk Energy Storage Will Grow Much Faster Than People ExpectMuch ado about energy storage at the Intersolar 2015 opening keynote.
July 14, 2015
By Jennifer Runyon, Chief Editor
At the standing-room-only opening keynote at Intersolar 2015, all the talk was on the future of solar and how energy storage was helping to pave the way for greater adoption of it. Dr. Eicke R. Weber, the director of the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE) opened the show outlining the great progress that solar has made in the past two years by stabilizing supply and demand. “Therefore in 2016, 17, 18 you will see production capacity and the market catch up, which means we should not expect further falling prices for PV modules,” he said, adding “You can expect stable prices and maybe even some modest increases.”
Next up was Tesla Co-Founder and Chief Technical Officer JB Straubel who offered a vision for the future of energy storage and PV. Straubel believes that the energy storage industry is “right at the precipice” of massive cost declines like PV experienced.
“The next decade is going to look very different because all of the demand [for energy storage technology] coming from stationary energy storage and from electric vehicles — from many different companies not just Tesla — will change the demand curve and slope in a huge way,” he said. “It’s kind of like the difference between solar used for pocket calculators and satellites VS solar used for buildings. The demand is orders of magnitude higher and puts it on a different trajectory for cost declines.”
To put it in numbers, Straubel believes that the demand for batteries coming from just his company will be something like 35GWh of energy storage by 2020. “That is more lithium-ion capacity than existed in the entire world in 2013.”
Tesla will be demanding some of this battery technology for its Powerpack, a utility-scale battery that the company has recently unveiled.
The Powerpack is about 10 times bigger than the Powerwall, which is designed for behind-the-meter residential applications. It is a 100kWh “building block” that is designed to be scaled up into an array.
The Powerpack has a 10-year lifetime. Straubel showed the audience a conceptual drawing of a theoretical 100MWh/25MW power plant.
“There is a clear and present value for transmission and distribution support,” he said.
Straubel closed with some very aggressive predictions that seem more like a wish list than what may actually take place. “In our view battery costs are going to decline much faster than most people expect.”
He believes that in less than 10 years nearly all cars will be electric. Also he said bulk storage with batteries will grow faster than predicted. “Our view is that batteries are really going to win” over other energy storage technologies like pumped hydro, compressed air energy storage, even flow batteries, he said. “We are seeing price declines that make a lot of those technologies somewhat stranded,” he added.
“So if we can have solar generation at $0.02-0.03 per kWh and if you can have a levelized cost of a battery that may fall below $0.10 per kWh you suddenly get to have energy that is 100 percent firm and buffered from photovoltaics that is cheaper than fossil energy,” he said. That goal is in “grasping distance” according to Straubel.
8 Potential Battery Breakthroughs
Lab innovations have come to light almost weekly in the last quarter.www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/Eight-Potential-Battery…
Jason Deign
August 14, 2015
Even with plenty of 2015 left, it is a safe bet that the Tesla Powerwall launch in May will be energy storage’s biggest moment this year. The announcement of a $3,500 residential storage system got the world talking about batteries, and not all in a positive light.
Skeptics have pointed out that Tesla did nothing to change the fundamental economics of battery manufacturing, and that long-term price reductions might be difficult to achieve given potential constraints on raw materials. But while it is true that Tesla is banking on economies of scale, rather than technology breakthroughs, to achieve its gigawatt-level storage ambitions, it is also the case that battery research is growing apace.
In fact, since Tesla’s announcement barely a week has gone by without news of some new potential breakthrough. Here are eight of the top developments to emerge from labs worldwide over the last quarter.
1. Aqueous solar flow: Ohio State University researchers unveiled a "solar air" battery in 2014, but this June they went one step further and integrated their lithium-iodine (Li-I) technology with a solar cell to boost its efficiency. “The charging voltage reduction translates to energy savings of close to 20 percent compared to conventional Li-I batteries,” said the team. “This concept also serves as a guiding design that can be extended to other metal-redox flow battery systems.”
2. Battery anodes from reed leaves: Chinese and German scientists announced in June that reed leaves might hold the key to better silicon anodes for lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. Silicon beats carbon as a Li-ion anode, they say, but current manufacturing methods are complicated, expensive and energy-intensive. With the calcination and magnesiothermic reduction of leaves, though, you get anodes with “a remarkable Li-ion storage performance.”
3. A new Li-ion battery: July saw a team of South Korean scientists unveiling a new high-performance Li-ion battery that is stable at high temperatures. The battery is made from pumpkin-shaped molecules of a substance called cucurbit[6]uril, arranged in a honeycomb-like structure, and can operate at temperatures of almost 100ºC with no thermal runaway and “hardly any change in conductivity.”
4. Doubling the capacity of Li-ion: In June it emerged that experts at Samsung Electronics had developed a way of coating silicon cathodes with high-crystal graphene to almost double the capacity of Li-ion batteries. Business Korea pointed out that this breakthrough could benefit mobile phones and electric vehicles, and said the technology may need two or three years for commercialization.
5. Copying photosynthesis for storage: Scientists at the University of California, Los Angeles have been inspired by photosynthesis in creating a solar cell design that allows energy to be stored for weeks. The cells are made of plastic and use polymers and nano-scale fullerenes arranged in a manner that has been described as “small bundles of uncooked spaghetti with precisely placed meatballs.”
6. High-capacity batteries from wood pulp: A team from KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden and Stanford University in the U.S. has produced “an elastic, foam-like battery material that can withstand shock and stress,” according to a press release in May. The nanocellulose-based material is made from tree fibers and can pack a surface area equivalent to the size of a football pitch into a single cubic decimeter. It could be used in electric car bodies and even clothing, the team said.
7. Calcium batteries to beat Li-ion: research being carried out in France and Spain aims to create advanced calcium batteries that could give Li-ion a run for its money, according to reports in June. The Advanced Calcium Batteries project aims to come up with rechargeable calcium cells that could be used in the same way as Li-ion but without any of the supply-chain concerns associated with lithium.
8. Melanin as a storage material: Melanin, the skin pigment, is being tested for its potential in energy storage, said news reports in May. The work is being carried out by River Road Research and the Rochester Institute of Technology in the U.S. on the back of a $35,000 grant from the Department of Environmental Conservation. Initial results hint at the possibility of cheaper, safer batteries with lower environmental impact.
Greensmith liefert Software
www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/AEP-Invests-5M-in-Green… Großspeicher ist wirtschaftlicher als gedacht
22.09.2015 12:00 -Der Großspeicher des Energieversorgers Wemag übertrifft mit seinen Erlösen alle Erwartungen, die der Betreiber vor der Installation hatte. So gewannen die Schweriner alle Ausschreibungen von Primärregelleistung trotz der systematischen Benachteiligung von Speichertechnologien.
Der Berliner Speicherintegrator Younicos hat Bilanz für das Betriebsjahr des Großspeichers der Wemag in Schwerin gezogen. Das Ergebnis: Europas erster kommerzieller Batteriespeicher hat die in ihn gesetzten Erwartungen voll und ganz erfüllt. Das sogar trotz weiterhin systematischer Benachteiligung von Speichern gegenüber konventionellen Kraftwerken, betonen die Speicherexperten aus Berlin. Damit geht das Geschäftskonzept auf, das die Wemag als Betreiber der Lithium-Ionen-Anlage anvisiert hat.
Dieses Modell steht auf zwei Beinen. Zum einen kann die Wemag mit dem Speicher die an ihrem Netz angeschlossenen Ökostromanlagen besser integrieren, ohne das Netz üppig ausbauen zu müssen. Immerhin werden schon mehr als 80 Prozent der im Netzgebiet der Schweriner verbrauchten Strommenge mit Windkraft- und Photovoltaikanlagen produziert. So spart die Wemag mit dem Speicher schon einmal viel Geld.
Zusätzlich Geld verdienen
Doch die Schweriner wollen mit dem Speicher auch zusätzlich Geld verdienen. Deshalb haben sie zumindest mit dem größten Teil der Leistung des Speichers an der Ausschreibung von Primärregelleistung teilgenommen, die die Übertragungsnetzbetreiber täglich durchführen. Dabei konnte die Wemag mit den ihrem Speicher alle Ausschreibungen gewinnen, an denen sie sich beteiligt hatte. Die Schweriner erzielten damit durchschnittlich einen Erlös von 3.810 Euro pro Megawatt. „Dank stabiler Preise am Primärregelleistungsmarkt und eines optimierten Gebotsverfahrens durch unseren Energiehandel erwirtschaftet der Batteriespeicher ein Jahr nach Inbetriebnahme Umsätze, die weit über den Erwartungen zum Zeitpunkt der Investitionsentscheidung lagen“, rechnet Thomas Pätzold, Technikvorstand der Wemag, vor. „Und das, obwohl ein weiteres Megawatt der Leistung noch nicht durch die vier Übertragungsnetzbetreiber präqualifiziert wurde. Wir haben alle erforderlichen technischen Voraussetzungen erfüllt und sind zuversichtlich, bald auch die vollen fünf Megawatt vermarkten zu können und damit unsere Erlöse zu steigern“, kündigte Pätzold an.
Benachteiligung macht Energiewende unnötig teuer
Allerdings sehen die Übertragungsnetzbetreiber die Speicher nicht gern am Regelleistungsmarkt. Sie wollen lieber konventionelle Kraftwerken die Geschäftsmodelle retten. „Deshalb werden Batteriespeicher, die nicht über einen Pool im Verbund mit konventionellen Kraftwerken vermarktet werden, am Markt noch systematisch benachteiligt“, kritisiert Clemens Triebel, Gründer von Yxouicos und dort für die unternehmerische Vision zuständig. „Und das obwohl sie nachweislich das Stromsystem entlasten, während die Must-run-Leistung konventioneller Kraftwerke die Leitungen für saubere Energie verstopft. Mit der systematischen Benachteiligung von Speichern machen wir die Energiewende unnötig teuer.“
Deutschland hängt hinterher
Dass sich intelligente Kurzzeitspeicher sowohl aus betriebswirtschaftlicher als auch aus volkswirtschaftlicher Sicht lohnen, hat die Wemag mit ihrer Anlage eindrücklich gezeigt. Doch Deutschland hängt da leider international mittlerweile hinterher“, weiß Clemens Triebel. „In Amerika etwa wird längst auch Schnelligkeit und Präzision honoriert.“ Deshalb ist in den USA auch für die Präqualifizierung nicht nur die Zeitdauer bei der Ausschreibung von Regelleistung von Bedeutung. Vielmehr geht es hier um Schnelligkeit, mit der der Speicher das Stromnetz im Notfall stützen kann. Da sind sie gegenüber den konventionellen Kraftwerken im Vorteil. Diese regeln nicht selten sogar zunächst in die falsche Richtung, weil sie für die Bereitstellung von Primärregelleistung eigentlich viel zu träge sind. (Sven Ullrich)
Batteries May Curb Sales by Power Companies, Moody’s Says
September 25, 2015By Mark Chediak and Jim Polson, Bloomberg
Batteries that allow large users to lower their reliance on the most expensive electricity threaten to cripple sales for U.S. independent power producers and utilities, posing credit challenges, according to Moody’s Investors Service.
Lithium-ion batteries sold by companies including Tesla Motors Inc. are on a path to becoming economically competitive for some applications in three to five years if prices continue to fall, Moody’s analysts led by Swami Venkataraman wrote in a report published Thursday.
The technology offers the potential to curb commercial demand for electricity during high-use periods and will help integrate large wind and solar plants with the power grid, the authors said. That may drive down revenue from selling power at independent power producers and utilities including Calpine Corp., NRG Energy Inc. and Dynegy Inc.
“It is likely to result in lower capacity prices and lower energy prices,” the authors wrote. “More widespread use of batteries will be credit negative” for power companies.
Businesses in states like New York that pay fixed fees based on their peak power use stand to benefit from battery storage, Moody’s said. They will be able to charge batteries at night when electricity is cheapest and tap into that power when prices rise.
Gas-Price Slump
“Expectations for a recovery in power markets have faded,” Bloomberg Intelligence Analyst Stacy Nemeroff said in research published Sept. 23. Power prices have fallen with natural gas while cheap oil makes exports of U.S. gas less competitive, potentially extending the gas-price slump, she said.
Shares of power producers dropped a fifth consecutive trading day on Sept. 24. The Bloomberg Intelligence North America Independent Power Producers Valuation Peers Index fell as much as 4 percent in intraday trading and is down about 15 percent for the week.
Dynegy fell 6.4 percent to $19.21 at 11:55 a.m. on Sept. 24 in New York, leading a fifth consecutive day of declines among power producers. NRG fell 2 percent to $15.12 and Calpine Corp. fell 3.5 percent to $14.15.
Falling Prices
Meanwhile, batteries are poised to take off in the power sector. Installations in 2019 may reach 858 MW, up 13-fold from 2014, according to GTM Research.
That’s driven in part by falling prices for batteries, down more than 50 percent since 2010, according to the Moody’s report.
For independent power producers, wider use of battery storage may lead to lower payments to keep capacity available for periods when demand climbs, as well as lower prices as businesses use less, according to the report.
“We’re probably eight years to 10 years away from that stuff actually happening,” Jay Rhame, who helps manage $2.6 billion including utility funds at Reaves Asset Management in Jersey City, N.J., said in an interview. “In 10 years, it will make a lot of sense for commercial and industrial customers.”
Rate Increases?
For regulated utilities, batteries can reduce monthly bills for commercial and industrial customers, forcing utilities to raise prices for other customers to make up the difference, Moody’s said. That’s an issue that state regulators will eventually have to address.
“A lot of commercial and industrial customers, they pay very high demand charges for their peak load,” Venkataraman said in a phone interview. “They can put in a battery, charge it at night and use that to serve a part of their load during the day. The peak load will be cut.”
Markets poised to take advantage of batteries include New York City and other locations in the U.S. Northeast, California and Hawaii, Venkataraman said. Pairing batteries with home solar installations likely won’t be economically competitive to grid power for at least a decade, he said.
“The credit impact won’t be immediate,” Venkataraman said. “Battery penetration will have to be material for it to have an impact.”
ESSI-Players according to Navigant

Quelle: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/2015/09/who-s-l…
Dyson steigt in den Li-ion Markt ein:
http://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/sakti3-batteries… interessant:
http://blogs.barrons.com/stockstowatchtoday/2015/10/30/tesla…Will stationary storage be profitable?…We believe Tesla’s sales target of $2-5bn in 2017 will fall short. More importantly, conversations with project developers & industry consultants highlight that storage competitors like LG, Samsung & BYD are aggressive with systems offered in the $400-500/kWh range (Tesla’s $250/kWh doesn’t include installation which can be 2x cell cost). These large competitors appear willing to lose money initially in order to win business & demonstrate their technology. Even if Tesla hits its sales targets, profits may disappoint.
Will the gigafactory give Tesla a cost advantage? Is competition increasing? At General Motors’ (GM) investor day, we were impressed by General Motors’ Lithium (Li) battery cell cost est. of $145/kWh trending to $100-125/kWh by 2022. This compares to Tesla’s $200- 300/kWh pack costs & $100/kWh target (est. pack currently adds about $100- 125/kWh). This would imply General Motors-LG battery costs are comparable to Tesla today & coming down without incurring the cost of building the gigafactory. Also, luxury EV competition is increasing. At the Frankfurt Auto Show, Audi revealed the e-tron quattro (2018), Porsche revealed the Mission E, & Mercedes announced plans to sell an EV by 2018 with 250-310 mile range. In addition, media reports indicate that Apple (AAPL) plans to ‘ship’ an EV by 2019, possibly putting Apple in competition with Tesla.
wissenschaftliche Quelle zu Li-ion Kosten:
http://www.nature.com/articles/nclimate2564.epdf Exportschlager Direktvermarktung: Next Kraftwerke expandiert nach Frankreich
20.11.2015, 15:36 Uhr Meldung drucken | Artikel empfehlenKöln – Die Direktvermarktung von Strom aus erneuerbaren Energiequellen ist in Deutschland bereits ein etabliertes Geschäftsfeld. Für die Pioniere der Branche werden inzwischen auch immer mehr Auslandsmärkte interessant. Nun geht der Kölner Direktvermarkter Next Kraftwerke nach Frankreich.
Centrales Next SAS heißt die französische Tochtergesellschaft, die das Unternehmen Next Kraftwerke in Frankreich gegründet hat. In dem neuen Büro in Paris bereiten mehrere Mitarbeiter seit Anfang Juni 2015 den Markteintritt der Tochtergesellschaft vor. Das Leipziger Energiehandelshaus Energy2market (e2m) ist kürzlich zum „Wachstumschampions 2016“ in der Kategorie „Energie & Versorgung“ gekürt worden. Auch e2m drängt es in neue Märkte.
Frankreich ermöglicht ab 2016 Direktvermarktung von EE-Strom
Centrales Next wird in Frankreich Produkte im Bereich der Stromvermarktung und auch im Bereich der „Aggregation von Flexibilität“ anbieten. Centrales Next kann mit der Direktvermarktung von Strom aus erneuerbaren Energien („Vente Directe“) in den französischen Markt einsteigen, da das französische Energiewendegesetz für grünes Wachstum einen verbindlichen Rechtsrahmen dafür setzen wird, teilte das Unternehmen aus Köln mit.
Die neue Rechtslage erlaube es Anlagenbetreibern, ihren Strom ab dem Januar 2016 nicht mehr nur über die dortigen Netzbetreiber zu vermarkten, sondern nun auch über professionelle Stromhändler der erneuerbaren Energien an die Strombörsen zu bringen – ähnlich der deutschen Marktprämienverordnung im EEG 2012.
Ziel ist es außerdem, die Flexibilität der vernetzten dezentralen Anlagen zu bündeln, um diese dem Stromsystem zur Verfügung zu stellen. Erste Gespräche, etwa zur Regelenergiebereitstellung für den französischen Übertragungsnetzbetreiber RTE, haben diesbezüglich bereits stattgefunden.
Paradigmenwechsel hin zu erneuerbaren Energien in Frankreich vorantreiben
„Mit der Entscheidung zum zügigen Ausbau der erneuerbaren Energien hat die französische Regierung starke Anreize zur Umgestaltung des Energiesystems gesetzt. Diesen Paradigmenwechsel – weg von der Atomkraft, hin zu erneuerbaren Energien – möchten wir auch in Frankreich mit vorantreiben. Unsere Erfahrungen im Bereich der Vernetzung und Vermarktung von dezentralen erneuerbaren Energien werden uns und unseren Kunden dabei helfen – etwa auch deutschen Projektierern und Betreibern, die in Frankreich Erneuerbare-Energien-Anlagen bewirtschaften“, sagt Jochen Schwill, Gründer und Geschäftsführer der Next Kraftwerke GmbH, anlässlich des Markteintritts. „Wir sind sehr optimistisch, mit unserem Geschäftsmodell auch in Frankreich erfolgreich zu sein, umso mehr, als wir kein Fremdkapital für diese Expansion benötigen. Die ersten Kundenkontakte ermutigen uns, diesen nächsten Schritt in der Internationalisierung unseres Unternehmens anzugehen. Expansionen in weitere Länder werden bald folgen.“
Next Kraftwerke wurde 2009 gegründet und vernetzt dezentrale Stromerzeuger und Stromverbraucher im virtuellen Kraftwerk Next Pool, das bereits über 2.700 Einheiten mit rund 1.500 Megawatt (MW) Leistung umfasst. Das Unternehmen ist in Deutschland, Österreich, Belgien und nun Frankreich aktiv.
e2m steht derzeit vor Markteintritt in zwei weiteren europäischen Ländern
Auch der Leipziger Direktvermarkter e2m erschließt sich neue Märkte. 2015 wurden bereits Tochtergesellschaften in Polen und Österreich gegründet. Außerdem ist e2m Joint Venture Partner der Alpenenergie GmbH in Österreich. Gründungen bzw. die Aufnahme des Geschäftsbetriebs in mindestens zwei weiteren europäischen Ländern stehen nach Angaben des Unternehmens unmittelbar bevor.
e2m wächst derzeit rasant. Das Magazin Focus zeichnete e2m als einen der überzeugendsten Wachstumschampions 2016 aus. Insgesamt wurden von Focus und dem Statistik-Portal Statista bundesweit 13.500 eigenständige Unternehmen bewertet, von denen 500 in die engere Auswahl kamen. Im Gesamt-Ranking belegt e2m einen hervorragenden fünften Platz und in der Kategorie „Energie & Versorgung“ ist der Leipziger Direktvermarkter sogar Sieger.
Tesvolt - Li-Player
http://www.tesvolt.com/über-tesvolt.html E.On ist bei Greensmith eingestiegen
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/E.ON-Joins-AEP-… Amber Kinetics - Langzeit-Flywheels:
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/Amber-Kinetics-… UET erhält 28 MUSD aus Japan:
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/Flow-Battery-Bu…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 51.413.241 von R-BgO am 05.01.16 11:35:11
In a previous interview, Weed said that a typical installation will cost “somewhere between $700 and $800 per kilowatt-hour,” a figure that includes all the components needed to interconnect with the grid, adding, “When we scale up to where we’re going, we’re going to be $500 per kilowatt-hour, all in." He adds that UET “beats the competition both on dollar per kilowatt-hour and on levelized cost.” Weed said that customers should require a figure that “includes all the installation costs and components needed to operate the system and interconnect with the grid, all in" before deciding on a particular technology.
Auszug:
Russ Weed, VP of business development at UET, told GTM that the company's battery works well in a microgrid, in commercial and industrial applications, and in utility applications.In a previous interview, Weed said that a typical installation will cost “somewhere between $700 and $800 per kilowatt-hour,” a figure that includes all the components needed to interconnect with the grid, adding, “When we scale up to where we’re going, we’re going to be $500 per kilowatt-hour, all in." He adds that UET “beats the competition both on dollar per kilowatt-hour and on levelized cost.” Weed said that customers should require a figure that “includes all the installation costs and components needed to operate the system and interconnect with the grid, all in" before deciding on a particular technology.
GTM hat einen neuen report zu storage-BoS-costs rausgebracht
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/grid-scale-ener…was mich etwas irritiert, ist dass sie dauernd mit kW anstatt kWh hantieren...
Auszug:
Today, grid-scale energy storage balance-of-system costs average $670 per kilowatt. These costs include hardware like inverters and containers, soft costs like customer acquisition and interconnection, and engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) expenses. According to the latest report from GTM Research, Grid-Scale Energy Storage Balance of Systems 2015-2020: Architectures, Costs and Players, these costs will fall 41 percent over the next five years.

=> 670 ./. 41% = 395$
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 51.428.166 von R-BgO am 06.01.16 20:49:02
Sie zerlegen das Batteriesystem in die zwei Teile
*Batterie selbst -Preis in Euro/kWh- und
*BoS, also alles außer der eigentlichen Batterie (Inverter, Gehäuse, PC, etc.) mit Preis in EUR/kW.
Logik dahinter ist wohl, dass es teurer wird, wenn ich die gleiche Strommenge in kürzerer Zeit (=höhere Leistung) rein- oder rausholen will.
OK, jetzt hab' ich es kapiert:
http://www.photovoltaik.eu/Archiv/Meldungsarchiv/Systemkoste…Sie zerlegen das Batteriesystem in die zwei Teile
*Batterie selbst -Preis in Euro/kWh- und
*BoS, also alles außer der eigentlichen Batterie (Inverter, Gehäuse, PC, etc.) mit Preis in EUR/kW.
Logik dahinter ist wohl, dass es teurer wird, wenn ich die gleiche Strommenge in kürzerer Zeit (=höhere Leistung) rein- oder rausholen will.
Open Energi: Turning Hot Asphalt Tanks Into Fast-Acting Grid Batteries
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/Open-Energi-Tur…U.K. startup sees big potential for industrial systems as grid assets. So does U.K. grid operator National Grid.
by Jeff St. John
January 19, 2016
Keeping power grid frequency in balance doesn’t necessarily require expensive, fast-responding power plants or utility-scale batteries. With the right technology, the same job can be done with supermarket refrigerators, or water pumps, or even tanks of hot asphalt -- or bitumen, as they call it in the U.K.
Since 2011, London-based startup Open Energi has been integrating its control systems into flexible loads at supermarket chain Sainsbury’s, water treatment plants and pumps at northwest UK water utility United Utilities, and concrete plants of Aggregate Industries.
Last month, it announced its newest partner, Tarmac -- the century-old company that owns the trademark name for the tar-and-crushed rock mixture that’s used to surface most of the world’s roadways.
Before it’s turned into roads, bitumen must be kept in enormous tanks at temperatures of about 150 degrees Celsius, a task that requires a lot of electricity. But this enormous electrical load also comes with “a huge amount of thermal inertia,” Chris Kimmett, Open Energi’s commercial manager, said in an interview this month.
In other words, they stay hot for a long time without electricity, losing only about 1.5 degrees Celsius over half an hour of being turned off, he said. And that makes for a very useful grid resource for Open Energi’s targeted grid service: fast-responding, short-duration dynamic frequency response for U.K. grid operator National Grid.
Right now, it’s working on installing its control systems at about 200 bitumen tanks at 70 sites across the U.K., he said. Each can be turned on and off, based on Open Energi’s moment-by-moment analysis of what grid operator National Grid needs to keep its system at a stable frequency of 50 hertz.
This service, known as frequency regulation in the United States, is technically challenging, requiring large-scale resources to ramp up and down within seconds. This is a much more challenging set of tasks, compared to those required from traditional demand response programs in the U.S., or the U.K.’s Short-Term Operating Reserve (STOR) program, or its new capacity markets.
Frequency response in the U.K., as in the U.S., has traditionally been done by large power plants that ramp generation up and down, Kimmett said. But that’s a rather slow and inefficient way to react to quick grid frequency changes, particularly those that can arise with more and more intermittent wind and solar power coming onto the grid.
Indeed, a 2015 study by Open Energi, National Grid and Cardiff University found that the startup was able to deliver full response from field-tested bitumen tanks within 2 seconds, compared to 5 to 10 seconds for a thermal generator. And compared to the inefficient (and thus greenhouse-gas-intensive) method of quickly ramping power plants up and down, demand-side flexibility is essentially carbon-free, he said.
Open Energi isn’t the only company targeting demand-side resources for frequency regulation. In the United States, startup Enbala has hooked up megawatts' worth of flexible loads to bid into frequency regulation markets run by mid-Atlantic grid operator PJM and Ontario, Canada’s IESO. Other demand-response providers are starting to focus on faster-acting resources to target new opportunities beyond the traditional fields of capacity markets, which deal with slower response times.
Batteries can also act much more quickly than power plants. Purpose-built, grid-scale batteries have become a significant part of PJM’s frequency regulation market, and are starting to emerge as cost-effective alternatives in new regimes being developed by Texas grid operator ERCOT, for example. But batteries also cost millions of dollars per megawatt-hour, whereas demand-side resources are already paid for.
The limitation of demand-side resources is that they weren’t built to be grid-balancing agents, but rather to do very specific and valuable jobs -- move water, or heat materials, or keep food cold. Whatever flexibility they may have must be very carefully managed, to ensure that it isn’t interfering with the critical business processes involved, Kimmett said.
“That’s what our secret sauce is -- taking a long list of constraints from all our sites, and turning it into dynamic demand,” Kimmett said. “We want to be invisible to the end customers, but invaluable to National Grid.”
The U.K. could see a much larger market for demand-side frequency response in years to come, under National Grid’s “Power Responsive” campaign, he added. Launched last year, the campaign is pushing for demand-side resources to serve from one-third to one-half of the country’s frequency response needs, which today stand at about 2 gigawatts for a nationwide peak demand of about 45 gigawatts.
Open Energi has so far taken on a long list of responsibilities to enable the industrial loads it’s signed up, he said. Those range from identifying cost-effective targets and instrumenting them to ensure their proper integration into National Grid’s market, to managing the verification and settlement of payments they receive and share with their customers.
The company, founded in 1999 to target household refrigerators as grid assets and reconfigured to address industrial loads in 2008, has received financial backing, including a £5 million round in 2012 (equivalent to about $8 million at the time), from Ombu Group, a venture firm that’s backed by pension fund Invesco.
Emerging Market Microgrid Company Powerhive Snags Caterpillar as Equity Investor
Innovative renewable energy company that brings solar PV + energy storage microgrids to areas without energy is now $20M richer.January 27, 2016
By Jennifer Runyon
Startup Powerhive, a company that provides off-grid energy access to people in emerging markets said on January 25 that it completed a Series A $20M financing round led by Prelude Ventures with participation from Caterpillar Ventures, Total Energy Ventures, Tao Capital Partners, Pi Investments, and select other private investors.
Powerhive provides development expertise, software and control systems for microgrids in emerging markets. Its pilot project is an 80-kW capacity microgrid set up in four sites in Kisii, Kenya serving approximately 300 customers that it built in 2012. The company helps developers identify potential sites, source equipment (generally solar PV and energy storage), find and sign up customers and manage the energy delivery process. Customers prepay for electricity through mobile banking accounts and receive alerts when their accounts get too low, similar to a pre-pay automobile toll service like E-ZPass in the eastern U.S. There is a low up-front commitment.
The financing round comes on the heels of an $11M equity investment by Enel Green Power, which will help expand the company's Kisii project to 1 MW, bringing electricity to about 90,000 people in western Kenya.
According to the company, the $20M will support Powerhive's expansion into new markets in Africa and the Asia-Pacific, as well as continued growth in Kenya.
Caterpillar said in a press release that its investment into Powerhive builds on a commitment to developing products and services that contribute to sustainable power generation and utilization of all energy resources. Over the past year, Caterpillar Inc. has invested in Fluidic Energy for energy storage and signed a strategic alliance with First Solar, both to serve the microgrid market. First Solar is also a strategic investor in Powerhive.
Powerhive announced in December that Leonardo DiCaprio, actor, producer, and environmental activist, and Lord Gregory Barker, former member of British Parliament and Minister of State for Energy and Climate Change had joined its newly formed strategic advisory board.
Raj Prabhu, CEO of analyst firm Mercom Capital said in early January that a little more than $100 million went into companies that are selling distributed products such as solar lanterns and pay-as-you-go solar to markets in Africa and India in 2015. “That’s a first,” he said.
"Bringing sustainable and scalable electricity to these communities will be life changing for millions of people," said Prelude Ventures managing director Tim Woodward, adding that Prelude is excited to be partnering with “partners like Enel to scale the Powerhive opportunity."
es geht los:
Uniper AG: Rechtsgutachten bestätigt: Gesetzliche Grundlage benachteiligt Betreiber von ReservekraftwerkenDGAP-Media / 2016-02-26 / 12:01
Betreiber des Gemeinschaftskraftwerks Irsching erheben Klage auf angemessene Vergütung für Beitrag zu Netzstabilität und Versorgungssicherheit
Die Eigentümer des bayerischen Gemeinschaftskraftwerks Irsching (GKI), ENTEGA, Mainova,
N-ERGIE und Uniper, hatten im März 2015 - ebenso wie Uniper für das Kraftwerk Irsching 4 - die vorläufige Stilllegung des Kraftwerksblocks angezeigt, weil er unter den herrschenden Rahmenbedingungen in Deutschland nicht wirtschaftlich zu betreiben ist. Daraufhin ordnete der Übertragungsnetzbetreiber TenneT aufgrund der von ihm angenommenen Systemrelevanz im Hinblick auf die Anlage die Betriebsbereitschaft an, so dass sie weiterhin als Reserve für die Erhaltung der Netzstabilität betrieben werden muss.
Die GKI-Eigentümer fordern für die Phase dieses Reservebetriebs, nicht weiterhin schlechter gestellt zu werden, als die Betreiber nicht systemrelevanter Kraftwerke. Für die Inanspruchnahme ihres Eigentums im Allgemeininteresse an einer sicheren Stromversorgung fordern sie eine angemessene Vergütung, die nach den verfassungsrechtlichen Vorgaben mindestens eine Erstattung sämtlicher anfallender Kosten enthält.
Diese Auffassung wird durch ein von den GKI-Gesellschaftern in Auftrag gegebenes Rechtsgutachten von Professor Udo di Fabio, Institut für öffentliches Recht der Rheinischen Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn, bestätigt: Die derzeitigen Regelungen der Reservekraftwerksverordnung und auch die geplante Neuregelung im Rahmen des Strommarktgesetzes werden den verfassungsrechtlichen Anforderungen nicht gerecht. Solange sich die Erstattung der Kosten nur auf die Betriebsstunden beziehe, in denen das Kraftwerk tatsächlich Strom zur Erhaltung der Netzstabilität einspeist, werde der Betreiber eines systemrelevanten Kraftwerks dadurch schlechter gestellt, so das Ergebnis des Rechtsgutachtens. Eine tatsächliche Vollerstattung der durch die Indienstnahme des Kraftwerks verursachten Kosten müsse zudem auch die Abschreibungen und Kapitalkosten berücksichtigen.
Eckhardt Rümmler, als Chief Operating Officer bei Uniper unter anderem für die Stromerzeugung verantwortlich: "Die Vergütungen für die Vorhaltung von Kraftwerken für die Netzreserve muss fair geregelt werden. Dass der jetzige Zustand nicht haltbar ist, belegt nicht zuletzt das vorliegende Rechtsgutachten."
"Schon nach der Entscheidung des OLG Düsseldorf im Frühjahr 2015 hätte es eine Neuregelung geben müssen, die unsere Leistungen für den Netzbetreiber angemessen vergütet. Darauf warten wir noch heute. Dieser Zustand ist untragbar", so Josef Hasler, Vorstandsvorsitzender der N-ERGIE AG.
"Wir werden gegen unseren Willen gezwungen, das Kraftwerk weiter zu betreiben. Wir erhalten als Betreiber dafür keine Vergütung, die unsere gesamten Kosten deckt. Dies ist ein enteignungsgleicher Eingriff. Wir fordern daher eine kostendeckende Entschädigung für den weiteren Betrieb des Kraftwerks", erklärte Dr. Constantin H. Alsheimer, Vorstandsvorsitzender der Mainova AG.
"Das GKI ist ein besonders flexibles und klimafreundliches Gaskraftwerk neuester Bauart. Leider ist aber unter den heutigen Bedingungen im deutschen Strommarkt eine alte Braunkohleanlage viel profitabler als ein hochmodernes Gaskraftwerk. Hier muss der Gesetzgeber aktiv werden", so Dr. Marie-Luise Wolff-Hertwig, Vorstandsvorsitzende der ENTEGA AG.
GKI-Eigentümer reichen Klage gegen TenneT ein
Die GKI-Eigentümer haben heute Klage beim Landgericht Düsseldorf eingereicht. Die Unternehmen fordern eine angemessene Vergütung für die Vorhaltung und die erfolgten Einsätze des Kraftwerks im Auftrag des Netzbetreibers TenneT in den letzten drei Jahren. Nach Ansicht der GKI-Eigentümer hätte TenneT einer Anpassung des 2013 abgeschlossenen Vertrages zustimmen müssen. Das Oberlandesgericht Düsseldorf hatte am 28. April 2015 in einem Musterverfahren geurteilt, dass die von der Bundesnetzagentur festgelegten Grundsätze zu einer unangemessen niedrigen Vergütung geführt haben.
Die bisher von TenneT erhaltenen Zahlungen aus der 2013 geschlossenen Vereinbarung decken nicht die vollen Kosten für Vorhaltung und Betrieb des Kraftwerks zur Netzstabilisierung. Auch die mit dem Netzbetreiber vereinbarte Vergütung beruhte auf den vom Oberlandesgericht Düsseldorf als unangemessen gerügten Regelungen. Zudem hatte TenneT in Erwartung einer Neuregelung im Rahmen des Strommarktgesetzes - das es bis heute nicht gibt - die vertraglich vereinbarten Abschlagszahlungen seit Mai 2015 sogar deutlich reduziert.
Das Gemeinschaftskraftwerk Irsching hat eine Leistung von 846 Megawatt und ging im Jahr 2010 in Betrieb. Mit einem Wirkungsgrad von fast 60 Prozent gehört es zu den modernsten Gaskraftwerken Europas. Es wird im Auftrag der Eigentümergesellschaften von der Uniper Kraftwerke GmbH betrieben. Uniper hält 50,2 Prozent der Anteile, N-ERGIE 25,2 Prozent, Mainova 15,6 Prozent und ENTEGA 9 Prozent.
Novel Israeli Iron Flow Battery Will Drive Down Costs For Energy Storage
http://www.pveurope.eu/News/Energy-Storage/Novel-Israeli-Iro…3/11/16, 2:00 PM -
Electric Fuel Energy (EFE) has developed a novel Iron Flow energy storage technology that is projected to be less costly, safer, and more environmentally friendly than other large-scale battery storage solutions.
EFE is a newly formed subsidiary of Arotech Corporation, a provider of advanced power supplies and multimedia interactive simulators and trainers. The EFE development team was drawn from leading Arotech experts with over 20 years of experience, and EFE thus holds a broad knowledge base regarding every aspect of battery development and energy storage.
As considerable market growth is expected for stationary storage applications, EFE has made the strategic decision to enter this market segment and has successfully developed a tailor-made solution.
Patent pending on the new battery
The patent-pending Iron Flow battery will bring a breakthrough solution for stationary energy storage that is environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and safe. The new battery's technology is particularly suited for renewable integration, load shifting, peak shaving, and other long-duration storage application.
The new Iron Flow technology consists of a proprietary iron anode and a liquid cathode. This combination provides a solid foundation for a low-cost battery with an overall system price of USD 200 per kilowatt hour, even at low manufacturing volumes.
Lower costs, neither toxic nor dangerous materials
The EFE solution achieves advantages beyond mere cost reduction, as its anode and cathode materials are neither toxic nor dangerous. In sharp contrast to flow batteries based on bromine, vanadium or strong acids, the Iron Flow battery’s electrolyte hydroxides are well known, safe, easily disposable, and contain no toxic chemicals.
The membrane is non-fluorinated and available at low cost. Even very large batteries are safe to operate in all environments, and are environmentally friendly during operation and disposal. The new solution is particularly robust and has a long cycle-life.
Key success for solar and wind power applications
Current battery solutions are not always optimized for storing energy for several hours. For the future growth of solar and wind applications, a cost-efficient multi-hour storage solution is a key success factor. “In many commercial and industrial applications our new system can make the difference and help renewables to compete fully with electricity from the grid and from diesel gensets,” points out Ronen Badichi, President of Arotech's Power Systems Division and CEO of EFE. “We have tested the technology successfully and will deliver the first commercial systems in 2016. At the moment, we are extending our network of select competent technology partners in the main storage markets.” (HS)
How Soon Can Tesla Get Battery Cell Costs Below $100 per Kilowatt-Hour?
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/How-Soon-Can-Te…Its $100 per kilowatt-hour goal could be reached sooner than expected—and well ahead of the competition.
by Eric Wesoff
March 15, 2016
Where does the lithium-ion battery industry -- and most notably, Tesla/Panasonic -- stand today on battery costs?
Solar veterans will recall a time not so long ago when the industry's biggest dream was a PV module with a cost of 99 cents per watt. Obviously, the solar industry has long left that figure in the dust -- module costs of 40 cents per watt are a reality in today's market.
In fact, the 99-cent figure was more a VC-funding, press-ready construct than a real economic calculation.
Which is reminiscent of the equally arbitrary $100 per kilowatt-hour battery cost goal now put forth by the battery industry and the press. (Although it does help to have a concrete target to aim for.)
Ben Kallo at equity analyst firm RW Baird believes that Tesla's current battery costs are ~$150 to ~$200 per kilowatt-hour, well below the industry average pack costs of ~$350 per kilowatt-hour (as estimated by Bloomberg New Energy Finance). Kallo suggests that the Chevy Bolt's battery costs "are significantly higher" than those of Tesla.
Kallo suggests that Tesla "could reach its <$100 per kilowatt-hour target in the intermediate term as Gigafactory production ramps." He continued, “Additionally, we believe TSLA is ahead of expectations on reducing battery costs, and continues to have a significant lead on competing EVs.” (Kallo upped his Tesla stock target to $300 per share based on improved Model X production.)
GM sees its battery cell cost hitting $100 per kilowatt-hour in 2022. (GM is quoting cell cost, while Kallo is talking about battery packs. A complete battery pack "typically adds 20 percent above the cost of cells," according to David Snydacker, a battery expert at Dosima Research.)
Snydacker listed some ways Tesla could scrub out cost.
"Tesla can achieve cost savings through a variety of innovations related to manufacturing and battery technologies. For example, new approaches to electrode solvents (used to deposit electrodes) and formation cycling (initial charging at the factory) can help Tesla outperform recent forecasts for battery costs."
"Tesla and their suppliers may achieve savings by adding excess lithium or by replacing cobalt with cheaper manganese. They can eliminate dead weight in the cell by engineering inactive layers to be stronger and thinner, and by making active layers thicker. Cells can be made larger through better thermal performance. These innovations are marginal, but they add up to enhanced performance and lower cost."
"Many of these trends are reflected in Argonne Lab’s model for battery costs, which is a gold standard in the industry and is called BatPaC." BatPaC version 2 was released in December 2012 and showed Tesla-type batteries costing $163/kWh for 90-kWh packs at 500,000 per year. In December 2015, BatPaC version 3 was released, showing $109/kWh. The next version of BatPaC could easily predict prices below $100/kWh, in accordance with predictions by Baird and others."
This drop in battery costs will make battery electric vehicles "competitive with internal combustion engine cars in Europe by 2021 and in China by 2025," according to UBS.
If the parallels for the solar industry and the battery industry hold true, then battery costs will fall below the $100 per kilowatt-hour mark much sooner than expected.
Ravi Manghani, GTM's senior energy storage analyst adds, "In addition to mass-scale adoption of BEVs in global markets, a $100/kWh cell cost will have profound impacts on the growth of stationary energy storage markets. GTM Research's 2020 U.S. energy storage forecast of 1.7 gigawatts of annual deployments is based on battery pack costs reaching $200/kWh (by 2020). If we accelerate the cost reductions to below $100/kWh before the end of this decade, it could open up additional markets and applications even sooner."
A Spanish Company Makes Bold Claims About a New Graphene Battery. Experts Say There’s No Evidence
Graphenano’s promises to revolutionize storage are met with skepticism.by Mike Stone
March 22, 2016
23
Graphene has long been touted as a material with near-miraculous properties. The incredibly tough, conductive, one-atom-thick carbon lattice offers promise for everything from electronics to bioengineering -- as well as energy storage.
According to Graphenano and its subsidiary Grabat Energy, that potential is about to be realized.
In recent media coverage, the Spain-based company claims that it will not only be offering “graphene polymer cells” by the summer, but that it will have perfected the industrial processes to produce large quantities of high-quality raw material.
Its promises are very bold.
According to CEO and President Martín Martínez, Graphenano is producing batteries with energy densities of 1,000 watt-hours per kilogram -- around five times that of current lithium-ion cells. A Tesla Model S equipped with these batteries would increase its range from 334 to 1,013 kilometers, he claimed.
Martínez also claimed that the new batteries are considerably lighter and safer than lithium-ion equivalents, saying researchers from TÜV Rhineland showed that the batteries are “not prone to explosions like lithium batteries.” What’s more, these revolutionary new batteries will retail at more or less the same price as their outmoded lithium-ion equivalents, he said.
Graphenano will be offering three types of batteries within months via its subsidiary, each composed of its graphene-based modular cells -- one for electric bicycles, another designed for motorbikes, and a third for stationary domestic storage.
Full production will be underway by October, with Grabat’s projected 200 employees producing 80 million cells per year at the company’s factory in Yecla in the Spanish region of Murcia.
The business has secured a fair amount of financial backing. Chinese electrical transmission and distribution company Chint has paid 18 million euros ($20 million) for a 10 percent stake in the company.
Martínez and one of China’s richest men, Nan Cunhui, attended the recent press launch -- along with Spain’s minister of industry. At the event, Martínez proudly displayed the company’s TÜV certification alongside impressive-looking battery prototypes and a well-produced corporate video.
Unsurprisingly, the Graphenano phenomenon has attracted plenty of media interest in Spain. Heavyweight national daily El Mundo ran an enthusiastic article on the company. Martínez has appeared on both local and national radio, expounding the merits of graphene-based energy storage and repeating his claims for his batteries.
But do these claims stand up to solid scrutiny?
Professor Andrea Ferrari, director of Cambridge University’s Graphene Center and chairman of the executive board of the European-Union-funded Graphene Flagship project, is skeptical of the batteries. But he does think it's possible for a company to be producing large quantities of graphene for use in them.
Although producing "true" monolayer graphene is still highly expensive, there are other less-tricky-to-prepare types of graphene -- such as platelets -- that could be manufactured cost-effectively.
Uncertainty surrounds the true nature of Graphenano’s cells, or what industrial technique the company is using to produce graphene. Although Martínez alluded to gas deposition onto a copper substrate in a radio interview, he claims this is just one technique employed by the company. Graphenano did not respond to a GTM request for clarification.
So is it credible that a company can be weeks away from utilizing graphene to produce a better battery commercially? And if so, how much better could that battery really be?
Jesús de la Fuente, founder and CEO of the respected Spanish graphene company Graphenea, confirmed that research is being carried out into replacing carbon black with graphene in lithium-ion battery electrodes. However, he said, this would only bring about modest improvements in battery performance.
The real breakthrough, explained de la Fuente, could be in so-called “post-lithium-ion” chemistries -- such as using graphene in the cathodes of lithium-sulfur cells. However, this type of technology is at least five years away from commercialization, he said. Anything even more innovative would likely be more than a decade away.
A number of influential blogs, such as Falacias Ecologistas, have been scathing in their assessment of the performance of Graphenano’s new batteries, using the Spanish expression "vendehúmos," or snake-oil salesman.
A senior figure in the graphene industry, speaking anonymously, pointed out that if such a revolutionary product were being produced, the company would be flourishing a sheaf of patents and white papers. Neither Graphenano or Grabat has publicly produced either.
“To make such a breakthrough, you would need a huge team of researchers -- at least a team of 100. This company says it has seven. There is no technical data and no support for their claims," said the source.
Furthermore, the TÜV certificate, proudly displayed at both the company’s media event and on its Facebook page, just seems to be the front page of a test report upon closer inspection.
María Buendía Bazán, a spokesperson with TÜV Rheinland’s Spanish marketing and communication department, said via email: “These companies are not certified by TÜV Rheinland.”
It is not impossible that Graphenano and Grabat could offer a groundbreaking product. But extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence -- and that evidence has not yet been produced.
New Iron Flow Battery Company Makes Big Claims About Cost. Will It Prove Itself?
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/new-iron-flow-b…Electric Fuel Energy has the technical backing of its parent company, Arotech. But it’s years behind flow battery rivals.
by Mike Stone
April 04, 2016
Electric Fuel Energy and its parent company are making some bold claims about a new flow battery. If they can live up to those claims, other flow battery companies may have some stiff competition.
Flow batteries provide long-duration electrochemical storage with the promise of 10-hour-plus discharge times.
“Flow batteries are particularly suited for applications that require long-discharge durations, such as load-shifting. The majority of flow battery deployments in the U.S. thus far have been utility-scale systems," explained Brett Simon, a storage analyst with GTM Research.
Flow batteries come in a variety of types, championed by different industry players. UniEnergy, Imergy and CellCube are in the vanadium space; iron chromium is the chemistry favored by EnerVault; and Primus Power, ZBB and Redflow specialize in zinc-bromine technology.
Electric Fuel Energy (EFE) is based in Israel, wholly owned by U.S.-based Arotech Corporation and run by CEO Ronen Badichi, who is also president of Arotech’s Power Systems Division. In a recent interview with GTM, Badichi pointed out that EFE is part of a company with 20+ years of experience in batteries -- and not reliant on angel investors -- giving it a key advantage.
That relationship and experience allowed the company to solve problems faster. “The goal was to create a very low-cost battery that, combined with renewable energy, could compete with diesel generation,” said Badichi.
The electrolyte, he said, is a harmless, inexpensive, unregulated organic solution frequently used as a food additive.
The end result will be a container-sized 150-kilowatt flow battery unit that delivers storage at a price of between $250 and $300 per kilowatt-hour, he claimed. Badichi also said his company intends to target developing economies, where the grid systems are weak and isolated, and also off-grid markets, including island communities. (This is where competitor Imergy has focused.)
“Places with stronger grids, such as Europe and the U.S., would not be our first choice -- but if and when subsidies for existing storage are dropped and existing storage needs to be retired, maybe there would be possibilities,” he said.
EFE is hoping to have a field demonstration project up and running by the end of this year, adding four more in 2017 and 2018; a full commercial launch is planned for 2019. The first production facility, based in Israel, is currently under construction, Badichi said.
If it does enter the market, EFE faces competition on at least three fronts. First, the current installed base of battery energy storage is predominantly lithium-ion. It has a deep advantage as a technology with a long track record.
Badichi countered that his company's flow battery can out-compete the current technology on price, even with very low economies of scale: “We don’t need a 50-gigawatt plant to make our product competitive,” he said, clearly referring to Tesla’s Gigafactory in Nevada. The battery should also have a lifespan around twice as long as current lithium-ion deployments.
Also, like other flow batteries with their typically long charging and discharging cycles, the technology can be used in areas less suited to lithium-ion. The product wouldn’t, for example, be targeting the crowded frequency-response market. “We are in the lithium battery business ourselves, so we’re well aware of what they can do -- and what they can’t,” he said.
The second challenge comes from other flow battery providers. Many are already deploying product and are much further down the development pipeline than EFE’s iron cell.
The company’s big advantage here is its technology’s ecological and safety credentials, said Badichi. To quote his company’s website: “The Iron Flow Battery offers superior safety and sound environmental characteristics...in sharp contrast to batteries based on bromine, vanadium or strong acids."
The iron flow battery also avoids plating and dendrite formation, which affects some other types of flow batteries, adding to their maintenance costs, according to EFE.
Given all these factors, how do EFE’s claims stack up? What are its chances of commercial success?
Dean Frankel, an analyst at Lux Research, has been following Arotech’s efforts in developing an iron flow battery for the last three years. It's a company with solid energy storage credentials, and any proposal it has should not be dismissed out of hand, he said.
He does urge caution, however. Frankel notes that the projected price of between $250 and $300 per kilowatt-hour is very aggressive -- especially when talking about a fully installed unit that includes installer profit, inverters, shipping and the cost of land: “For a system, without power electronics and without installation, it is believable but still aggressive.”
Energy Storage Systems, which is planning on deploying iron flow batteries for $500 per kilowatt-hour, has a more realistic target when taking into account real-world conditions, said Frankel. But even that figure is ambitious.
Frankel also sees the dominance of lithium-ion technology as a potential obstacle for any flow battery company seeking to break into the stationary energy storage market. As he points out, there were three orders of magnitude more lithium-ion batteries in operation in 2015 than flow batteries. And as the production of lithium-ion ramps up, prices continue to plummet.
Frankel acknowledges that flow batteries generally should have a big advantage in price -- if they have a chance to prove themselves.
E3/DC-Interview
http://www.pveurope.eu/News/Energy-Storage/How-will-prices-f…Auszüge:
"2015 was the first normal year of operation for E3/DC. We sold 1,500 of our home-power-stations. Compared to the previous year we were able to double our turnover, and have now achieved 15 million euros – almost breaking even."
"In 2016 we hope to sell between 2,100 and 2,500 units. In 2017 it could be 3,300 to 3,600, and more than 4,000 in 2018. Additionally, E3/DC will offer a commercial solution as well as upgrades, which are not included in these figures."
"Effectively, prices will not fall in 2016, because large producers like Samsung have realised that storage is a loss-making business. Take a look at the wholesale price for Tesla’s Powerwall, which at seven kilowatt hours is now more than 4,500 euros. When it was announced on 1 May, 2015, they were talking about 3,500 US dollars for ten kilowatt hours. Also, individual customers are not able to by the Powerwall and the wholesale dealer seller signs up to ‘authorised reselling’. As soon as one has to actually do what one announced, everything turns out differently."
"If market volume doubles, the price will fall by 10 to 15 percent, which can be achieved through economies of scale alone. In 2018, the new batteries for EVs will be introduced, with a capacity twice that of today’s batteries. That is like half the costs."
"You have to tell people the truth, especially if you are about to take thousands of euros off them. Indicating the number of cycles is a deception to the consumer, because he at home will never get anywhere near more than 3,000 to 4,000 cycles before the battery has reached the end of its lifespan as far as time is concerned. The customer ends up buying a battery that promises a certain number of kilowatt hours, but cannot deliver on that promise. What good does the price information do him, if he has no idea how much power he will be able to collect and discharge? The market is far from ready for guaranties of more than ten years of lifespan. The same is true for cars, where the warranty covers eight years."
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 52.221.283 von R-BgO am 19.04.16 10:33:25
They will of course fall. To 250 euros per kilowatt hour by 2018, with a purchase price for battery systems of currently 350 euros per kilowatt hour. A number of producers will introduce more and more risky configurations of devices, just to keep up with the competitor’s prices. For us, that cannot be the way to go. We want to sell our products at the highest possible price, which is why we have added all kinds of features to our home-power-station. The latest example is the emergency power capability or SG Ready as standard or significantly more functionality in the area of automation and the integration of EVs."
=>Wenn ich die 3.000-4.000 Zyklen nehme, lande ich also bei
8,75c bis 11,7c @350 Euro
6,25c bis 8,33c @250 Euro
für die reine Investitionsausgabe; not counting capital cost, operating cost, losses, etc.
hatte einen Abschnitt vergessen:
"How will battery prices develop?They will of course fall. To 250 euros per kilowatt hour by 2018, with a purchase price for battery systems of currently 350 euros per kilowatt hour. A number of producers will introduce more and more risky configurations of devices, just to keep up with the competitor’s prices. For us, that cannot be the way to go. We want to sell our products at the highest possible price, which is why we have added all kinds of features to our home-power-station. The latest example is the emergency power capability or SG Ready as standard or significantly more functionality in the area of automation and the integration of EVs."
=>Wenn ich die 3.000-4.000 Zyklen nehme, lande ich also bei
8,75c bis 11,7c @350 Euro
6,25c bis 8,33c @250 Euro
für die reine Investitionsausgabe; not counting capital cost, operating cost, losses, etc.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 50.040.657 von R-BgO am 24.06.15 13:24:11
Thread: GS Yuasa - macht JV mit Bosch - JV will Leistungsdichte verdoppeln
Thread: LG Chem(ical) - verwässert durch Chemie
Thread: Sekisui Chemical :Technischer Durchbruch bei Lithium-Akkus für Elektroautos - dlrowralos Liebling
Thread: Nicht billig aber klasse - SAFT GROUPE S.A. ACTIONS NOMINATIVES EO 1 - manche verdienen sogar Geld mit Li-Ion
Thread: ELectrovaya - Li-Ionen-Batterien - nicht nur Elon hat WILDE Träume
Thread: Leclanché - Schweizer Li-Ionen Produzent - dto.
Thread: Homeowners Can Save Energy and Prevent Unexpected Repairs With New Johnson Controls Smart Thermostat - verwässert durch Auto & Haustechnik
Thread: BYD CO LTD - mit Zukunft ?
Thread: Samsung SDI - scheint an Boden zu gewinnen
Thread: LION E-Mobility AG - Zukunftsbranche
Thread: Asahi Kasei - Membran-Zulieferer
andere Batterie-/oder Energiespeicher-Player
Thread: NGK Insulators - NaS Batteriehersteller - Flow-Batterien aus Japan
Thread: Einstieg Enersys - Weltmarktführer Pb-Zn
Thread: McPhy - französischer Wasserstoff-Speicher-Hersteller - Wasserstoffspeicher
Thread: ITM Power - Elektrolyse und Brennstoffzelle
Thread: Axion Power - neue WKN nach reverse split - PbC
Thread: ZBB Energy
Thread: Active Power - UPS - Flywheels
Thread: Redflow - The Holy Grail? - Zink-Bromid
Thread: EnerNOC: Smart Grid Business Models Taking Shape - Demand Response, allerdings rückläufig
Thread: Ideal Power Inc. Announces Third Quarter 2015 Results - Elektronik-Zulieferer
vorbörsliche
mit Einzelthread
Thread: Sonnenbatterie
Thread: Younicos
ohne Einzelthread
www.24-m.com/
www.alevo.com
http://amberkinetics.com
www.ambri.com
http://www.aquionenergy.com/
electric fuel energy
http://www.enstorageinc.com/
http://greensmithenergy.com/about/
www.imergy.com
http://www.itnes.com/news-ARPA-E_VRB.html
https://www.next-kraftwerke.de
http://www.openenergi.com/our-technology/
http://www.pdenergy.com/
http://www.powerhive.com
http://www.primuspower.com/
http://seeo.com/
www.solarwatt.de
http://www.tesvolt.com
http://www.uetechnologies.com/
www.viznenergy.com
update ggü. 24.6.2015:
Thread: Presse: Panasonic will Solarzellen-Produktion in Europa schließen - Tesla-LieferantThread: GS Yuasa - macht JV mit Bosch - JV will Leistungsdichte verdoppeln
Thread: LG Chem(ical) - verwässert durch Chemie
Thread: Sekisui Chemical :Technischer Durchbruch bei Lithium-Akkus für Elektroautos - dlrowralos Liebling
Thread: Nicht billig aber klasse - SAFT GROUPE S.A. ACTIONS NOMINATIVES EO 1 - manche verdienen sogar Geld mit Li-Ion
Thread: ELectrovaya - Li-Ionen-Batterien - nicht nur Elon hat WILDE Träume
Thread: Leclanché - Schweizer Li-Ionen Produzent - dto.
Thread: Homeowners Can Save Energy and Prevent Unexpected Repairs With New Johnson Controls Smart Thermostat - verwässert durch Auto & Haustechnik
Thread: BYD CO LTD - mit Zukunft ?
Thread: Samsung SDI - scheint an Boden zu gewinnen
Thread: LION E-Mobility AG - Zukunftsbranche
Thread: Asahi Kasei - Membran-Zulieferer
andere Batterie-/oder Energiespeicher-Player
Thread: NGK Insulators - NaS Batteriehersteller - Flow-Batterien aus Japan
Thread: Einstieg Enersys - Weltmarktführer Pb-Zn
Thread: McPhy - französischer Wasserstoff-Speicher-Hersteller - Wasserstoffspeicher
Thread: ITM Power - Elektrolyse und Brennstoffzelle
Thread: Axion Power - neue WKN nach reverse split - PbC
Thread: ZBB Energy
Thread: Active Power - UPS - Flywheels
Thread: Redflow - The Holy Grail? - Zink-Bromid
Thread: EnerNOC: Smart Grid Business Models Taking Shape - Demand Response, allerdings rückläufig
Thread: Ideal Power Inc. Announces Third Quarter 2015 Results - Elektronik-Zulieferer
vorbörsliche
mit Einzelthread
Thread: Sonnenbatterie
Thread: Younicos
ohne Einzelthread
www.24-m.com/
www.alevo.com
http://amberkinetics.com
www.ambri.com
http://www.aquionenergy.com/
electric fuel energy
http://www.enstorageinc.com/
http://greensmithenergy.com/about/
www.imergy.com
http://www.itnes.com/news-ARPA-E_VRB.html
https://www.next-kraftwerke.de
http://www.openenergi.com/our-technology/
http://www.pdenergy.com/
http://www.powerhive.com
http://www.primuspower.com/
http://seeo.com/
www.solarwatt.de
http://www.tesvolt.com
http://www.uetechnologies.com/
www.viznenergy.com
Flow - RedT
http://www.energy-storage.news/interviews/go-with-the-flow-r…Auszug:
"You would never buy a flow battery for an application where you only require half an hour’s storage. A flow battery is not economic on a power basis. There are much cheaper forms of [storage for] backup or short-term grid services. However on a more than three hour duration basis that’s where the flow battery is far more economic than conventional lead and lithium. You add more liquid for every hour of duration you need and once you get over that three hour duration requirement the flow battery is much cheaper.
Typically our customers are seeing a four to six hour range as optimal at full power. But then because it’s a non-degrading product, our customers want to use this as much as possible during the day to provide as many services as possible because they can – and they can either save costs or make money.
So that’s why you get into the revenue stacking business. I describe it as an asset like an aircraft. You want high utilisation. You wouldn’t run an aircraft at 20% passenger levels. That’s what long duration or long-term storage is about. You might buy cheap one hour backup and only use it half an hour a day but when you’re talking long duration storage, you then want to use it to do many cycles of energy storage per day.
The interesting thing is if you buy a flow battery for long-term services, it provides the short-term services very easily as well. So it has a very fast response time and essentially you end up getting those short-term services for free as well. So it can do both."
Daimler macht auch Speichersysteme?:
http://www.pv-magazine.de/index.php?id=9&tx_ttnews[tt_news]=… Preispunkt Tesla -wenn sie nicht lügen-
http://electrek.co/2016/04/26/tesla-model-3-battery-pack-cos…"Tesla’s Vice-President of Investor Relations, Jeff Evanson, jumped in on the call between Langan and Bereisa to correct their analysis. Evanson stated that Tesla’s battery pack cost is already below $190/kWh"
Report: Batteries Will Not Be the Future of Grid Balancing in Germany
Power-to-heat and demand-side management are the most cost-effective measures for the country’s grid up to 2030, concludes a government-funded study.
by Mike Stone
April 26, 2016
A three-year study of Germany’s energy storage market funded by the government is not likely to favor batteries.
Although the full conclusions won’t be published for a while, a study supported by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy has found that grid-scale and behind-the-meter batteries are insufficient to meet Germany’s energy needs.
That’s according to Christoph Pellinger, the coordinator for the study, called Merit Order for Energy Storage Systems 2030.
Instead, residential and industrial power-to-heat systems, along with demand-side management of industrial and residential energy consumption, are the country’s best options to manage large amounts of renewable energy on the German grid, said Pellinger. The report will also favor vehicle-to-grid technologies as an economic grid-balancing option by 2030.
The study looked at the role of different storage systems on the grid and assessed what system infrastructure would be needed to ensure a reliable energy supply in the next decade and a half. The analysts assume that adoption of renewable energy will continue as part of Germany’s commitment to its energy transition policy, called Energiewende. In fact, they think that projections for renewables in Germany’s generation mix are on the conservative side -- predicting that renewables will account for 60 percent of energy in 2025 and 85 percent in 2035.
An executive summary from the study is due to be published late this month or early next. Pellinger said the study will emphasize the potential for power-to-heat and demand response as the best ways to manage the grid. However, he concedes that regulatory reforms will be needed in order to give them the opportunity to grow.
“I can think of lithium-ion battery storage for primary frequency control; however, the market is rather small, with less than 600 megawatts in Germany and 3,000 megawatts in Europe. So far we do not see batteries on the grid scale for load-shifting purposes in Germany,” said Pellinger.
He is also cautious about the role of residential storage. “Batteries for residential storage might have an impact, but they are even less economically viable than most analysts think. Home storage units often consume a surprising amount of electricity themselves in standby mode, and this is rarely taken into account,” he said, citing a figure of between 20 and 70 watts, published in a recent German-language article.
However, these conclusions are not without their critics.
“It’s notoriously difficult to make predictions in this field, as the technology and prices are changing so rapidly,” said Philip Hiersemenzel, a spokesperson for the German energy storage company Younicos.
Professor Volker Quaschning of the Berlin University of Applied Sciences said he actually foresees a “strong role” for batteries at the grid level. And despite some current problems, he believes the residential storage industry is seeing prices fall at a promising rate.
Hiersemenzel criticized the emphasis on power-to-heat systems, saying that the researchers were giving too much credit to “old solutions” with little room for economic improvement.
Quaschning agreed with Pellinger’s assertion that a large fleet of electric vehicles could be useful for storing cheap excess energy. However, he stressed that the 3 million to 4 million EVs needed on Germany’s roads to enable meaningful vehicle-to-grid storage are not a given, even by 2030.
Hiersemenzel also has his doubts about using EVs to help balance the German grid. “The investigation has certainly asked the right questions -- but whether it has provided the correct answers remains to be seen,” he said.
Power-to-heat and demand-side management are the most cost-effective measures for the country’s grid up to 2030, concludes a government-funded study.
by Mike Stone
April 26, 2016
A three-year study of Germany’s energy storage market funded by the government is not likely to favor batteries.
Although the full conclusions won’t be published for a while, a study supported by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy has found that grid-scale and behind-the-meter batteries are insufficient to meet Germany’s energy needs.
That’s according to Christoph Pellinger, the coordinator for the study, called Merit Order for Energy Storage Systems 2030.
Instead, residential and industrial power-to-heat systems, along with demand-side management of industrial and residential energy consumption, are the country’s best options to manage large amounts of renewable energy on the German grid, said Pellinger. The report will also favor vehicle-to-grid technologies as an economic grid-balancing option by 2030.
The study looked at the role of different storage systems on the grid and assessed what system infrastructure would be needed to ensure a reliable energy supply in the next decade and a half. The analysts assume that adoption of renewable energy will continue as part of Germany’s commitment to its energy transition policy, called Energiewende. In fact, they think that projections for renewables in Germany’s generation mix are on the conservative side -- predicting that renewables will account for 60 percent of energy in 2025 and 85 percent in 2035.
An executive summary from the study is due to be published late this month or early next. Pellinger said the study will emphasize the potential for power-to-heat and demand response as the best ways to manage the grid. However, he concedes that regulatory reforms will be needed in order to give them the opportunity to grow.
“I can think of lithium-ion battery storage for primary frequency control; however, the market is rather small, with less than 600 megawatts in Germany and 3,000 megawatts in Europe. So far we do not see batteries on the grid scale for load-shifting purposes in Germany,” said Pellinger.
He is also cautious about the role of residential storage. “Batteries for residential storage might have an impact, but they are even less economically viable than most analysts think. Home storage units often consume a surprising amount of electricity themselves in standby mode, and this is rarely taken into account,” he said, citing a figure of between 20 and 70 watts, published in a recent German-language article.
However, these conclusions are not without their critics.
“It’s notoriously difficult to make predictions in this field, as the technology and prices are changing so rapidly,” said Philip Hiersemenzel, a spokesperson for the German energy storage company Younicos.
Professor Volker Quaschning of the Berlin University of Applied Sciences said he actually foresees a “strong role” for batteries at the grid level. And despite some current problems, he believes the residential storage industry is seeing prices fall at a promising rate.
Hiersemenzel criticized the emphasis on power-to-heat systems, saying that the researchers were giving too much credit to “old solutions” with little room for economic improvement.
Quaschning agreed with Pellinger’s assertion that a large fleet of electric vehicles could be useful for storing cheap excess energy. However, he stressed that the 3 million to 4 million EVs needed on Germany’s roads to enable meaningful vehicle-to-grid storage are not a given, even by 2030.
Hiersemenzel also has his doubts about using EVs to help balance the German grid. “The investigation has certainly asked the right questions -- but whether it has provided the correct answers remains to be seen,” he said.
Flow Battery Funding Flows On: ViZn Lands $10M for Zinc-Based Energy Storage
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/flow-battery-fu…Flow Battery Funding Flows On: ViZn Lands $10M for Zinc-Based Energy Storage
Montana-based startup joins UET and Primus Power in raising funds for long-duration energy storage.
by Jeff St. John
April 22, 2016
Investments are flowing in the flow battery business, with ViZn Energy Systems the latest to raise funds to scale up its zinc-based chemistry. The startup has raised another $10 million of an ongoing round of investment, according to a regulatory filing.
The newly disclosed investment adds to $1.4 million added in April 2015 and $5.3 million added in October, and brings ViZn’s total funding in this round to $16.8 million of a target of $22.9 million. Back in June 2015, CEO Ron Van Dell told us the company was seeking about that amount to scale up from its then-pilot scale level of deployments.
Since then, ViZn has landed a 2-megawatt order with Hecate Energy for a storage project in the territory of Canadian grid operator Ontario IESO, as well as establishing a contract manufacturing relationship with Jabil. The company had raised $20 million previously from “high-net-worth individuals,” Van Dell said.
ViZn’s key differentiator is its use of zinc -- a cheap and plentiful metal, but a tricky one to use in flow batteries. Specifically, it tends to gum up the electrode materials in the cells used to generate electricity in flow batteries. ViZn’s solutions, built around technology developed by Lockheed Martin, takes into account “how to do the zinc morphology, how to manage the fluid mechanics of your design, how to deal with shunt current,” the CEO said.
Other zinc-based flow battery makers include Australia’s
*Redflow Energy Storage Solutions, which is bringing a residential-sized battery to market, and U.S.-based
*Primus Power, which raised $25 million in September. While not a flow battery,
*Eos Energy Storage’s zinc-aqueous batteries have landed multi-megawatt contracts with California utilities.
Vanadium is the metal used by the other key class of flow battery companies. While it’s more expensive and harder to find, it offers some unique benefits -- namely, a chemical quirk that allows it to work without any additive chemicals, as required by other metal-based systems.
Several generations of vanadium redox flow batteries exist. The earlier technologies are from Sumitomo, which is installing a 60-megawatt-hour system in Japan, and Gildemeister-DMG Mori Seiki, which makes the CellCube system now being deployed in Europe and in New York City. The newer-generation technologies make use of advanced vanadium electrolytes developed in part through Department of Energy-funded research, and are made by companies such as Imergy and UET.
Flow batteries share the common characteristic of de-linking power from energy in the storage equation. That is to say, they can add extra kilowatt- or megawatt-hour capacity simply by adding more tanks of electrolyte to the same system, which processes it through its electrochemical cells to generate power. That’s different than a solid, cell-based battery, where the relationship between power density and energy storage capacity has to be made beforehand, in the choice of particular lithium chemistries, for example.
Lithium-ion batteries still vastly outnumber flow batteries in terms of megawatts deployed in real-world energy storage systems. They’re also being used for storage projects that require up to 4 hours of discharge at a time, although that’s considered a pretty rough duty cycle for batteries.
But flow battery boosters say they’re more cost-effective for 4-hour cycling and beyond, considering the potential for lithium-ion batteries doing such duty to require earlier-than-expected replacement. As with so many questions for the energy storage industry, only time will tell.
Moving the markets: The Tesvolt commercial energy storage system sets a benchmark for the new technology
5/6/16, 11:04 AM -
http://www.pveurope.eu/News/Energy-Storage/Moving-the-market…
Tesvolt is one of the leading companies that offer lithium ion storage systems for commercial use and utility scale. The commercial storage system Tesvolt is made of batteries up to 120 kilowatt hours of storage capacity. Some systems might be expanded to reach higher capacity. The utility scale storage systems range up to three Megawatt hours, as recently contracted in inner Africa. “We have stopped building lead acid storage units altogether,” Daniel Hannemann, CEO of Tesvolt says.
Farewell to lead acid technology
Initially, Tesvolt started out in lead acid technology and gathered extensive experience in large-scale storage systems. Nowadays, they exclusively use lithium iron phosphate batteries. “The price advantage of lead batteries is no longer significant in high-performance commercial applications. They are now only 15 to 20 percent cheaper than batteries made with lithium iron phosphate,” Simon Schandert says. He is head of engineering at Tesvolt. “You can only half discharge a lead acid cell, so in effect you need twice the gross capacity compared to lithium storage systems. If you factor in their considerably greater number of charging cycles, lithium iron phosphate batteries make much more sense, economically.”
Tesvolt buy in their high-performance cells from an Asian producer that also makes batteries for electric cars and busses as well as boats and telecoms back-up systems. The power electronics units are based on SMA’s (Sunny Island) charging controller.
High level of efficiency for the overall system
The battery is managed and controlled using an app on a tablet. It is connected through Bluetooth and constantly gets updated with operational data. If a cell weakens, the app will show that immediately. “We are also able to selectively move energy from one cell to another,” Simon Schandert says. “This not only allows us to charge and discharge quickly and seamlessly, we also achieve an extremely high level of efficiency for the overall system.”
The storage system can be expanded to up to four battery cabinets with up to three Sunny Islands (for example, 240 kilowatt hours at 18 kilowatts of charging capacity from three Sunny Islands 8.0H units). The units started to be sold at the Intersolar in June of 2015, one year ago. Until now the demand has not slackened since. First enquiries are also coming in from Austria, Switzerland and Italy.
Tesvolt’s storage unit makes use of 80 to 83 percent of the energy. So far, 70 to 76 percent has been the standard for lithium batteries. The reason why Tesvolt collaborates so closely with SMA is that the Sunny Island has an almost unbeatable advantage: The efficiency stays nearly constant at 92 percent from very low partial loads of 5 percent all the way to full load. Other inverters often show much higher losses, especially at partial load. That is why Tesvolt storage units can achieve 83 percent efficiency under real-life conditions.
Designed like an off-grid system
Furthermore, the Sunny Island has an emergency back-up function and off-grid capability. The UK and Russia have strict ordinances regulating that storage units must not feed electricity back into the grid, but have to run in zero-feed-in mode. “So you have to design this unit like an off-grid system,” Schandert explains. “In off-grid mode, the three inverters can produce up to 900 amperes of current. The battery has to be able to deal with that.”
The battery management system has been certified by the TÜV Rheinland. Until the end of the year, the unit should also have earned all other tests and certificates that the safety guidelines require.
In Europe, such storage units are deployed in agriculture or in small enterprises. A dairy farmer in northern Germany uses batteries to run his milking parlour on solar energy. Cows are usually milked in the early morning between 5 and 6 o’clock and again in the late evening after 7.
While refrigeration and the feeding system are the base load, the mechanic milking system generates a significant load spike – just at times of day when PV not yet or no longer produces electricity. “In that case, the storage unit acts like a phase shifter,” Simon Schandert explains. In combination, PV and commercial storage are much more economic than a solar generator by itself.”
In Russia, for the first time storage units do not run in combination with PV systems, but in tandem with cogeneration plants. The Sunny Island can deal with any kind of generator. One of Tesvolt’s partners is a Russian builder of cogeneration plants whose power consumption sank due to the storage unit and using fuel more efficiently.
Tesvolt grants the usual product warranty of two years, a cell value replacement warranty lasting seven years and the performance warranty for ten years. Return and recycling is free, in accordance with the relevant regulations for batteries.
Once a month, Tesvolt trains 30 technicians in correctly setting up the Li storage units. “Commercial storage opens up a whole new market segment,” Daniel Hannemann is certain. “We see great opportunities in the area of petrol and service stations, in supermarkets, hotels, manufacturing companies and in agriculture.” (HS/IR)
5/6/16, 11:04 AM -
http://www.pveurope.eu/News/Energy-Storage/Moving-the-market…
Tesvolt is one of the leading companies that offer lithium ion storage systems for commercial use and utility scale. The commercial storage system Tesvolt is made of batteries up to 120 kilowatt hours of storage capacity. Some systems might be expanded to reach higher capacity. The utility scale storage systems range up to three Megawatt hours, as recently contracted in inner Africa. “We have stopped building lead acid storage units altogether,” Daniel Hannemann, CEO of Tesvolt says.
Farewell to lead acid technology
Initially, Tesvolt started out in lead acid technology and gathered extensive experience in large-scale storage systems. Nowadays, they exclusively use lithium iron phosphate batteries. “The price advantage of lead batteries is no longer significant in high-performance commercial applications. They are now only 15 to 20 percent cheaper than batteries made with lithium iron phosphate,” Simon Schandert says. He is head of engineering at Tesvolt. “You can only half discharge a lead acid cell, so in effect you need twice the gross capacity compared to lithium storage systems. If you factor in their considerably greater number of charging cycles, lithium iron phosphate batteries make much more sense, economically.”
Tesvolt buy in their high-performance cells from an Asian producer that also makes batteries for electric cars and busses as well as boats and telecoms back-up systems. The power electronics units are based on SMA’s (Sunny Island) charging controller.
High level of efficiency for the overall system
The battery is managed and controlled using an app on a tablet. It is connected through Bluetooth and constantly gets updated with operational data. If a cell weakens, the app will show that immediately. “We are also able to selectively move energy from one cell to another,” Simon Schandert says. “This not only allows us to charge and discharge quickly and seamlessly, we also achieve an extremely high level of efficiency for the overall system.”
The storage system can be expanded to up to four battery cabinets with up to three Sunny Islands (for example, 240 kilowatt hours at 18 kilowatts of charging capacity from three Sunny Islands 8.0H units). The units started to be sold at the Intersolar in June of 2015, one year ago. Until now the demand has not slackened since. First enquiries are also coming in from Austria, Switzerland and Italy.
Tesvolt’s storage unit makes use of 80 to 83 percent of the energy. So far, 70 to 76 percent has been the standard for lithium batteries. The reason why Tesvolt collaborates so closely with SMA is that the Sunny Island has an almost unbeatable advantage: The efficiency stays nearly constant at 92 percent from very low partial loads of 5 percent all the way to full load. Other inverters often show much higher losses, especially at partial load. That is why Tesvolt storage units can achieve 83 percent efficiency under real-life conditions.
Designed like an off-grid system
Furthermore, the Sunny Island has an emergency back-up function and off-grid capability. The UK and Russia have strict ordinances regulating that storage units must not feed electricity back into the grid, but have to run in zero-feed-in mode. “So you have to design this unit like an off-grid system,” Schandert explains. “In off-grid mode, the three inverters can produce up to 900 amperes of current. The battery has to be able to deal with that.”
The battery management system has been certified by the TÜV Rheinland. Until the end of the year, the unit should also have earned all other tests and certificates that the safety guidelines require.
In Europe, such storage units are deployed in agriculture or in small enterprises. A dairy farmer in northern Germany uses batteries to run his milking parlour on solar energy. Cows are usually milked in the early morning between 5 and 6 o’clock and again in the late evening after 7.
While refrigeration and the feeding system are the base load, the mechanic milking system generates a significant load spike – just at times of day when PV not yet or no longer produces electricity. “In that case, the storage unit acts like a phase shifter,” Simon Schandert explains. In combination, PV and commercial storage are much more economic than a solar generator by itself.”
In Russia, for the first time storage units do not run in combination with PV systems, but in tandem with cogeneration plants. The Sunny Island can deal with any kind of generator. One of Tesvolt’s partners is a Russian builder of cogeneration plants whose power consumption sank due to the storage unit and using fuel more efficiently.
Tesvolt grants the usual product warranty of two years, a cell value replacement warranty lasting seven years and the performance warranty for ten years. Return and recycling is free, in accordance with the relevant regulations for batteries.
Once a month, Tesvolt trains 30 technicians in correctly setting up the Li storage units. “Commercial storage opens up a whole new market segment,” Daniel Hannemann is certain. “We see great opportunities in the area of petrol and service stations, in supermarkets, hotels, manufacturing companies and in agriculture.” (HS/IR)
Nissan and Eaton develop home energy storage solution
AUTOMOTIVE leader Nissan and power management leader Eaton, have joined forces to unveil a new residential energy storage unit – designed to be the most affordable in the market today.
Available to pre-order from September 2016, the ‘xStorage’ solution will give consumers the power to control how and when they use energy in their own homes.
Connected to residential power supply or renewable energy sources such as solar panels, the unit can save customers money on their utility bills by charging up when renewable energy is available or energy is cheaper (e.g. during the night) and releasing that stored energy when demand and costs are high. If a home is equipped with solar technology, this means that consumers can power their homes using clean energy stored in their xStorage system, and be rewarded financially for doing so by avoiding expensive daytime energy tariffs.
The home energy storage system also provides the ultimate back-up solution to consumers, ensuring that the lights never go out – ideal at a time when energy grids are coming under enormous strain. Moreover, customers can also generate additional revenues by selling stored energy back to the grid when demand and costs are high.
The xStorage unit will be the first device of its kind in the market to provide a fully integrated energy storage solution for homeowners. This means, unlike other storage devices, this factory made integrated unit ensures safety and performance when storing and distributing clean power to consumers. Once set-up by a certified installer, it is ready to go, giving consumers the ability to plug in and power up easily. It will also have smartphone connectivity to allow consumers to flick between energy sources at the touch of a button.
Paul Willcox, Chairman, Nissan Europe said: “It is high time consumers were given the flexibility and power to control how and when they use energy in their own homes. The new xStorage solution combines Nissan’s expertise in vehicle design and reliable battery technology with Eaton’s leadership in power quality and electronics, resulting in a formidable second life battery solution. We want to make energy storage exciting and affordable to everyone, not least because it delivers real consumer benefits whilst ensuring smarter and more sustainable energy management for the grid.”
Beyond its high specification functionality, the xStorage system has also been designed with aesthetics and usability in mind to ensure it fits seamlessly into the home environment. This design expertise comes directly from the brains at Nissan Design Europe, UK who are renowned for their world-class vehicle design and styling.
Providing a sustainable ‘second life’ for Nissan’s electric vehicle (EV) batteries after their first life in cars is over, the new unit is powered by twelve Nissan EV battery modules and has the potential to revolutionise the way people manage energy usage in their own home, providing added flexibility and multiple cost savings.
Cyrille Brisson, Vice President Marketing, Eaton Electrical EMEA said: “The collaborative development between Eaton and Nissan enabled us to optimize development and production costs and deliver a well-integrated offer to consumers. Our system will be provided to end-users completely ready to use, with all required elements including cabling and installation by a certified professional, at a starting price of €4,000 (£3200) for 4.2KWh nominal. Our policy is to avoid hidden extra costs and achieve a lower total cost of ownership than other major offers already announced.
Both companies have a well-established footprint in Europe, Africa and the Middle-East. At Eaton, we have a network of over 1,000 distributors working with qualified installers in 77 countries. We ensure that consumers access, store and use clean power safely and efficiently in the comfort of their own home.”
The new xStorage system unveiled today marks the start of a longer-term commitment by Nissan and Eaton to widen the portfolio of energy storage solutions available to both private and commercial customers. Nissan and Eaton expect to sell more than 100,000 xStorage units within the next five years as the consumer appetite for this type of technology continues to grow.
AUTOMOTIVE leader Nissan and power management leader Eaton, have joined forces to unveil a new residential energy storage unit – designed to be the most affordable in the market today.
Available to pre-order from September 2016, the ‘xStorage’ solution will give consumers the power to control how and when they use energy in their own homes.
Connected to residential power supply or renewable energy sources such as solar panels, the unit can save customers money on their utility bills by charging up when renewable energy is available or energy is cheaper (e.g. during the night) and releasing that stored energy when demand and costs are high. If a home is equipped with solar technology, this means that consumers can power their homes using clean energy stored in their xStorage system, and be rewarded financially for doing so by avoiding expensive daytime energy tariffs.
The home energy storage system also provides the ultimate back-up solution to consumers, ensuring that the lights never go out – ideal at a time when energy grids are coming under enormous strain. Moreover, customers can also generate additional revenues by selling stored energy back to the grid when demand and costs are high.
The xStorage unit will be the first device of its kind in the market to provide a fully integrated energy storage solution for homeowners. This means, unlike other storage devices, this factory made integrated unit ensures safety and performance when storing and distributing clean power to consumers. Once set-up by a certified installer, it is ready to go, giving consumers the ability to plug in and power up easily. It will also have smartphone connectivity to allow consumers to flick between energy sources at the touch of a button.
Paul Willcox, Chairman, Nissan Europe said: “It is high time consumers were given the flexibility and power to control how and when they use energy in their own homes. The new xStorage solution combines Nissan’s expertise in vehicle design and reliable battery technology with Eaton’s leadership in power quality and electronics, resulting in a formidable second life battery solution. We want to make energy storage exciting and affordable to everyone, not least because it delivers real consumer benefits whilst ensuring smarter and more sustainable energy management for the grid.”
Beyond its high specification functionality, the xStorage system has also been designed with aesthetics and usability in mind to ensure it fits seamlessly into the home environment. This design expertise comes directly from the brains at Nissan Design Europe, UK who are renowned for their world-class vehicle design and styling.
Providing a sustainable ‘second life’ for Nissan’s electric vehicle (EV) batteries after their first life in cars is over, the new unit is powered by twelve Nissan EV battery modules and has the potential to revolutionise the way people manage energy usage in their own home, providing added flexibility and multiple cost savings.
Cyrille Brisson, Vice President Marketing, Eaton Electrical EMEA said: “The collaborative development between Eaton and Nissan enabled us to optimize development and production costs and deliver a well-integrated offer to consumers. Our system will be provided to end-users completely ready to use, with all required elements including cabling and installation by a certified professional, at a starting price of €4,000 (£3200) for 4.2KWh nominal. Our policy is to avoid hidden extra costs and achieve a lower total cost of ownership than other major offers already announced.
Both companies have a well-established footprint in Europe, Africa and the Middle-East. At Eaton, we have a network of over 1,000 distributors working with qualified installers in 77 countries. We ensure that consumers access, store and use clean power safely and efficiently in the comfort of their own home.”
The new xStorage system unveiled today marks the start of a longer-term commitment by Nissan and Eaton to widen the portfolio of energy storage solutions available to both private and commercial customers. Nissan and Eaton expect to sell more than 100,000 xStorage units within the next five years as the consumer appetite for this type of technology continues to grow.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 50.984.478 von R-BgO am 02.11.15 13:03:53
an den 145$ scheint was dran zu sein:
http://insideevs.com/lg-chem-ticked-gm-disclosing-145kwh-bat…
Solare Heimspeicher ab 2018 wirtschaftlich
18.05.2016 10:20 -
http://www.photovoltaik.eu/Archiv/Meldungsarchiv/Solare-Heim…
Um rentabel zu sein, müssen Solarstromspeicher im Eigenheim die Grenze von 1.000 Euro unterschreiten. Das bezieht sich auf die nutzbare Speicherkapazität und Endkundenpreise. Erreicht wird dieser Wert auch mit der neuen KfW-Förderung noch nicht. Aber in ein bis zwei Jahren werden Speicher – nur für sich – wirtschaftlich arbeiten.
Für Hauseigentümer mit neuen Photovoltaikanlagen wird es immer reizvoller, ihren Solarstrom selbst zu verbrauchen, da er nur halb so teuer wie vom Energieversorger ist. Mit Batteriesystemen lässt sich der gewinnbringende Eigenverbrauchsanteil auf rund 60 Prozent verdoppeln. Lange waren die Solarstromspeicher aber nicht wirtschaftlich. „Aktuelle Zahlen zeigen jetzt, dass das bei Hausspeichern in ein oder zwei Jahren der Fall sein wird“, sagt Carsten Tschamber vom Solar Cluster Baden-Württemberg. „Die Kombination von Photovoltaik und Speicher wird sich angesichts der bevorstehenden Wirtschaftlichkeit immer mehr verbreiten.“ Und das nicht nur im Eigenheim: Neue Konzepte setzen auf zentrale Speicher für ganze Quartiere oder wollen Speicher im Land zu einem virtuellen Großspeicher vernetzen.
Die seit März wieder finanziell geförderten Batteriespeicher werden sich künftig als ein integraler Teil von Solaranlagen etablieren. Das ist nur noch eine Frage der Zeit. Bereits jetzt legt sich die Hälfte aller privaten Solaranlagenkäufer ein Speichersystem zu. Rund 19.000 Speicher wurden seit dem Start des Förderprogramms finanziell unterstützt. Anfang 2016 waren im Bundesgebiet insgesamt 34.000 Stück installiert. Das ergibt der von der RWTH Aachen im Auftrag des Bundeswirtschaftsministeriums erstellte Speichermonitoring-Bericht 2016, der Ende Mai veröffentlicht wird.
1.300 Euro für die nutzbare Kilowattstunde
Der Zuwachs liegt besonders an den stark gesunkenen Kosten der Batterieakkus. In den Jahren 2014 und 2015 sind die Systempreise für Lithiumspeicher pro genutzter Kilowattstunde um jeweils 18 Prozent gefallen. „Ähnlich wie bei der Photovoltaik sehen wir auch bei Speichern eine Lernkurve, die bei jeder Verdoppelung der Installationszahlen eine Preisreduktion von rund 20 Prozent vorhersagt“, erklärt Kai-Phillip Kairies von der RWTH Aachen.
„Derzeit ist ein Speichersystem auf Lithium-Ionen-Basis inklusive Wechselrichter und Installation bereits ab rund 1.300 Euro pro genutzter Kilowattstunde Speicherkapazität erhältlich“, berichtet Tschamber. Die Grenze, unter der die Kleinspeicher mehr einbringen als sie kosten, liegt bei rund 1.000 Euro. Erreicht wird sie auch mit der kürzlich neu aufgelegten Förderung noch nicht. Peter Eckerle vom Verein Storegio Energiespeichersysteme prognostiziert aber künftig weiter fallende Speicherpreise – rund 10 Prozent pro Jahr sind ihm zufolge realistisch. Steigt der Haushaltsstrompreis und fallen die PV-Anlagenkosten dann noch weiter wie bisher, könnten die Speicher 2017 oder 2018 wirtschaftlich sein. (Niels H. Petersen)
18.05.2016 10:20 -
http://www.photovoltaik.eu/Archiv/Meldungsarchiv/Solare-Heim…
Um rentabel zu sein, müssen Solarstromspeicher im Eigenheim die Grenze von 1.000 Euro unterschreiten. Das bezieht sich auf die nutzbare Speicherkapazität und Endkundenpreise. Erreicht wird dieser Wert auch mit der neuen KfW-Förderung noch nicht. Aber in ein bis zwei Jahren werden Speicher – nur für sich – wirtschaftlich arbeiten.
Für Hauseigentümer mit neuen Photovoltaikanlagen wird es immer reizvoller, ihren Solarstrom selbst zu verbrauchen, da er nur halb so teuer wie vom Energieversorger ist. Mit Batteriesystemen lässt sich der gewinnbringende Eigenverbrauchsanteil auf rund 60 Prozent verdoppeln. Lange waren die Solarstromspeicher aber nicht wirtschaftlich. „Aktuelle Zahlen zeigen jetzt, dass das bei Hausspeichern in ein oder zwei Jahren der Fall sein wird“, sagt Carsten Tschamber vom Solar Cluster Baden-Württemberg. „Die Kombination von Photovoltaik und Speicher wird sich angesichts der bevorstehenden Wirtschaftlichkeit immer mehr verbreiten.“ Und das nicht nur im Eigenheim: Neue Konzepte setzen auf zentrale Speicher für ganze Quartiere oder wollen Speicher im Land zu einem virtuellen Großspeicher vernetzen.
Die seit März wieder finanziell geförderten Batteriespeicher werden sich künftig als ein integraler Teil von Solaranlagen etablieren. Das ist nur noch eine Frage der Zeit. Bereits jetzt legt sich die Hälfte aller privaten Solaranlagenkäufer ein Speichersystem zu. Rund 19.000 Speicher wurden seit dem Start des Förderprogramms finanziell unterstützt. Anfang 2016 waren im Bundesgebiet insgesamt 34.000 Stück installiert. Das ergibt der von der RWTH Aachen im Auftrag des Bundeswirtschaftsministeriums erstellte Speichermonitoring-Bericht 2016, der Ende Mai veröffentlicht wird.
1.300 Euro für die nutzbare Kilowattstunde
Der Zuwachs liegt besonders an den stark gesunkenen Kosten der Batterieakkus. In den Jahren 2014 und 2015 sind die Systempreise für Lithiumspeicher pro genutzter Kilowattstunde um jeweils 18 Prozent gefallen. „Ähnlich wie bei der Photovoltaik sehen wir auch bei Speichern eine Lernkurve, die bei jeder Verdoppelung der Installationszahlen eine Preisreduktion von rund 20 Prozent vorhersagt“, erklärt Kai-Phillip Kairies von der RWTH Aachen.
„Derzeit ist ein Speichersystem auf Lithium-Ionen-Basis inklusive Wechselrichter und Installation bereits ab rund 1.300 Euro pro genutzter Kilowattstunde Speicherkapazität erhältlich“, berichtet Tschamber. Die Grenze, unter der die Kleinspeicher mehr einbringen als sie kosten, liegt bei rund 1.000 Euro. Erreicht wird sie auch mit der kürzlich neu aufgelegten Förderung noch nicht. Peter Eckerle vom Verein Storegio Energiespeichersysteme prognostiziert aber künftig weiter fallende Speicherpreise – rund 10 Prozent pro Jahr sind ihm zufolge realistisch. Steigt der Haushaltsstrompreis und fallen die PV-Anlagenkosten dann noch weiter wie bisher, könnten die Speicher 2017 oder 2018 wirtschaftlich sein. (Niels H. Petersen)
guter Übersichtsartikel zu Batterien:
http://seekingalpha.com/article/3976731-teslas-huge-mistake-…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 52.222.594 von R-BgO am 19.04.16 12:15:08
Thread: GS Yuasa - macht JV mit Bosch - JV will Leistungsdichte verdoppeln
Thread: LG Chem(ical) - verwässert durch Chemie
Thread: Sekisui Chemical :Technischer Durchbruch bei Lithium-Akkus für Elektroautos - dlrowralos Liebling
Thread: Nicht billig aber klasse - SAFT GROUPE S.A. ACTIONS NOMINATIVES EO 1 - manche verdienen sogar Geld mit Li-Ion
Thread: ELectrovaya - Li-Ionen-Batterien - nicht nur Elon hat WILDE Träume
Thread: Leclanché - Schweizer Li-Ionen Produzent - dto.
Thread: Homeowners Can Save Energy and Prevent Unexpected Repairs With New Johnson Controls Smart Thermostat - verwässert durch Auto & Haustechnik
Thread: BYD CO LTD - mit Zukunft ?
Thread: Samsung SDI - scheint an Boden zu gewinnen
Thread: LION E-Mobility AG - Zukunftsbranche
Thread: Asahi Kasei - Membran-Zulieferer
andere Batterie-/oder Energiespeicher-Player
Thread: NGK Insulators - NaS Batteriehersteller - Flow-Batterien aus Japan
Thread: Einstieg Enersys - Weltmarktführer Pb-Zn
Thread: McPhy - französischer Wasserstoff-Speicher-Hersteller - Wasserstoffspeicher
Thread: ITM Power - Elektrolyse und Brennstoffzelle
Thread: Axion Power - neue WKN nach reverse split - PbC
Thread: ZBB Energy
Thread: Active Power - UPS - Flywheels
Thread: Redflow - The Holy Grail? - Zink-Bromid
Thread: EnerNOC: Smart Grid Business Models Taking Shape - Demand Response, allerdings rückläufig
Thread: Ideal Power Inc. Announces Third Quarter 2015 Results - Elektronik-Zulieferer
vorbörsliche
mit Einzelthread
Thread: Sonnenbatterie
Thread: Younicos
ohne Einzelthread
www.24-m.com/
www.alevo.com
http://amberkinetics.com
www.ambri.com
http://www.amprius.com
http://www.aquionenergy.com/
http://www.boston-power.com
electric fuel energy
http://www.enstorageinc.com/
http://www.faradion.co.uk/technology/sodium-ion-technology/
http://greensmithenergy.com/about/
www.imergy.com
http://www.itnes.com/news-ARPA-E_VRB.html
https://www.next-kraftwerke.de
http://www.openenergi.com/our-technology/
http://www.pdenergy.com/
http://www.pelliontech.com/technology.htm
http://www.powerhive.com
http://www.primuspower.com/
http://sakti3.com
http://seeo.com/
www.solarwatt.de
http://www.tesvolt.com
http://www.uetechnologies.com/
www.viznenergy.com
19.4.2016 plus Ergänzungen aus dem Modus-Artikel von #135:
Thread: Presse: Panasonic will Solarzellen-Produktion in Europa schließen - Tesla-LieferantThread: GS Yuasa - macht JV mit Bosch - JV will Leistungsdichte verdoppeln
Thread: LG Chem(ical) - verwässert durch Chemie
Thread: Sekisui Chemical :Technischer Durchbruch bei Lithium-Akkus für Elektroautos - dlrowralos Liebling
Thread: Nicht billig aber klasse - SAFT GROUPE S.A. ACTIONS NOMINATIVES EO 1 - manche verdienen sogar Geld mit Li-Ion
Thread: ELectrovaya - Li-Ionen-Batterien - nicht nur Elon hat WILDE Träume
Thread: Leclanché - Schweizer Li-Ionen Produzent - dto.
Thread: Homeowners Can Save Energy and Prevent Unexpected Repairs With New Johnson Controls Smart Thermostat - verwässert durch Auto & Haustechnik
Thread: BYD CO LTD - mit Zukunft ?
Thread: Samsung SDI - scheint an Boden zu gewinnen
Thread: LION E-Mobility AG - Zukunftsbranche
Thread: Asahi Kasei - Membran-Zulieferer
andere Batterie-/oder Energiespeicher-Player
Thread: NGK Insulators - NaS Batteriehersteller - Flow-Batterien aus Japan
Thread: Einstieg Enersys - Weltmarktführer Pb-Zn
Thread: McPhy - französischer Wasserstoff-Speicher-Hersteller - Wasserstoffspeicher
Thread: ITM Power - Elektrolyse und Brennstoffzelle
Thread: Axion Power - neue WKN nach reverse split - PbC
Thread: ZBB Energy
Thread: Active Power - UPS - Flywheels
Thread: Redflow - The Holy Grail? - Zink-Bromid
Thread: EnerNOC: Smart Grid Business Models Taking Shape - Demand Response, allerdings rückläufig
Thread: Ideal Power Inc. Announces Third Quarter 2015 Results - Elektronik-Zulieferer
vorbörsliche
mit Einzelthread
Thread: Sonnenbatterie
Thread: Younicos
ohne Einzelthread
www.24-m.com/
www.alevo.com
http://amberkinetics.com
www.ambri.com
http://www.amprius.com
http://www.aquionenergy.com/
http://www.boston-power.com
electric fuel energy
http://www.enstorageinc.com/
http://www.faradion.co.uk/technology/sodium-ion-technology/
http://greensmithenergy.com/about/
www.imergy.com
http://www.itnes.com/news-ARPA-E_VRB.html
https://www.next-kraftwerke.de
http://www.openenergi.com/our-technology/
http://www.pdenergy.com/
http://www.pelliontech.com/technology.htm
http://www.powerhive.com
http://www.primuspower.com/
http://sakti3.com
http://seeo.com/
www.solarwatt.de
http://www.tesvolt.com
http://www.uetechnologies.com/
www.viznenergy.com
Wäre ja ganz interessant:
http://www.flowbatteryforum.com/general-information,insbesondere wegen der Besichtigung;
leider zu teuer
PV-Tech Liste mit 20 disruptors
http://www.pv-tech.org/features/20-energy-storage-disruptors Kreisel unterbietet Speicherpreise von Tesla deutlich
16.06.2016 10:42 -Heimstromspeicher sind das große Thema auf der Intersolar in München. Das Startup Kreisel Electric stellt nun vorab einen schlanken Speicher in schickem Design vor. Besonders interessant ist auch der Preis des DC-Systems: Mit 700 Euro pro nutzbarer Kilowattstunde sind die Österreicher billiger als Tesla.
Aus der Garage in Oberösterreich auf die große Bühne: Das Unternehmen Kreisel Electric aus Freistadt stellt mit viel Tamtam und Live Band seinen neuen Heimspeicher Mavero vor. Dazu hat sich das Startup eine entsprechende Lokation gesucht. Auf dem Fabrikgeländes des Motorwerks Berlin-Weißensee wurden bereits vor knapp 100 Jahren 1921 Elektromotoren und Generatoren gebaut, die unter anderem in Zeppelin-Luftschiffen eingesetzt wurden.
Ab acht Kilowattstunden nutzbarer Kapazität
Als das Gerät enthüllt wird, zeigt sich der wandhängende Heimspeicher, bei dem besonders auf Design geachtet wurde. Der Mavero misst 140 mal 105 Zentimeter und wird in vier verschiedenen Kapazitäten mit 10 bis 28 Kilowattstunden angeboten. Die kleinste Version liegt bei acht Kilowattstunden nutzbarer Kapazität. Je nach Kapazität ist der Speicher nun 15 oder 27,5 Zentimeter flach, könnte man sagen. Das DC-Systems ist modular aufgebaut und das Gewicht liegt dementsprechend zwischen 70 bis 170 Kilogramm. Ein sogenanntes „Ambient Interface“ mit LED-Lichtdesign zeigt den Akku-Ladestand an. „Das Licht kann aber auch ausgeschaltet werden“, sagt Kreisel-Manager Christian Schlögl.
Entladen wird das Gerät je nach Bedarf zwischen 4,8 bis 9,6 Kilowatt im Spannungsbereich von 288 bis 384 Volt. Auch hier haben die Techniker nachgedacht und lassen dem Anwender einen größeren Spielraum. Klar ist, dass das Gerät mit höherer Voltzahl effektiver arbeitet. „Eigene Tests des Unternehmens zeigen einen Gesamtwirkungsgrad von 96 Prozent“, sagt Techniker Johann Kreisel. Das sollen nun noch externe Gutachter bestätigen. Die Batteriezellen für das Gerät liefert der Samsung-Konzern.
In 22 Minuten alleine aufgebaut
Nicht unwichtig für den Vertrieb: „Ein Installateur baut den Speicher in rund 22 Minuten alleine auf“, sagt Kreisel. Eine direkte Kampfansage ist allerdings der Preis. Der Endkundenpreis des Mavero liegt mit 700 Euro pro nutzbarer Kilowattstunde deutlich unter dem Preis von Tesla und damit in einem Preissegment, der für Haushalte auch ohne KfW-Förderung wirtschaftlich ist. Das Gerät kann schon vorbestellt werden, auch wenn der Batteriespeicher voraussichtlich erst Anfang 2017 lieferbar ist. Auch hier haben die Österreicher offenbar von Tesla-Chef Musk gelernt.
Zum noch eher unbekannten Unternehmen selbst: Kreisel Electric wurde von den drei Brüdern Philipp, Johann und Markus Kreisel 2014 als Startup gegründet. Es gehört als eigene Sparte zum Unternehmen Kreisel, das bereits seit 30 Jahren am Markt ist und unter anderem als Automobilzulieferer für Porsche arbeitet. Bislang ist das Startup eigenfinanziert – VW-Manager waren allerdings bei der Präsentation anwesend. (Niels H. Petersen)
Aquino geht in den Markt:
http://blog.aquionenergy.com/aquion-launches-24-volt-battery Preispunkt "pumped hydro"
http://cleantechnica.com/2016/06/16/gold-mine-recycled-as-au…1.000 AUD (=650 EUR) pro KW
Enerkeep
will Übersicht in den Speicher-Dschungel bringen: http://enerkeep.com/DE/de lt. KFW-Monitoringbericht:
http://www.speichermonitoring.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Speic…Der Speichermarkt wächst, die Zahl neuer Hersteller und Produkte steigt, der Wettbewerb nimmt zu und mit fallenden Preisen wird auch die Nachfrage steigen. Aber der Markt wirkt dadurch auch sehr unübersichtlich für den Käufer.
Laut des neuen KfW-Monitoringbericht der RWTH haben sich die vier Hersteller Sonnen, Deutsche Energieversorgung (Senec), SMA und E3/DC etwa 60 Prozent des bisherigen Marktes geteilt.
Auch wenn das KfW-Monitoring nur rund die Hälfte der Installationen erfasst und der Marktentwicklung rund neun Monate hinterherhinkt.
http://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/Advanced-Microgr…
Auszüge:
*"Susan Kennedy, CEO of Advanced Microgrid Solutions, has observed, “The entire electrical distribution system is designed around a single premise: You cannot store energy.”
The premise of her company: “Equipping a building with the technology to store and manage its own electricity turns that building into a standalone storage unit,” and if you “combine a dozen buildings into a fleet, you have the utility equivalent of a peaker plant.” She told GTM recently, “We're offering utilities a customized solution using energy storage behind the customer's meter, harnessing that load to provide specifically what the utility needs in a particular region. It’s a clean, fast, flexible product that doesn't exist in the utility world today."
*"Batteries by themselves are just very expensive, so the only way a battery is ever going to be economic is if you can stack multiple functions off both the host side and the utilities side, and on the customer side, it's backup. It's load-shifting. But it doesn't reduce your costs. It's only demand management, and that's a very...regulatory-sensitive value stream. If you have solar, now you're actually reducing the customer's electricity costs, and so it adds value to the solar."
Auszüge:
*"Susan Kennedy, CEO of Advanced Microgrid Solutions, has observed, “The entire electrical distribution system is designed around a single premise: You cannot store energy.”
The premise of her company: “Equipping a building with the technology to store and manage its own electricity turns that building into a standalone storage unit,” and if you “combine a dozen buildings into a fleet, you have the utility equivalent of a peaker plant.” She told GTM recently, “We're offering utilities a customized solution using energy storage behind the customer's meter, harnessing that load to provide specifically what the utility needs in a particular region. It’s a clean, fast, flexible product that doesn't exist in the utility world today."
*"Batteries by themselves are just very expensive, so the only way a battery is ever going to be economic is if you can stack multiple functions off both the host side and the utilities side, and on the customer side, it's backup. It's load-shifting. But it doesn't reduce your costs. It's only demand management, and that's a very...regulatory-sensitive value stream. If you have solar, now you're actually reducing the customer's electricity costs, and so it adds value to the solar."
Nanoflowcell aus der Schweiz will an die Börse gehen
http://www.energy-storage.news/news/nanoflowcell-considers-s… neues Flywheel-Design:
http://www.lancaster.ac.uk/news/articles/2016/lancaster-engi…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 52.459.458 von R-BgO am 23.05.16 11:30:56
Imergy ist platt:
http://www.energy-storage.news/news/imergy-enters-insolvency… Indien will in großem Stil
Pumpspeicherkraftwerke bauen: http://energy.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/renewable/in…10 GW (?) - finde komisch, dass nur Leistungs- und nicht Kapazitätsangabe...
vielleicht meinen sie 10 GWh
Keawatt ist ein französischer organic Redox-Flow-Player
http://www.kemwatt.com/kemwatt-achieves-a-world-premiere-in-… Watt' es nich' alles jibt:
...jetzt bauen sie schon Wechselrichter, die klassische Turbinen nachmachen:Wechselrichter bekommt Schwungmasse
5.10.2016 11:57 -
http://www.photovoltaik.eu/Archiv/Meldungsarchiv/Wechselrich…
Das israelische Elektronik- und Softwareunternehmen Synvertec hat einen Algorithmus entwickelt, der es Solarwechselrichtern ermöglicht, sich wie ein konventioneller Generator mit Schwungmasse zu verhalten. Zusammen mit Q3 Energie und Solutronic Energy haben die Israelis die Erprobung der Technologie in der Praxis gestartet.
Mit einem komplexen Algorithmus in Wechselrichtern wollen die beiden Wechselrichterhersteller Solutronic Energy und Q3 Energie Solaranlagen noch besser in das bestehende Stromnetz einbinden.
Das Problem ist, dass die Solaranlagen über die Wechselrichter ihren Strom einspeisen.
Früher haben das die konventionellen Kraftwerke mit ihren Turbinen getan. Der Vorteil einer solchen Turbine ist: Sie hat Schwungmasse, die das Netz stabil hält. Diese fehlt den Wechselrichtern.
Um die Netzstabilität auch bei steigendem Anteil von Solaranlagen gewährleisten zu können, hat der israelische Hersteller Synvertec einen Algorithmus entwickelt, der die Wechselrichter dazu bringt, sich so zu verhalten, als wäre er ein klassischer Generator mit Schwungmasse.
Direkt auf die Netzsituation reagieren
Dazu bildet der Synchroverter-Algorithmus die mechanischen und elektrischen Eigenschaften eines Synchrongenerators nach und kommuniziert mit den Schaltern im Wechselrichter. Dabei berechnet der Synchroverter permanent die induzierte Spannung an einer Statorspule eines virtuellen Generators. Dadurch kann das System aktiv und reaktiv die Stromeinspeisung ins Netz regulieren und damit direkt auf die konkrete Spannungs- und Frequenzsituation im Netz eingehen. Der Algorithmus kann aber auch auf die Anforderungen des Netzbetreibers reagieren und die Einspeisung der Solaranlage entsprechend steuern.
Zum Produkt weiterentwickeln
Synvertec hat die Technologie bis zum Prototypenstadium weiterentwickelt. Jetzt wollen die beiden Partner in Europa diese zusammen mit den Israelis den Synchroverter-Algorithmus in klassische Photovoltaikwechselrichter integrieren und die Technologie in der Praxis erproben. Die drei Unternehmen haben gerade mit der Entwicklung begonnen und wollen in den kommenden zwei Jahren ein fertiges Produkt auf den Markt bringen.
Denkbar ist es, den Algorithmus in die Firmware von Wechselrichtern zu integrieren oder ein kleines elektronisches Bauteil zu entwickeln, das neben den bestehenden Wechselrichter geschraubt wird und über eine Datenkommunikation die Solaranlagen mit dem Algorithmus steuert. (su)
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 52.670.270 von R-BgO am 22.06.16 13:44:41
Titan SmartStorage Seamlessly Incorporates Aquion's Saltwater-Based Aspen Batteries for a Clean, Safe, and Cost-Effective Complete Home Solar Storage System
PITTSBURGH, PA and SOUTH MELBOURNE, AUSTRALIA -- (Marketwired) -- 10/03/16 --
Aquion Energy, Inc., manufacturer of Aspen saltwater batteries and energy storage systems, and Fusion Power Systems, a leading Australian power and energy systems integrator, have announced Titan SmartStorage, a fully integrated solar energy storage solution for residential applications in Australia. The Titan SmartStorage product will be unveiled today at the All-Energy 2016 conference in Melbourne, Australia, and is now available to order.
Fusion's Titan SmartStorage is Australia's first fully integrated, safe, and easy-to-install residential solar energy storage system. The system combines clean and cost-effective Aquion Energy Aspen saltwater batteries with an Australian-made, purpose-built inverter and charge controller, designed and built to withstand Australian conditions.
Titan SmartStorage provides energy storage that outperforms traditional battery systems and is ideal for off-grid applications, solar self-consumption, and storing solar energy for nighttime use. The systems are modular and scalable for maximum flexibility. Fusion energy storage systems are free of toxic chemicals, 100% recyclable, noncombustible, and completely fire-safe.
"We're excited to see our batteries incorporated into an off-the-shelf storage solution for energy storage customers in Australia," said Tim Poor, Aquion Energy Chief Commercial Officer. "Solar self-consumption is a perfect application for our batteries, and the Titan product makes it easy for installers to deploy a fully integrated system to end users, both for new solar installations and as a retrofit for existing systems. Australian homeowners who install Titan can sleep well at night knowing that the Aquion batteries used in Titan are the safest and most environmentally friendly batteries in the world."
"We are extremely proud of the release of the Titan SmartStorage product line, powered by Aquion's saltwater-based batteries," said Nathaniel Allen, Fusion Power Systems Chief Operating Officer. "Aquion has played an important role in the world's second largest residential storage project and more recently replaced lead-gel battery technology at Lady Island Resort off the coast of Queensland. Our choice was clear for the Titan product line -- these systems are powered by the safest battery in the world. They provide long discharge cycles and are designed specifically to meet the needs of the Australian market."
Built on Aquion's unique environmentally friendly saltwater-based Aqueous Hybrid Ion (AHI) chemistry, Aspen batteries are clean, sustainable, and long-lasting. The batteries are designed for daily deep cycling, can operate at high ambient temperatures, and do not degrade from partial state of charge cycling, making them ideal for residential solar applications. Aspen batteries are the first and only batteries in the world to be Cradle to Cradle Certified, an esteemed quality mark for products made from sustainable materials and manufacturing processes.
...jetzt auch in OZ:
Aquion Energy and Fusion Power Systems Announce Fully Integrated Titan SmartStorage System for Australian Residential Solar MarketTitan SmartStorage Seamlessly Incorporates Aquion's Saltwater-Based Aspen Batteries for a Clean, Safe, and Cost-Effective Complete Home Solar Storage System
PITTSBURGH, PA and SOUTH MELBOURNE, AUSTRALIA -- (Marketwired) -- 10/03/16 --
Aquion Energy, Inc., manufacturer of Aspen saltwater batteries and energy storage systems, and Fusion Power Systems, a leading Australian power and energy systems integrator, have announced Titan SmartStorage, a fully integrated solar energy storage solution for residential applications in Australia. The Titan SmartStorage product will be unveiled today at the All-Energy 2016 conference in Melbourne, Australia, and is now available to order.
Fusion's Titan SmartStorage is Australia's first fully integrated, safe, and easy-to-install residential solar energy storage system. The system combines clean and cost-effective Aquion Energy Aspen saltwater batteries with an Australian-made, purpose-built inverter and charge controller, designed and built to withstand Australian conditions.
Titan SmartStorage provides energy storage that outperforms traditional battery systems and is ideal for off-grid applications, solar self-consumption, and storing solar energy for nighttime use. The systems are modular and scalable for maximum flexibility. Fusion energy storage systems are free of toxic chemicals, 100% recyclable, noncombustible, and completely fire-safe.
"We're excited to see our batteries incorporated into an off-the-shelf storage solution for energy storage customers in Australia," said Tim Poor, Aquion Energy Chief Commercial Officer. "Solar self-consumption is a perfect application for our batteries, and the Titan product makes it easy for installers to deploy a fully integrated system to end users, both for new solar installations and as a retrofit for existing systems. Australian homeowners who install Titan can sleep well at night knowing that the Aquion batteries used in Titan are the safest and most environmentally friendly batteries in the world."
"We are extremely proud of the release of the Titan SmartStorage product line, powered by Aquion's saltwater-based batteries," said Nathaniel Allen, Fusion Power Systems Chief Operating Officer. "Aquion has played an important role in the world's second largest residential storage project and more recently replaced lead-gel battery technology at Lady Island Resort off the coast of Queensland. Our choice was clear for the Titan product line -- these systems are powered by the safest battery in the world. They provide long discharge cycles and are designed specifically to meet the needs of the Australian market."
Built on Aquion's unique environmentally friendly saltwater-based Aqueous Hybrid Ion (AHI) chemistry, Aspen batteries are clean, sustainable, and long-lasting. The batteries are designed for daily deep cycling, can operate at high ambient temperatures, and do not degrade from partial state of charge cycling, making them ideal for residential solar applications. Aspen batteries are the first and only batteries in the world to be Cradle to Cradle Certified, an esteemed quality mark for products made from sustainable materials and manufacturing processes.
Eos Energy / Zinkbatterie will $160/kWh erreichen
Finanzierungsrunde: http://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/eos-energy-stora…
aktuelle Marktübersicht von EuPD:
http://www.pveurope.eu/News/Energy-Storage/EuPD-Research-Ger…
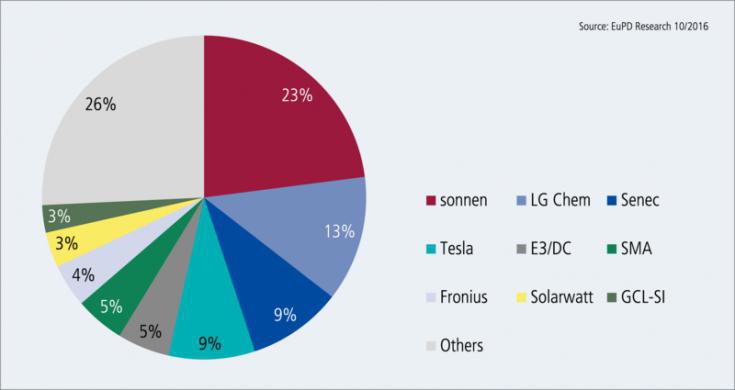
Cumulated energy storage market shares Europe, USA and Australia (October 2016).
Despite the late start of the new subsidy scheme and the changed framework conditions the German market for solar energy storage products showed a distinctive growth within the first six months in 2016 compared to the previous year, according to EuPD Research.
Decreasing system prices and increasing offerings
Decreasing system prices and increasing offerings for storage solutions of domestic as well as foreign companies pushed the sales figures in Germany. Tesla and Mercedes Benz Energy have made a decisive contribution with strong end-customer marketing; but this is not yet reflected in current sales figures, the market research company notes.
More than 12,700 systems sold in the first half of 2016
EuPD Research’s best case scenario expects 25,000 energy storage systems to be sold in Germany in 2016. In the first half 2016 around 60 companies offered energy storage solutions to German end customers. All in all more than 12,700 solar energy storage systems were sold within the first half of 2016. For the full year 2016 EuPD Research expects an ongoing growth, reaching 23,000 (worst case scenario) to 25,000 (best case scenario) storage systems in Germany. Compared to last year the sales market in Germany will increase by around 40% in 2016.
sonnen leading, followed by SENEC and E3/DC
According to a recent analysis by EuPD Research, sonnen was the largest solar battery provider in the first half of 2016 with around 3,300 systems sold and a resulting market share of 27%. German-based company Deutsche Energieversorgung (SENEC) achieved a market share of 19%, followed by E3/DC (10%), LG Chem (9%) and Solarwatt (6%).
Strong international presence
However, German companies not only show a strong presence in their domestic market. The analysis shows that in growing markets like the USA and Australia the German market leader sonnen for example has a strong position as well with a market share of 17% respectively 13%. In total, sonnen holds a cumulated market share of 23% across Europe, the USA and Australia in the first half of 2016, followed by LG Chem and Deutsche Energieversorgung (SENEC).
Tesla leading in the U.S.
The strong position of German companies can be deduced to their dominance in the German market. In contrast U.S. companies like Tesla and Trojan, that have a market share of 24% respectively 17% in the domestic market cannot hold the position on an international level, says EuPD Research. “The international presence of German companies shows that they react to country-specific requirements and provide high-quality products at affordable prices,” Martin Ammon, Head of Energy Industry at EuPD Research, summarizes. “Coming from the European market, our analysis makes evident that they are already very well established in non-European countries as well.” (HCN)
http://www.pveurope.eu/News/Energy-Storage/EuPD-Research-Ger…

Cumulated energy storage market shares Europe, USA and Australia (October 2016).
Despite the late start of the new subsidy scheme and the changed framework conditions the German market for solar energy storage products showed a distinctive growth within the first six months in 2016 compared to the previous year, according to EuPD Research.
Decreasing system prices and increasing offerings
Decreasing system prices and increasing offerings for storage solutions of domestic as well as foreign companies pushed the sales figures in Germany. Tesla and Mercedes Benz Energy have made a decisive contribution with strong end-customer marketing; but this is not yet reflected in current sales figures, the market research company notes.
More than 12,700 systems sold in the first half of 2016
EuPD Research’s best case scenario expects 25,000 energy storage systems to be sold in Germany in 2016. In the first half 2016 around 60 companies offered energy storage solutions to German end customers. All in all more than 12,700 solar energy storage systems were sold within the first half of 2016. For the full year 2016 EuPD Research expects an ongoing growth, reaching 23,000 (worst case scenario) to 25,000 (best case scenario) storage systems in Germany. Compared to last year the sales market in Germany will increase by around 40% in 2016.
sonnen leading, followed by SENEC and E3/DC
According to a recent analysis by EuPD Research, sonnen was the largest solar battery provider in the first half of 2016 with around 3,300 systems sold and a resulting market share of 27%. German-based company Deutsche Energieversorgung (SENEC) achieved a market share of 19%, followed by E3/DC (10%), LG Chem (9%) and Solarwatt (6%).
Strong international presence
However, German companies not only show a strong presence in their domestic market. The analysis shows that in growing markets like the USA and Australia the German market leader sonnen for example has a strong position as well with a market share of 17% respectively 13%. In total, sonnen holds a cumulated market share of 23% across Europe, the USA and Australia in the first half of 2016, followed by LG Chem and Deutsche Energieversorgung (SENEC).
Tesla leading in the U.S.
The strong position of German companies can be deduced to their dominance in the German market. In contrast U.S. companies like Tesla and Trojan, that have a market share of 24% respectively 17% in the domestic market cannot hold the position on an international level, says EuPD Research. “The international presence of German companies shows that they react to country-specific requirements and provide high-quality products at affordable prices,” Martin Ammon, Head of Energy Industry at EuPD Research, summarizes. “Coming from the European market, our analysis makes evident that they are already very well established in non-European countries as well.” (HCN)
Greenbird / Software
(Düsseldorf/Oslo, 8 November 2016) Statkraft Ventures and ETF Partners invest 5 million US dollars in smart meter software leader Greenbird
Statkraft Ventures, with participation of ETF Partners, led the 5 million US dollars investment into the European smart meter software company Greenbird Integration Technology AS.
Greenbird is a profitable and rapidly growing software vendor and IT integration specialist based in Norway. The company is the clear leader in its home market, having served utilities representing more than 80 % of the Norwegian market, and it is continuing to build its international customer base. Its Software as a Service (SaaS) offerings Metercloud.io and Ghostwriter enable utilities to quickly implement flexible IT architectures for modern smart meter operations.
Smart meter software architectures are complex, yet they need to be integrated quickly and remain flexible and ever-evolving. Metercloud.io can be understood as an 'integration as a service' offering, which efficiently handles metering data and provides connectors to all of the common smart meter software applications. New applications are therefore on-boarded within days rather than months. And the system evolves with changes in the industry, regulation or security requirements, and thereby future-proofs a utility's systems without repeated integration efforts or dependency on a single software supplier.
"At Statkraft Ventures we are well aware of the software integration challenge utilities are facing as the grid is becoming increasingly intelligent. In order to capitalise on the smart grid opportunity, the IT systems need to adapt quickly. Greenbird provides exactly that flexibility and delivers it conveniently as a cloud service. Having proven its case in Norway, we see a big opportunity for Greenbird to further expand globally," says Matthias Dill, Managing Director of Statkraft Ventures.
"What convinced us about Greenbird was the vision and energy of its team," says Arne Morteani, Partner at ETF Partners. "They identified a real need in the market and leading utilities have already adopted their Metercloud.io service. We are delighted to provide additional capital to enable Greenbird's further growth."
"Traditional system integration is not suitable for smart meter operations," says Thorsten Heller, CEO at Greenbird. "What is needed is a brand new approach. Metercloud.io is a cloud-native integration platform that cuts integration times from 6-12 months to less than 1 month. More importantly, it creates a flexible, multi-vendor architecture that readily evolves as utilities seek to capture the more advanced benefits of smart meters. We are not competing with other software or big data vendors, but we are lowering the barriers for everyone in the ecosystem - we are truly making data fly!"
Ice Energy
gibt's immer noch: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/2016/11/cheap-i…
01. Dezember 2016 Batterien
Ultrahochleistungs-Speicher mit extrem kurzen Lade- und Entladezeiten
ZSW entwickelt Stromspeicher mit nanostrukturierten Elektroden und wässrigem Elektrolyt.
Ultrahochleistungs-Speicher können innerhalb von kurzer Zeit viel Strom abgeben und aufnehmen. Für viele Industrieanwendungen und Hybridautos ist das besonders interessant. Wissenschaftler am Zentrum für Sonnenenergie- und Wasserstoff-Forschung Baden-Württemberg (ZSW) haben nun Elektroden für neuartige Stromspeicher entwickelt, die die Lade- und Entladegeschwindigkeit bis auf drei Sekunden reduzieren können.
Möglich wurde der technische Fortschritt durch eine nanostrukturierte Oberfläche der Elektroden. Als Elektrolyt verwendeten die Forscher eine wasserbasierte, nicht brennbare Lösung – der Speicher kann so auch bei hohen und tiefen Temperaturen genutzt werden. Das ZSW erzielte die Forschungsergebnisse im Rahmen des Projekts FastStorage BW II, das vom Land Baden-Württemberg mit drei Millionen Euro gefördert wird.
https://www.zsw-bw.de/fileadmin/user_upload/PDFs/Pressemitte…
Ultrahochleistungs-Speicher mit extrem kurzen Lade- und Entladezeiten
ZSW entwickelt Stromspeicher mit nanostrukturierten Elektroden und wässrigem Elektrolyt.
Ultrahochleistungs-Speicher können innerhalb von kurzer Zeit viel Strom abgeben und aufnehmen. Für viele Industrieanwendungen und Hybridautos ist das besonders interessant. Wissenschaftler am Zentrum für Sonnenenergie- und Wasserstoff-Forschung Baden-Württemberg (ZSW) haben nun Elektroden für neuartige Stromspeicher entwickelt, die die Lade- und Entladegeschwindigkeit bis auf drei Sekunden reduzieren können.
Möglich wurde der technische Fortschritt durch eine nanostrukturierte Oberfläche der Elektroden. Als Elektrolyt verwendeten die Forscher eine wasserbasierte, nicht brennbare Lösung – der Speicher kann so auch bei hohen und tiefen Temperaturen genutzt werden. Das ZSW erzielte die Forschungsergebnisse im Rahmen des Projekts FastStorage BW II, das vom Land Baden-Württemberg mit drei Millionen Euro gefördert wird.
https://www.zsw-bw.de/fileadmin/user_upload/PDFs/Pressemitte…
Nidec-ASI
installiert 49MW für EDF in UK: http://www.energy-storage.news/news/nidec-asi-will-be-suppli…;ist die italienische Tochter eines großen börsennotierten Japaners.
Kathode aus Vanadat-Borat-Glas:
http://www.computerbild.de/artikel/cb-News-PC-Hardware-ETH-Z…soll deutliche Leistungssteigerung für Li-Ion bewirken können.
Angeblich forscht auch eine Bude des Swatch-Gründers daran.
Hat-tip an Der Tscheche.
http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/print/volume-20…
Capacity Expansion in 2017
According to ESA, in terms of megawatt-hours, the U.S. market grew 284 percent in 2016 alone and deployment of energy storage systems through 2017 looks set for exponential growth again.
Navigant reports that 520 MW of new energy storage capacity was deployed globally in 2014 and 2015; bringing non-hydro energy storage to some 2,276 MW by year’s end.
“In 2017 we expect the global market to grow 47 percent from the already record breaking year in 2016 in terms of new storage capacity deployed,” said Eller.
Through 2020, Eller pointed out that Navigant forecasts over 29.4 GW of new storage capacity to be deployed worldwide across all sectors, and a compound annual growth rate of 60 percent.
Technology Expansion in 2017
For the near future, the dominant form of energy storage, pumped hydropower, is sure to remain the principal method of storing energy, occupying a global market share of over 95 percent. Aside from pumped hydro, a plethora of energy storage technologies exist with a growing number of new solutions being tried, tested and installed on a commercial basis. An even larger number reside anywhere between blueprint designs and various levels of research and development.
Going forward, battery storage — of the lithium-ion variety — is expected to retain its majority market share, according to Roberts.
“Global trends are feeding into that…partly because major applications of today lend themselves to batteries. Equally, lithium-ion dominates on account of cost; but it has reached that cost because of demand driving production.”
This favorable increasing-demand/decreasing-cost trend is not expected to slow down through 2017. Bloomberg New Energy Finance expects battery technology to fall to $120 per kWh by 2030 compared with more than $300 now and $1,000 in 2010.
Capacity Expansion in 2017
According to ESA, in terms of megawatt-hours, the U.S. market grew 284 percent in 2016 alone and deployment of energy storage systems through 2017 looks set for exponential growth again.
Navigant reports that 520 MW of new energy storage capacity was deployed globally in 2014 and 2015; bringing non-hydro energy storage to some 2,276 MW by year’s end.
“In 2017 we expect the global market to grow 47 percent from the already record breaking year in 2016 in terms of new storage capacity deployed,” said Eller.
Through 2020, Eller pointed out that Navigant forecasts over 29.4 GW of new storage capacity to be deployed worldwide across all sectors, and a compound annual growth rate of 60 percent.
Technology Expansion in 2017
For the near future, the dominant form of energy storage, pumped hydropower, is sure to remain the principal method of storing energy, occupying a global market share of over 95 percent. Aside from pumped hydro, a plethora of energy storage technologies exist with a growing number of new solutions being tried, tested and installed on a commercial basis. An even larger number reside anywhere between blueprint designs and various levels of research and development.
Going forward, battery storage — of the lithium-ion variety — is expected to retain its majority market share, according to Roberts.
“Global trends are feeding into that…partly because major applications of today lend themselves to batteries. Equally, lithium-ion dominates on account of cost; but it has reached that cost because of demand driving production.”
This favorable increasing-demand/decreasing-cost trend is not expected to slow down through 2017. Bloomberg New Energy Finance expects battery technology to fall to $120 per kWh by 2030 compared with more than $300 now and $1,000 in 2010.
Large-scale dispatchable solar-plus-storage costs could drop below 10 cents per kWh, Eos claims
By Andy Colthorpe Feb 07, 2017
http://www.energy-storage.news/news/large-scale-dispatchable…
Solar PV paired with energy storage at scale could be provided to utilities at just US$0.10 per kilowatt hour, using advanced battery technology, one manufacturer has claimed.
Philippe Bouchard, VP of business development at Eos Energy Storage, which makes its own novel zinc hybrid cathode batteries at grid-scale, told Energy-Storage.News that the company is increasingly interested in supplying solar-plus-storage solutions to utilities in the US.
Eos claims to have perfected a DC battery, available in 1MW/4MWh blocks as part of its Aurora grid-scale storage system, at just US$160 per kWh, which it says is 30% to 40% lower cost than a comparable lithium ion system. Eos’ battery, branded Znyth, can provide four hours of continuous discharge. At the end of last month Eos announced a manufacturing and assembly partnership with Environment One Corporation to make the company’s patented Energy Stack plug-and-play DC module in New York with a dedicated facility planned in mid-2017 and an expected output of 400MWh per year. Energy Stacks are aggregated together to form each Aurora system.
“The integration of renewables is obviously an acute need for many utilities. Some geographies, both in the US and internationally have such high penetrations of solar that within that specific region they don’t want or need any more solar,” Bouchard said.
“In fact, you’ll have so much energy production coming online around noon or 1pm, when the solar assets are peaking, you’re pushing the locational marginal pricing negative so the independent system operators will pay off-takers to consume that electricity.”
Bouchard referred to regions of the US with high solar penetration such as California or Arizona where this is the case and that many utilities are anticipating introducing time of production tariffs. He said that by using a battery such as Eos’ at large-scale, utilities can help smooth out the variability of solar generation and meet their evening peak of demand, typically from 5pm to 9pm.
According to Bouchard, Eos is already in talks with a number of solar developers with an eye to developing projects during 2017. He said leveraging the synergies between the solar and storage elements of such projects could help lower costs and give utilities a renewable but dispatchable energy or capacity service.
“We’re looking at a combined asset, maybe a 90MW solar plant with a 50MW/200MWh battery so a fairly significant size, but the LCOE of that asset is already at today’s pricing below 10 cents per kWh, and riding our wave down the price curve with volume we believe we can get that below 8 cents per kWh,” Bouchard said.
A recent project by AES on the Hawaiian island of Kaua’i will deliver power to the local Kauaʻi Island Utility Cooperative (KIUC) at US$0.11 per kWh.
By Andy Colthorpe Feb 07, 2017
http://www.energy-storage.news/news/large-scale-dispatchable…
Solar PV paired with energy storage at scale could be provided to utilities at just US$0.10 per kilowatt hour, using advanced battery technology, one manufacturer has claimed.
Philippe Bouchard, VP of business development at Eos Energy Storage, which makes its own novel zinc hybrid cathode batteries at grid-scale, told Energy-Storage.News that the company is increasingly interested in supplying solar-plus-storage solutions to utilities in the US.
Eos claims to have perfected a DC battery, available in 1MW/4MWh blocks as part of its Aurora grid-scale storage system, at just US$160 per kWh, which it says is 30% to 40% lower cost than a comparable lithium ion system. Eos’ battery, branded Znyth, can provide four hours of continuous discharge. At the end of last month Eos announced a manufacturing and assembly partnership with Environment One Corporation to make the company’s patented Energy Stack plug-and-play DC module in New York with a dedicated facility planned in mid-2017 and an expected output of 400MWh per year. Energy Stacks are aggregated together to form each Aurora system.
“The integration of renewables is obviously an acute need for many utilities. Some geographies, both in the US and internationally have such high penetrations of solar that within that specific region they don’t want or need any more solar,” Bouchard said.
“In fact, you’ll have so much energy production coming online around noon or 1pm, when the solar assets are peaking, you’re pushing the locational marginal pricing negative so the independent system operators will pay off-takers to consume that electricity.”
Bouchard referred to regions of the US with high solar penetration such as California or Arizona where this is the case and that many utilities are anticipating introducing time of production tariffs. He said that by using a battery such as Eos’ at large-scale, utilities can help smooth out the variability of solar generation and meet their evening peak of demand, typically from 5pm to 9pm.
According to Bouchard, Eos is already in talks with a number of solar developers with an eye to developing projects during 2017. He said leveraging the synergies between the solar and storage elements of such projects could help lower costs and give utilities a renewable but dispatchable energy or capacity service.
“We’re looking at a combined asset, maybe a 90MW solar plant with a 50MW/200MWh battery so a fairly significant size, but the LCOE of that asset is already at today’s pricing below 10 cents per kWh, and riding our wave down the price curve with volume we believe we can get that below 8 cents per kWh,” Bouchard said.
A recent project by AES on the Hawaiian island of Kaua’i will deliver power to the local Kauaʻi Island Utility Cooperative (KIUC) at US$0.11 per kWh.
aktuelle Ausschreibung in Indien:
Zuschlag wurde für 4,4 US-cent/kWh erteilthttp://www.pv-tech.org/news/solar-becomes-cheapest-new-power…
neue Batteriechemie: Harnstoff
http://news.stanford.edu/2017/02/07/stanford-engineers-creat…Auszug:
According to Angell, grid storage is also the most realistic goal, because of the battery’s low cost, high efficiency and long cycle life. One kind of efficiency, called Coulombic efficiency, is a measurement of how much charge exits the battery per unit of charge that it takes in during charging. The Coulombic efficiency for this battery is high – 99.7 percent.
To meet the demands of grid storage, a commercial battery will need to last at least 10 years. By investigating the chemical processes inside the battery, Angell hopes to extend its lifetime. The outlook is promising. In the lab, these urea-based aluminum ion batteries can go through about 1,500 charge cycles with a 45-minute charging time.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 52.670.270 von R-BgO am 22.06.16 13:44:41
Aquion ist platt:
http://blog.aquionenergy.com/aquion-energy-inc.-files-volunt…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 36.402.747 von meinolf67 am 19.01.09 13:35:57
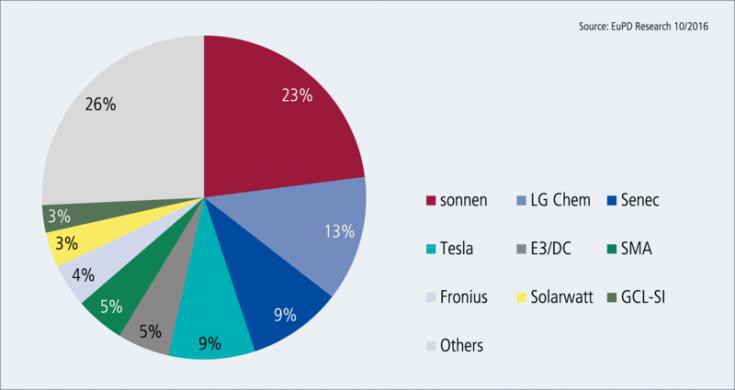
Cumulated energy storage market shares Europe, USA and Australia (October 2016).
Thread: Sonnenbatterie als weltweiter Retail-Marktführer für Speichersysteme
Thread: Younicos als einer der Marktführer für Systemintegration Commercial & Industrial
Thread: Nidec, bewegt nicht nur Industrie 4.0 Systemintegrator C&I
Thread: Tesla Motors w-Powerwall
Belelectric --- gekauft von Innogy
...die stärksten Li-Ion Zell-Lieferanten sind
Thread: Samsung SDI
Thread: LG Chem(ical)
Thread: Presse: Panasonic will Solarzellen-Produktion in Europa schließen (wegen Tesla)
Thread: BYD CO LTD - mit Zukunft ?
Thread: GS Yuasa - macht JV mit Bosch
...
Thread: ELectrovaya - Li-Ionen-Batterien
Thread: Leclanché
...andere etablierte Batterietechnologien
Thread: Einstieg Enersys - Zk-Pb
Thread: NGK Insulators - NaS Batteriehersteller - Na-S
...BMS, Microgrid & Co.
Thread: LION E-Mobility AG - Zukunftsbranche
Powerhive
...und dann gibt es noch
unproven Technologies:
Alevo
Ambri
Electric Fuel Energy (Fe-Flow)
Eos Energy (Zink-Flow, Ziel 10c)
ICE Energy (
Nanoflowcell (Voodoo)
Thread: Redflow - The Holy Grail? (Zink-Brom-Flow)
Seeo
Tesvolt
ViZn (Zink-flow)
siehe auch #136
Software:
Thread: Silver Spring Networks
Geli
Greensmith
Greenbird
gekauft:
SAFT (von Total)
verstorben:
A123
Aquino
Imergy
Enervault
versuche mal 'ne Statusübersicht:
...eine gewisse Rolle im Markt spielen
Cumulated energy storage market shares Europe, USA and Australia (October 2016).
Thread: Sonnenbatterie als weltweiter Retail-Marktführer für Speichersysteme
Thread: Younicos als einer der Marktführer für Systemintegration Commercial & Industrial
Thread: Nidec, bewegt nicht nur Industrie 4.0 Systemintegrator C&I
Thread: Tesla Motors w-Powerwall
Belelectric --- gekauft von Innogy
...die stärksten Li-Ion Zell-Lieferanten sind
Thread: Samsung SDI
Thread: LG Chem(ical)
Thread: Presse: Panasonic will Solarzellen-Produktion in Europa schließen (wegen Tesla)
Thread: BYD CO LTD - mit Zukunft ?
Thread: GS Yuasa - macht JV mit Bosch
...
Thread: ELectrovaya - Li-Ionen-Batterien
Thread: Leclanché
...andere etablierte Batterietechnologien
Thread: Einstieg Enersys - Zk-Pb
Thread: NGK Insulators - NaS Batteriehersteller - Na-S
...BMS, Microgrid & Co.
Thread: LION E-Mobility AG - Zukunftsbranche
Powerhive
...und dann gibt es noch
unproven Technologies:
Alevo
Ambri
Electric Fuel Energy (Fe-Flow)
Eos Energy (Zink-Flow, Ziel 10c)
ICE Energy (
Nanoflowcell (Voodoo)
Thread: Redflow - The Holy Grail? (Zink-Brom-Flow)
Seeo
Tesvolt
ViZn (Zink-flow)
siehe auch #136
Software:
Thread: Silver Spring Networks
Geli
Greensmith
Greenbird
gekauft:
SAFT (von Total)
verstorben:
A123
Aquino
Imergy
Enervault
Solarstrom in Form von Erdgas speichern
13.03.2017 13:29 - http://www.photovoltaik.eu/Archiv/Meldungsarchiv/Solarstrom-…
Österreichische Forscher und Entwickler haben eine Lösung gefunden, mit der überschüssiger Ökostrom in Form von Erdgas gespeichert wird. Dabei wird mit Solarstrom gewonnener Wasserstoff mittels Mikroorganismen in Erdgas umgewandelt. Die Technologie hat gleich mehrere Vorteile.
Die österreichische Betreiber von Erdgasspeichern Rohöl-Aufsuchungs AG (RAG) will überschüssigen Strom aus Solar- und Windkraftanlagen mit einem neuen Verfahren in Erdgas umwandeln. Mit Unterstützung des Klima- und Energiefonds und der Bundesregierung hat das Unternehmen das Projekt Underground Sun Conversion gestartet. Dabei geht es darum, mit dem Strom aus Photovoltaik- und Windkraftanlagen, der nicht sofort verbraucht wird, zunächst elektrolytisch Wasser in seine elementaren Bestandteile aufzutrennen. Dies wird in einer Anlage in Pilsbach in Oberösterreich geschehen.
Wasserstoff wird in Erdgas umgewandelt
Danach wird dieser Wasserstoff zusammen mit Kohlendioxid in die schon ausgebeuteten Erdgaslagerstätten der RAG in mehr als tausend Meter Tiefe gepumpt. Dort sollen natürlich vorhandeme Mikroorganismen das Gasgemisch innerhalb weniger Wochen in in Erdgas umwandeln, das hauptsächlich aus Methan besteht. Dies wird der gleiche Prozess sein, wie er einst vor mehreren Millionen Jahren auch abgelaufen ist, wodurch das heute in der Erde vorhandene Erdgas entstanden ist, mit dem entscheidenden Unterschied, dass die Umwandlung heute in sehr viel kürzerer Zeit ablaufen soll. Der bisherige Ansatz der großtechnischen Methanisierung von Wasserstoff aus der Elektrolyse mittels erneuerbarer Energien geht zwar schneller. Doch ist das Gas ohnehin als Langzeitspeicher geplant, so dass die mit der Lösung anvisierte Zeitdauer völlig ausreicht. Der Vorteil ist hier, dass kein zusätzlicher Solar- oder Windstrom für den Methanisisierungsprozess gebraucht wird.
Infrastruktur bereits vorhanden
Bisher haben die Entwickler bei der RAG den Prozess im Rahmen eines Vorgängerprojekts im Labor nachgestellt und dabei vielversprechende Ergebnisse erzielt. Die Entwickler versprechen sich viel von ihrer Lösung. „Die Erdgasproduktion aus Sonnen- und Windenergie hat neben der Zeitersparnis weitere Vorteile: Sie bindet Kohlendioxid und kann aus erneuerbaren Quellen gewonnene Energie speichern. Zudem ist die nötige Infrastruktur für Lagerung und Transport von Erdgas bereits vorhanden“, betonen sie. Am Projekt sind neben der RAG auch Forscher der Montanuniversität Leoben, der Universität für Bodenkultur Wien, des Austrian Centre of Industrial Biotechnology, des Energieinstituts der Johannes Kepler Universität Linz und von Axiom Angewandte Prozesstechnik beteiligt. (Sven Ullrich)
13.03.2017 13:29 - http://www.photovoltaik.eu/Archiv/Meldungsarchiv/Solarstrom-…
Österreichische Forscher und Entwickler haben eine Lösung gefunden, mit der überschüssiger Ökostrom in Form von Erdgas gespeichert wird. Dabei wird mit Solarstrom gewonnener Wasserstoff mittels Mikroorganismen in Erdgas umgewandelt. Die Technologie hat gleich mehrere Vorteile.
Die österreichische Betreiber von Erdgasspeichern Rohöl-Aufsuchungs AG (RAG) will überschüssigen Strom aus Solar- und Windkraftanlagen mit einem neuen Verfahren in Erdgas umwandeln. Mit Unterstützung des Klima- und Energiefonds und der Bundesregierung hat das Unternehmen das Projekt Underground Sun Conversion gestartet. Dabei geht es darum, mit dem Strom aus Photovoltaik- und Windkraftanlagen, der nicht sofort verbraucht wird, zunächst elektrolytisch Wasser in seine elementaren Bestandteile aufzutrennen. Dies wird in einer Anlage in Pilsbach in Oberösterreich geschehen.
Wasserstoff wird in Erdgas umgewandelt
Danach wird dieser Wasserstoff zusammen mit Kohlendioxid in die schon ausgebeuteten Erdgaslagerstätten der RAG in mehr als tausend Meter Tiefe gepumpt. Dort sollen natürlich vorhandeme Mikroorganismen das Gasgemisch innerhalb weniger Wochen in in Erdgas umwandeln, das hauptsächlich aus Methan besteht. Dies wird der gleiche Prozess sein, wie er einst vor mehreren Millionen Jahren auch abgelaufen ist, wodurch das heute in der Erde vorhandene Erdgas entstanden ist, mit dem entscheidenden Unterschied, dass die Umwandlung heute in sehr viel kürzerer Zeit ablaufen soll. Der bisherige Ansatz der großtechnischen Methanisierung von Wasserstoff aus der Elektrolyse mittels erneuerbarer Energien geht zwar schneller. Doch ist das Gas ohnehin als Langzeitspeicher geplant, so dass die mit der Lösung anvisierte Zeitdauer völlig ausreicht. Der Vorteil ist hier, dass kein zusätzlicher Solar- oder Windstrom für den Methanisisierungsprozess gebraucht wird.
Infrastruktur bereits vorhanden
Bisher haben die Entwickler bei der RAG den Prozess im Rahmen eines Vorgängerprojekts im Labor nachgestellt und dabei vielversprechende Ergebnisse erzielt. Die Entwickler versprechen sich viel von ihrer Lösung. „Die Erdgasproduktion aus Sonnen- und Windenergie hat neben der Zeitersparnis weitere Vorteile: Sie bindet Kohlendioxid und kann aus erneuerbaren Quellen gewonnene Energie speichern. Zudem ist die nötige Infrastruktur für Lagerung und Transport von Erdgas bereits vorhanden“, betonen sie. Am Projekt sind neben der RAG auch Forscher der Montanuniversität Leoben, der Universität für Bodenkultur Wien, des Austrian Centre of Industrial Biotechnology, des Energieinstituts der Johannes Kepler Universität Linz und von Axiom Angewandte Prozesstechnik beteiligt. (Sven Ullrich)
Tesvolt
setzt Samsung SDI-Zellen ein: http://www.pveurope.eu/Products/Storage/Batteries/Tesvolt-de…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 54.614.154 von R-BgO am 26.03.17 10:31:34Neues Geld für Tesvolt
28.03.2017 10:24 -
Nur zwei Wochen nach der Vorstellung des neuen Gewerbespeichers TS verschafft sich Tesvolt neue finanzielle Möglichkeiten, um seine eigene Technologie künftig weiter zu entwickeln. Ein Risikokapitalfonds beteiligt sich an der Firma.
Der von der bmp Beteiligungsmanagement verwaltete IBG Risikokapitalfonds III investiert „mehrere Millionen Euro“ in den Gewerbespeicherhersteller Tesvolt, verkündet der Fonds mit Sitz in Magdeburg. Ein genauerer Betrag wird nicht bekannt gegeben. „Die Investitionen der IBG sollen in die Weiterentwicklung der Technologie des Unternehmens fließen. Zudem werden Fertigungslinien so ausgebaut, dass sie eine steigende Nachfrage bedienen können, verkündet IBG. Weitere Mittel sollen für die Finanzierung von nationalen und internationalen Marketing- und Vertriebsaktivitäten verwendet werden.
Attraktiver Markt für Gewerbespeicher
Alleine in Deutschland wird sich die Zahl der installierten Stromspeicher laut Marktexperten bis 2020 schätzungsweise alle zwei Jahre verdoppeln. Gleichzeitig werden die Preise für Batteriespeichersysteme in den nächsten Jahren immer weiter fallen. „Vor diesem Hintergrund ist es umso wichtiger, jetzt ein schnelles weiteres Wachstum vorzulegen und unsere bestehenden Wettbewerbsvorteile gezielt auszubauen“, weiß Daniel Hannemann, Gründer und Geschäftsführer bei Tesvolt.
Die Firma aus Wittenberg hat nach eigenen Angaben ein innovatives Speichersystem entwickelt, dass sich durch einen neuen Sicherheitsstandard auszeichnet und eine kalendarische Lebensdauer von 30 Jahren aufweist. „Das Herzstück unserer Lösungen bildet unsere Active Battery Optimizer-Technologie, die eine gleichmäßige Ladeverteilung in allen miteinander verschalteten Zellen gewährleistet“, sagt Technikchef Simon Schandert. Das führe zu einer Effizienzsteigerung der Batterien und einen um 5 bis 10 Prozent höheren Gesamtwirkungsgrad gegenüber Batteriespeichern mit herkömmlichen Batteriemanagementsystemen.
Neuer TS-Speicher
Tesvolt hat zusammen mit Samsung SDI eine Hochvoltbatterie entwickelt und am 14. März 2017 in Düsseldorf auf der Energy Storage vorgestellt. Die Hochvoltbatterie der neuer Generation erreicht rund 6.000 Vollladezyklen bei einer Tiefenentladung von 100 Prozent. Laut Tesvolt kann also fast die gesamte Batteriekapazität ausgenutzt werden. Der Speicher funktioniert sowohl mit einer Niederspannung von 48 Volt DC als auch mit einer Hochspannung von bis zu 1.000 Volt DC für stationäre gewerbliche und industrielle Anwendungen. Die Hochvoltvarianten ab 60 Volt verfügen dabei über andere Schutzkontakte für die Installateure, damit ein Berührungsschutz gegeben ist. Mehr lesen über die neue TS-Serie von Tesvolt lesen. (nhp)
28.03.2017 10:24 -
Nur zwei Wochen nach der Vorstellung des neuen Gewerbespeichers TS verschafft sich Tesvolt neue finanzielle Möglichkeiten, um seine eigene Technologie künftig weiter zu entwickeln. Ein Risikokapitalfonds beteiligt sich an der Firma.
Der von der bmp Beteiligungsmanagement verwaltete IBG Risikokapitalfonds III investiert „mehrere Millionen Euro“ in den Gewerbespeicherhersteller Tesvolt, verkündet der Fonds mit Sitz in Magdeburg. Ein genauerer Betrag wird nicht bekannt gegeben. „Die Investitionen der IBG sollen in die Weiterentwicklung der Technologie des Unternehmens fließen. Zudem werden Fertigungslinien so ausgebaut, dass sie eine steigende Nachfrage bedienen können, verkündet IBG. Weitere Mittel sollen für die Finanzierung von nationalen und internationalen Marketing- und Vertriebsaktivitäten verwendet werden.
Attraktiver Markt für Gewerbespeicher
Alleine in Deutschland wird sich die Zahl der installierten Stromspeicher laut Marktexperten bis 2020 schätzungsweise alle zwei Jahre verdoppeln. Gleichzeitig werden die Preise für Batteriespeichersysteme in den nächsten Jahren immer weiter fallen. „Vor diesem Hintergrund ist es umso wichtiger, jetzt ein schnelles weiteres Wachstum vorzulegen und unsere bestehenden Wettbewerbsvorteile gezielt auszubauen“, weiß Daniel Hannemann, Gründer und Geschäftsführer bei Tesvolt.
Die Firma aus Wittenberg hat nach eigenen Angaben ein innovatives Speichersystem entwickelt, dass sich durch einen neuen Sicherheitsstandard auszeichnet und eine kalendarische Lebensdauer von 30 Jahren aufweist. „Das Herzstück unserer Lösungen bildet unsere Active Battery Optimizer-Technologie, die eine gleichmäßige Ladeverteilung in allen miteinander verschalteten Zellen gewährleistet“, sagt Technikchef Simon Schandert. Das führe zu einer Effizienzsteigerung der Batterien und einen um 5 bis 10 Prozent höheren Gesamtwirkungsgrad gegenüber Batteriespeichern mit herkömmlichen Batteriemanagementsystemen.
Neuer TS-Speicher
Tesvolt hat zusammen mit Samsung SDI eine Hochvoltbatterie entwickelt und am 14. März 2017 in Düsseldorf auf der Energy Storage vorgestellt. Die Hochvoltbatterie der neuer Generation erreicht rund 6.000 Vollladezyklen bei einer Tiefenentladung von 100 Prozent. Laut Tesvolt kann also fast die gesamte Batteriekapazität ausgenutzt werden. Der Speicher funktioniert sowohl mit einer Niederspannung von 48 Volt DC als auch mit einer Hochspannung von bis zu 1.000 Volt DC für stationäre gewerbliche und industrielle Anwendungen. Die Hochvoltvarianten ab 60 Volt verfügen dabei über andere Schutzkontakte für die Installateure, damit ein Berührungsschutz gegeben ist. Mehr lesen über die neue TS-Serie von Tesvolt lesen. (nhp)
ViZn
ist zumindest operativ, 1MWh-Projekt: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/vizn-partners-raychem-t…
Primus Power Announces Completion of $32M Financing Round
New funds help accelerate shipments of low cost, long duration flow battery systems
March 23, 2017 20:58 ET | Source: Primus Power Corporation
HAYWARD, Calif., March 23, 2017 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) --
Today Primus Power (“Primus”), a leader in stationary energy storage systems, announced that it has secured $32 million in equity financing. New investors include Hong Kong’s Success Dragon (HKG:1182) and Matador Capital, the investment office of a well known Saudi family. Existing investors Anglo American Platinum, DBL Partners, I2BF and the Russia Kazakhstan Nanotechnology Fund also participated. With this fundraising, Primus has raised $94 million in equity and $20 million in government grants since its founding in 2009.
The new funds will help accelerate the commercial momentum of EnergyPod® 2 - a safe, low-cost and long-duration electrical energy storage system. These modular battery systems pair a unique zinc bromide chemistry with patented innovations to deliver a multi-hour performance and a multi-decade life at an industry-leading low total cost of ownership.
“This is an incredibly exciting time for Primus customers, investors, employees and partners,” said Tom Stepien, Primus Power’s CEO. “The Primus team has risen to the challenge of designing and delivering a safe, powerful and low cost battery system with a 20-year life to meet the expanding demand for energy storage, and investors around the world are recognizing our progress. This is especially true in China where we will leverage Success Dragon’s financial support and deep business network to build a leading position in the energy storage industry.”
Ms. Li Xuehua, Chairman of Success Dragon, said, “Our Primus Power partnership marks Success Dragon’s first step into the renewable energy business. We look forward to bringing Primus’ flow battery systems into China and helping them capitalize on the rapid development of the country’s renewable energy and energy storage markets. The new partnership will also help drive Success Dragon’s business growth.”
China’s efforts to develop renewable energy have accelerated in recent years. According to the 13th Five-Year Plan for Renewable Energy Development issued by China’s National Energy Administration, China plans to invest $360 billion in the renewables sector over five years. Long-duration storage solutions, such as Primus Power’s EnergyPod® 2, are uniquely suited to integrate renewable energy. The power generated from renewable energy sources such as wind and solar fluctuates greatly depending on wind conditions and solar radiation. Long-duration energy storage systems can smooth out fluctuations in solar and wind power, and store excess renewable generation for later use during evening peak hours when energy is most valuable.
“The energy storage market in China is still in its infancy,” continued Ms. Li Xuehua, “and is set for rapid growth, given the country’s large-scale investment in renewable energy. We are confident that our partnership with Primus will give us a pioneering advantage and will see us emerge as a key player in China’s energy storage market.”
About Primus Power
Primus Power is a California-headquartered provider of low-cost, long-life and long-duration energy storage systems. The Company’s flow batteries are shipping to U.S. and international commercial/industrial, data center, microgrid, utility, and military customers. With technical innovations protected by 34 patents in 9 countries/regions, the Company’s EnergyPod systems offer exceptional reliability, modularity, and energy density at an industry-leading low total cost of ownership. www.primuspower.com
About Success Dragon International Holdings Limited
Success Dragon International Holdings Limited (“Success Dragon”, HKEx stock code: 1182) is a provider of information technology and outsourced business process management services for an array of companies across different sectors. Success Dragon currently operates in Macau and Vietnam, and is actively exploring opportunities to expand into the renewable energy business in China. Success Dragon also operates its traditional long-standing Kingbox packaging business, serving a number of top brands in Hong Kong, Europe, USA and Asian countries. http://successdragonintl.com/
About Matador Capital Partners
Matador Capital Partners (“MCP”) was founded in 2016 as the London-based investment office of a well known Saudi family. MCP is a global investment company focused on real estate, listed securities, direct investments and special situations.
Registered and common law trademarks of Primus Power include Primus Power®, EnergyPod®, Primus Power Smart Grid Storage®, No Fracking Worries® and Duration without Degradation®.
New funds help accelerate shipments of low cost, long duration flow battery systems
March 23, 2017 20:58 ET | Source: Primus Power Corporation
HAYWARD, Calif., March 23, 2017 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) --
Today Primus Power (“Primus”), a leader in stationary energy storage systems, announced that it has secured $32 million in equity financing. New investors include Hong Kong’s Success Dragon (HKG:1182) and Matador Capital, the investment office of a well known Saudi family. Existing investors Anglo American Platinum, DBL Partners, I2BF and the Russia Kazakhstan Nanotechnology Fund also participated. With this fundraising, Primus has raised $94 million in equity and $20 million in government grants since its founding in 2009.
The new funds will help accelerate the commercial momentum of EnergyPod® 2 - a safe, low-cost and long-duration electrical energy storage system. These modular battery systems pair a unique zinc bromide chemistry with patented innovations to deliver a multi-hour performance and a multi-decade life at an industry-leading low total cost of ownership.
“This is an incredibly exciting time for Primus customers, investors, employees and partners,” said Tom Stepien, Primus Power’s CEO. “The Primus team has risen to the challenge of designing and delivering a safe, powerful and low cost battery system with a 20-year life to meet the expanding demand for energy storage, and investors around the world are recognizing our progress. This is especially true in China where we will leverage Success Dragon’s financial support and deep business network to build a leading position in the energy storage industry.”
Ms. Li Xuehua, Chairman of Success Dragon, said, “Our Primus Power partnership marks Success Dragon’s first step into the renewable energy business. We look forward to bringing Primus’ flow battery systems into China and helping them capitalize on the rapid development of the country’s renewable energy and energy storage markets. The new partnership will also help drive Success Dragon’s business growth.”
China’s efforts to develop renewable energy have accelerated in recent years. According to the 13th Five-Year Plan for Renewable Energy Development issued by China’s National Energy Administration, China plans to invest $360 billion in the renewables sector over five years. Long-duration storage solutions, such as Primus Power’s EnergyPod® 2, are uniquely suited to integrate renewable energy. The power generated from renewable energy sources such as wind and solar fluctuates greatly depending on wind conditions and solar radiation. Long-duration energy storage systems can smooth out fluctuations in solar and wind power, and store excess renewable generation for later use during evening peak hours when energy is most valuable.
“The energy storage market in China is still in its infancy,” continued Ms. Li Xuehua, “and is set for rapid growth, given the country’s large-scale investment in renewable energy. We are confident that our partnership with Primus will give us a pioneering advantage and will see us emerge as a key player in China’s energy storage market.”
About Primus Power
Primus Power is a California-headquartered provider of low-cost, long-life and long-duration energy storage systems. The Company’s flow batteries are shipping to U.S. and international commercial/industrial, data center, microgrid, utility, and military customers. With technical innovations protected by 34 patents in 9 countries/regions, the Company’s EnergyPod systems offer exceptional reliability, modularity, and energy density at an industry-leading low total cost of ownership. www.primuspower.com
About Success Dragon International Holdings Limited
Success Dragon International Holdings Limited (“Success Dragon”, HKEx stock code: 1182) is a provider of information technology and outsourced business process management services for an array of companies across different sectors. Success Dragon currently operates in Macau and Vietnam, and is actively exploring opportunities to expand into the renewable energy business in China. Success Dragon also operates its traditional long-standing Kingbox packaging business, serving a number of top brands in Hong Kong, Europe, USA and Asian countries. http://successdragonintl.com/
About Matador Capital Partners
Matador Capital Partners (“MCP”) was founded in 2016 as the London-based investment office of a well known Saudi family. MCP is a global investment company focused on real estate, listed securities, direct investments and special situations.
Registered and common law trademarks of Primus Power include Primus Power®, EnergyPod®, Primus Power Smart Grid Storage®, No Fracking Worries® and Duration without Degradation®.
Microvast sammelt 400 MUSD ein: http://www.microvast.com/index.php/news/info/87
Spezialität scheint das "ultra"-Schnelladen zu sein
Spezialität scheint das "ultra"-Schnelladen zu sein
Vizn installiert ein Projekt in Indien: http://www.elp.com/articles/2017/04/vizn-energy-systems-rayc…
Pricing 'already' below US$100 per kWh
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/engie-to-test-eos-zinc-…
Eos has also been gathering interest for its systems with an interesting pricing strategy – the company’s batteries are available to order at below US$100 per kilowatt-hour, the price benchmark considered something of an inflection point across the industry.
However, the catch is that the batteries will be US$95 per kWh if shipped in the year 2022. The price for shipping during 2017 is at US$160 per kWh – which Eos argues is still as much as 30-40% lower than lithium-ion alternatives.
Philippe Bouchard of Eos said that he believed the batteries would still be competitive with lithium-ion even in five years’ time.
“We have evaluated and benchmarked against the most aggressive forward pricing for Li-ion manufacturers,” Bouchard said.
“Because it is a mature technology, Li-ion is further out on the asymptote of its cost curve: every billion dollars invested in manufacturing capacity and economies of scale has decreasing marginal returns in terms of cost reduction. Eos, on the other hand, is just beginning to ramp up volume and is seeing significant cost reduction,” adding that from the US$160 per kWh price of today to US$95 in 2022 "maintains that cost advantage five years out into the future".
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/engie-to-test-eos-zinc-…
Eos has also been gathering interest for its systems with an interesting pricing strategy – the company’s batteries are available to order at below US$100 per kilowatt-hour, the price benchmark considered something of an inflection point across the industry.
However, the catch is that the batteries will be US$95 per kWh if shipped in the year 2022. The price for shipping during 2017 is at US$160 per kWh – which Eos argues is still as much as 30-40% lower than lithium-ion alternatives.
Philippe Bouchard of Eos said that he believed the batteries would still be competitive with lithium-ion even in five years’ time.
“We have evaluated and benchmarked against the most aggressive forward pricing for Li-ion manufacturers,” Bouchard said.
“Because it is a mature technology, Li-ion is further out on the asymptote of its cost curve: every billion dollars invested in manufacturing capacity and economies of scale has decreasing marginal returns in terms of cost reduction. Eos, on the other hand, is just beginning to ramp up volume and is seeing significant cost reduction,” adding that from the US$160 per kWh price of today to US$95 in 2022 "maintains that cost advantage five years out into the future".
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 51.322.068 von R-BgO am 17.12.15 00:45:10Greensmith wird von Wärtsilä übernommen: http://www.wartsila.com/media/news/15-05-2017-wartsila-acqui…
Schön für E.On. Oder auch nicht.
Bin gespannt, ob man was zum Preis wir rauskriegen können...
Schön für E.On. Oder auch nicht.
Bin gespannt, ob man was zum Preis wir rauskriegen können...
Tesla kommt auf den sonnen-trip: https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/tesla-and-green…
Li-Ion gräbt anderen Technologien das Wasser ab...: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/flow-batteries-unlikely…
Ich nenne es das c-Si vs. thin-film Syndrom (oder Windows vs. alle)
Ich nenne es das c-Si vs. thin-film Syndrom (oder Windows vs. alle)
Habe den Brückentag heute mal für ein bisschen Housekeeping genutzt,
(nachdem ich ja sonst eher nachrichtengetrieben bin);der Bauch sagt: "es geht voran"
Neben den börsennotierten Playern, für die es alle eigene Threads gibt, empfinde ich die drei vorbörslichen Firmen
Thread: Varta will an die Börse zurück
Thread: Sonnenbatterie
Thread: Younicos
als sehr interessante Datenquellen.
Zu allen dreien habe ich heute was gepostet, weil es inzwischen aussagefähigere Abschlüsse gibt als noch vor einem Jahr.
Außerdem habe ich noch eine andere interessante Quelle aufgetan, die -typisch amerikanisch- mit den ganz dicken Hämmern um sich schlägt: https://static1.squarespace.com/static/585c3439be65942f022bb…
Hatte noch keine Zeit, sie mir gründlicher anzusehen, aber (s.o.) der Bauch sagt, es passiert was. Und Aussagen wie

oder
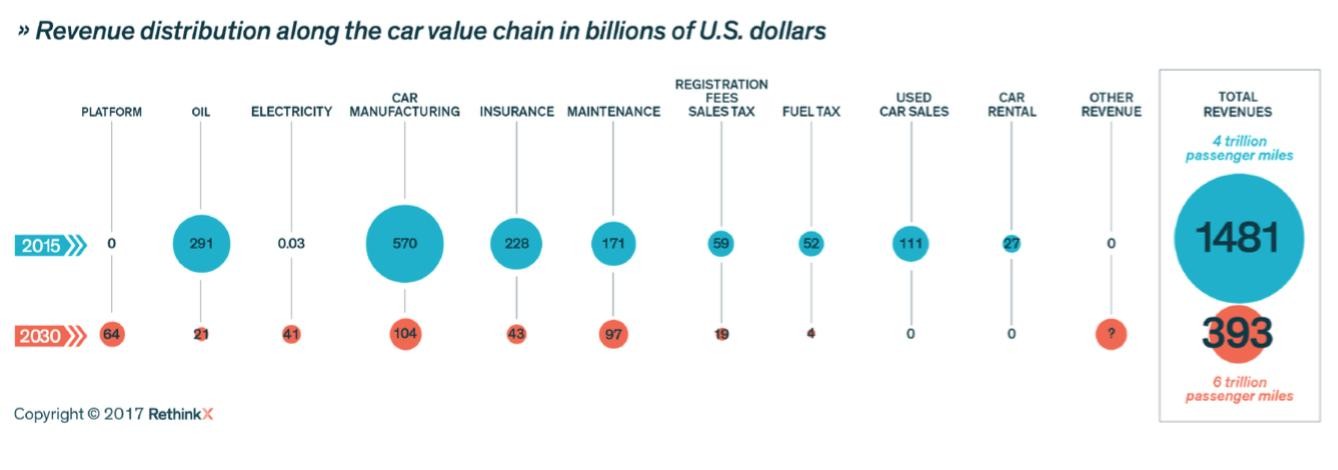
hätten gigantische Implikationen, selbst wenn sie nur teilweise eintreffen.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 54.508.446 von R-BgO am 10.03.17 10:26:37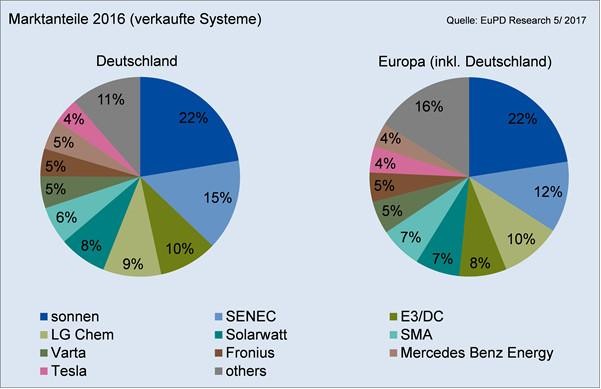

Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 55.047.037 von R-BgO am 31.05.17 08:52:12
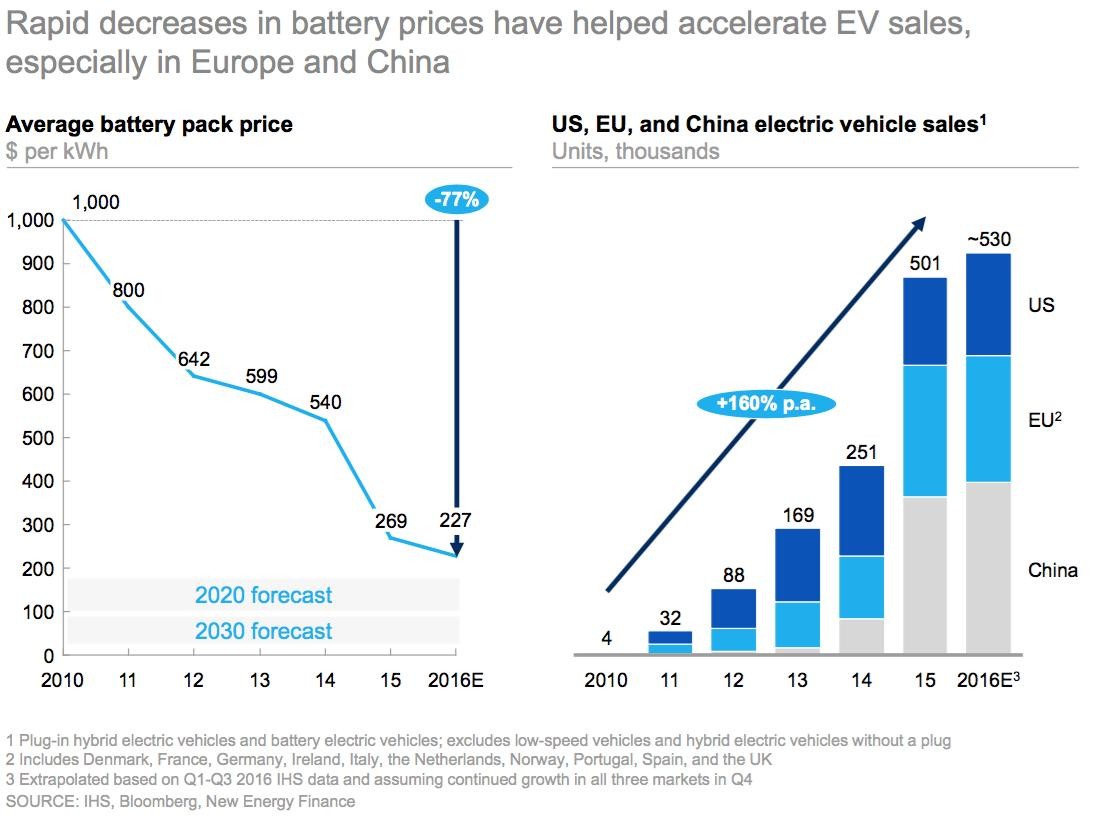
Aus einem McKinsey-Report von Jan2017:
http://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/McKinsey/Industries/Automoti…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 54.507.996 von R-BgO am 10.03.17 09:40:16Resteverwertung:
http://www.solarserver.de/solar-magazin/nachrichten/aktuelle…
BlueSky Energy will Aquion Energy kaufen
Der Oberösterreichische Stromspeicherspezialist BlueSky Energy hat ein verbindliches Angebot zum Kauf der Vermögenswerte der US Firma Aquion Energy abgegeben. Das Übernahmeangebot wurde von den amerikanischen Eigentümervertretern angenommen. Es ist geplant, dass bis Juli 2017 der Bieterprozess abgeschlossen ist.
„Wir arbeiten bereits seit Jahren mit der Technologie und den Produkten von Aquion und sehen in der Salzwassertechnologie einen Zukunftsmarkt für Stromspeicherung. Wir planen mit dieser stark zu expandieren“, erklärt Helmut Mayer, Geschäftsführer von BlueSky Energy den Grund für die geplante Übernahme. „Die Vorteile des Systems liegen eindeutig in der Sicherheit, Wartungsfreiheit und der Umweltfreundlichkeit. Bis jetzt haben wir diese Salzwasserzellen zugekauft und daraus unseren schlüsselfertigen Gesamtspeicher GREENROCK entwickelt.“
Aquion wurde 2008 vom amerikanischen Universitätsprofessor Jay F. Whitacre gegründet und mit Investoren wie Kleiner Perkins, Foundation Capital, Bill Gates, Nick and Jobey Pritzker, Bright Capital and Advanced Technology Ventures mit über 180 Millionen Dollar finanziert.
Die Salzwasserspeicher-Technologie eignet sich nach Aussage von Mayer perfekt für Eigenheime und kleine sowie mittlere Unternehmen, die ihren erzeugten Strom energieautark für den Eigenverbrauch optimieren möchten und dabei auf das Thema Sicherheit setzen. Diese ist nicht entflammbar oder explosiv, berührungssicher und wartungsfrei. Die Technologie habesich, so Mayer, weltweit bereits bei zigtausenden Haushalten erfolgreich im Einsatz bewährt. 2015 wurde die Salzwassertechnologie mit dem Umweltzertifikat „cradle to cradle“ ausgezeichnet. Es würden keine gesundheits- und umweltschädlichen Materialien mehr verwendet und alle Stoffe können dauerhaft wieder verwendet werden.
http://www.solarserver.de/solar-magazin/nachrichten/aktuelle…
BlueSky Energy will Aquion Energy kaufen
Der Oberösterreichische Stromspeicherspezialist BlueSky Energy hat ein verbindliches Angebot zum Kauf der Vermögenswerte der US Firma Aquion Energy abgegeben. Das Übernahmeangebot wurde von den amerikanischen Eigentümervertretern angenommen. Es ist geplant, dass bis Juli 2017 der Bieterprozess abgeschlossen ist.
„Wir arbeiten bereits seit Jahren mit der Technologie und den Produkten von Aquion und sehen in der Salzwassertechnologie einen Zukunftsmarkt für Stromspeicherung. Wir planen mit dieser stark zu expandieren“, erklärt Helmut Mayer, Geschäftsführer von BlueSky Energy den Grund für die geplante Übernahme. „Die Vorteile des Systems liegen eindeutig in der Sicherheit, Wartungsfreiheit und der Umweltfreundlichkeit. Bis jetzt haben wir diese Salzwasserzellen zugekauft und daraus unseren schlüsselfertigen Gesamtspeicher GREENROCK entwickelt.“
Aquion wurde 2008 vom amerikanischen Universitätsprofessor Jay F. Whitacre gegründet und mit Investoren wie Kleiner Perkins, Foundation Capital, Bill Gates, Nick and Jobey Pritzker, Bright Capital and Advanced Technology Ventures mit über 180 Millionen Dollar finanziert.
Die Salzwasserspeicher-Technologie eignet sich nach Aussage von Mayer perfekt für Eigenheime und kleine sowie mittlere Unternehmen, die ihren erzeugten Strom energieautark für den Eigenverbrauch optimieren möchten und dabei auf das Thema Sicherheit setzen. Diese ist nicht entflammbar oder explosiv, berührungssicher und wartungsfrei. Die Technologie habesich, so Mayer, weltweit bereits bei zigtausenden Haushalten erfolgreich im Einsatz bewährt. 2015 wurde die Salzwassertechnologie mit dem Umweltzertifikat „cradle to cradle“ ausgezeichnet. Es würden keine gesundheits- und umweltschädlichen Materialien mehr verwendet und alle Stoffe können dauerhaft wieder verwendet werden.
Storage goes Mainstream:
Vattenfall gründet eine dedicated business unit: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/vattenfall-establishes-…Aggreko kauft Younicos: Thread: Younicos
Wärtsilä closed die Greensmith-Akquisition: https://www.wartsila.com/usa/media/news/03-07-2017-wartsila-…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 55.280.513 von R-BgO am 07.07.17 12:38:26Energy storage cost-competitive for commercial applications McKinsey says
7/4/17, 2:26 PM -
Low-cost energy storage could transform the power landscape. The implications are profound according to global management consultancy McKinsey.
Energy storage costs are falling and providing growing business opportunities especially for commerical customers, McKinsey says.
Energy storage prices are dropping much faster than anyone expected, due to the growing market for consumer electronics and demand for electric vehicles (EVs), McKinsey states. Major players in Asia, Europe, and the United States are all scaling up lithium-ion battery manufacturing to serve electric cars and other power applications. Battery-pack costs are down to less than $230 per kilowatt-hour in 2016, compared with almost $1,000 per kilowatt-hour in 2010.
Reduce peak consumption levels
McKinsey research has found that energy storage is already economical for many commercial customers to reduce their peak consumption levels. At today’s lower prices, storage is starting to play a broader role in energy markets, moving from niche uses such as grid balancing to broader ones such as replacing conventional power generators for reliability, providing power-quality services, and supporting renewables integration
Evolving business case also for households
„Further, given regulatory changes to pare back incentives for solar in many markets, the idea of combining solar with storage to enable households to make and consume their own power on demand, instead of exporting power to the grid, is beginning to be an attractive opportunity for customers, sometimes referred to as partial grid defection. We believe these markets will continue to expand, creating a significant challenge for utilities faced with flat or declining customer demand. Eventually, combining solar with storage and a small electrical generator (known as full grid defection) will make economic sense—in a matter of years, not decades, for some customers in high-cost markets“, McKinsey states.
Unique flexibility as an asset of energy storage
“Energy storage can be deployed both on the grid and at an individual consumer’s home or business. A complex technology, its economics are shaped by customer type, location, grid needs, regulations, customer load shape, rate structure, and nature of the application. It is also uniquely flexible in its ability to stack value streams and change its dispatch to serve different needs over the course of a year or even an hour. These value streams are growing both in value and in market scale”, McKinsey says. (HCN)
7/4/17, 2:26 PM -
Low-cost energy storage could transform the power landscape. The implications are profound according to global management consultancy McKinsey.
Energy storage costs are falling and providing growing business opportunities especially for commerical customers, McKinsey says.
Energy storage prices are dropping much faster than anyone expected, due to the growing market for consumer electronics and demand for electric vehicles (EVs), McKinsey states. Major players in Asia, Europe, and the United States are all scaling up lithium-ion battery manufacturing to serve electric cars and other power applications. Battery-pack costs are down to less than $230 per kilowatt-hour in 2016, compared with almost $1,000 per kilowatt-hour in 2010.
Reduce peak consumption levels
McKinsey research has found that energy storage is already economical for many commercial customers to reduce their peak consumption levels. At today’s lower prices, storage is starting to play a broader role in energy markets, moving from niche uses such as grid balancing to broader ones such as replacing conventional power generators for reliability, providing power-quality services, and supporting renewables integration
Evolving business case also for households
„Further, given regulatory changes to pare back incentives for solar in many markets, the idea of combining solar with storage to enable households to make and consume their own power on demand, instead of exporting power to the grid, is beginning to be an attractive opportunity for customers, sometimes referred to as partial grid defection. We believe these markets will continue to expand, creating a significant challenge for utilities faced with flat or declining customer demand. Eventually, combining solar with storage and a small electrical generator (known as full grid defection) will make economic sense—in a matter of years, not decades, for some customers in high-cost markets“, McKinsey states.
Unique flexibility as an asset of energy storage
“Energy storage can be deployed both on the grid and at an individual consumer’s home or business. A complex technology, its economics are shaped by customer type, location, grid needs, regulations, customer load shape, rate structure, and nature of the application. It is also uniquely flexible in its ability to stack value streams and change its dispatch to serve different needs over the course of a year or even an hour. These value streams are growing both in value and in market scale”, McKinsey says. (HCN)
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 55.280.513 von R-BgO am 07.07.17 12:38:26GE bietet Batterien für alle seine Turbinen an:
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/ge-can-now-put-…
"GE's steam, gas and wind turbines make up one-third of electricity capacity around the world. Now the industrial giant has the capability to layer batteries on top of all those generators, if desired.
This week, the industrial and power giant unveiled a battery and controls package that can be integrated into any of its steam or gas turbines. Soon, it will be ready for solar, wind and hydroelectric generators. It's a solution that could change the way many power plants are used for real-time energy services."
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/ge-can-now-put-…
"GE's steam, gas and wind turbines make up one-third of electricity capacity around the world. Now the industrial giant has the capability to layer batteries on top of all those generators, if desired.
This week, the industrial and power giant unveiled a battery and controls package that can be integrated into any of its steam or gas turbines. Soon, it will be ready for solar, wind and hydroelectric generators. It's a solution that could change the way many power plants are used for real-time energy services."
Silicon-Air Batteries: http://www.pveurope.eu/News/Energy-Storage/Energy-storage-Si…
' Scientists at Jülich’s Institute of Energy and Climate Research (IEK) suspect another cause for the short running time: the consumption of the electrolyte. As part of the AlSiBat project funded by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Education and Research, the researchers developed a pump system in which the electrolyte fluid – potassium hydroxide dissolved in water – was refilled from time to time.
“If the silicon anode remains in contact with the electrolyte, the battery will continue running,” explains Hermann Tempel from the IEK’s Fundamental Electrochemistry. The battery is thus able to achieve a running time of over 1,100 hours, or almost 46 days, he adds. “Until the silicon is fully used up. The battery can subsequently be recharged by exchanging the anode, in other words mechanically.” '
' Scientists at Jülich’s Institute of Energy and Climate Research (IEK) suspect another cause for the short running time: the consumption of the electrolyte. As part of the AlSiBat project funded by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Education and Research, the researchers developed a pump system in which the electrolyte fluid – potassium hydroxide dissolved in water – was refilled from time to time.
“If the silicon anode remains in contact with the electrolyte, the battery will continue running,” explains Hermann Tempel from the IEK’s Fundamental Electrochemistry. The battery is thus able to achieve a running time of over 1,100 hours, or almost 46 days, he adds. “Until the silicon is fully used up. The battery can subsequently be recharged by exchanging the anode, in other words mechanically.” '
ViZn behauptet, Solar/Wind & Storage für 4c/kWh !!! bei 7% IRR liefern zu können: https://www.viznenergy.com/vizn-energy-systems-enables-247-s…
nota bene: mit ITC
nota bene: mit ITC
Eni testet Amber Kinetics' Flywheels: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/enel-will-put-amber-kin…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 55.113.685 von R-BgO am 09.06.17 19:19:49Aquion will wieder durchstarten: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/saltwater-battery-maker…
"New owner is unnamed US-majority investor
A couple of months ago, it was reported that a company based in Europe was bidding on Aquion’s assets, although it was never clear if the intention was to carry on the company and its name. However, that bidder appears to have lost interest, or to have been unsuccessful, as according to Aquion, the new owners are an as-yet unnamed “majority-American joint venture (JV)”.
Philip Juline, now CEO of Aquion, said the new leadership aimed to turn Aquion into a “billion-dollar company in the upcoming years”, claiming it was only limited by its “ability to ramp and scale” operations to meet demand.
“Aquion Energy will be a stronger company after emerging from this protection transition period. We are refocused on technology and go-to-market opportunities that will grow significant volume for the company in the coming years. Aquion's battery technology has always been world leading. We now need to focus on what we do best – creating the safest, cleanest, and lowest cost per kWh-cycle battery technology in the world – with a simple business model that can effectively compete in the marketplace,” Juline also said.
“With a renewed focus on expanding our product offerings into the growing markets in China and other global markets, we intend to deliver the lowest price per kWh-cycle battery in the world.” "
"New owner is unnamed US-majority investor
A couple of months ago, it was reported that a company based in Europe was bidding on Aquion’s assets, although it was never clear if the intention was to carry on the company and its name. However, that bidder appears to have lost interest, or to have been unsuccessful, as according to Aquion, the new owners are an as-yet unnamed “majority-American joint venture (JV)”.
Philip Juline, now CEO of Aquion, said the new leadership aimed to turn Aquion into a “billion-dollar company in the upcoming years”, claiming it was only limited by its “ability to ramp and scale” operations to meet demand.
“Aquion Energy will be a stronger company after emerging from this protection transition period. We are refocused on technology and go-to-market opportunities that will grow significant volume for the company in the coming years. Aquion's battery technology has always been world leading. We now need to focus on what we do best – creating the safest, cleanest, and lowest cost per kWh-cycle battery technology in the world – with a simple business model that can effectively compete in the marketplace,” Juline also said.
“With a renewed focus on expanding our product offerings into the growing markets in China and other global markets, we intend to deliver the lowest price per kWh-cycle battery in the world.” "
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 55.393.511 von R-BgO am 26.07.17 09:32:55https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/saltwater-aquio…
Heimspeicher liefern 400 Megawattstunden nutzbare Kapazität
27.07.2017 12:17
Ende April 2017 waren in Deutschland rund 61.000 Batteriespeicher installiert. Der Marktanteil von Strompuffern mit Lithiumakkus liegt derzeit bei über 95 Prozent. Das belegen Daten des aktuellen KfW-Speichermonitorings.
Das Monitoringprogramm führt das Institut für Stromspeichertechnik und Elektrische Antriebe (Isea) der RWTH Aachen im Auftrag des Bundeswirtschaftsministeriums durch. Das KfW-Förderprogramm 275 läuft noch bis Ende 2018. Die 61.000 hierzulande installierten Heimspeicher bringen es immerhin auf eine kumulierte nutzbare Speicherkapazität von 400 Megawattstunden, die ans deutsche Niederspannungsnetz angeschlossen sind. Zu dem Zubauboom kam es auch, weil die Kosten innerhalb von vier Jahren um 50 Prozent gesunken sind.
Preise unter 1.500 Euro pro Kilowattstunde
Die durchschnittlichen Preise für Lithiumsysteme, die Endverbraucher zahlen, liegen demnach bei unter 1.500 Euro pro Kilowattstunde. Auch werden fast nur noch Speicher mit Lithiumakkus (innerhalb der KfW-Förderung) verkauft. Dabei steigt die Erwartung eines profitablen Betriebs von 50 Prozent in 2013 auf derzeit 60 Prozent. Diese Tendenz wird sich weiter verstärken.
Dezentrale Speicher entlasten das Verteilnetz, weil weniger Erzeugungsspitzen eingespeist werden. Die Leistung der Solarstromanlage muss laut KfW-Förderbedingungen auf 50 Prozent der maximalen Einspeiseleistung verringert werden. Im Jahr 2016 wurden durch Photovoltaik-Speichersysteme 165 Gigawattstunden Solarstrom lokal selbstverbraucht. (Niels H. Petersen)
=> 400.000 kWh ./. 61.000 Systeme gleich 6,55 kWh pro System
=> 165 GWh ./. 61.000 Systeme gleich 2.705 kWh pro System, geteilt durch 6,55 kWh pro System ergibt 413 malige Nutzung der Kapazität pro Jahr ...
mehr als einmal pro Tag ???
Oder meinen sie nur PV-System, die auch einen Speicher haben, aber die kWh nicht zwingend da durch muss?
27.07.2017 12:17
Ende April 2017 waren in Deutschland rund 61.000 Batteriespeicher installiert. Der Marktanteil von Strompuffern mit Lithiumakkus liegt derzeit bei über 95 Prozent. Das belegen Daten des aktuellen KfW-Speichermonitorings.
Das Monitoringprogramm führt das Institut für Stromspeichertechnik und Elektrische Antriebe (Isea) der RWTH Aachen im Auftrag des Bundeswirtschaftsministeriums durch. Das KfW-Förderprogramm 275 läuft noch bis Ende 2018. Die 61.000 hierzulande installierten Heimspeicher bringen es immerhin auf eine kumulierte nutzbare Speicherkapazität von 400 Megawattstunden, die ans deutsche Niederspannungsnetz angeschlossen sind. Zu dem Zubauboom kam es auch, weil die Kosten innerhalb von vier Jahren um 50 Prozent gesunken sind.
Preise unter 1.500 Euro pro Kilowattstunde
Die durchschnittlichen Preise für Lithiumsysteme, die Endverbraucher zahlen, liegen demnach bei unter 1.500 Euro pro Kilowattstunde. Auch werden fast nur noch Speicher mit Lithiumakkus (innerhalb der KfW-Förderung) verkauft. Dabei steigt die Erwartung eines profitablen Betriebs von 50 Prozent in 2013 auf derzeit 60 Prozent. Diese Tendenz wird sich weiter verstärken.
Dezentrale Speicher entlasten das Verteilnetz, weil weniger Erzeugungsspitzen eingespeist werden. Die Leistung der Solarstromanlage muss laut KfW-Förderbedingungen auf 50 Prozent der maximalen Einspeiseleistung verringert werden. Im Jahr 2016 wurden durch Photovoltaik-Speichersysteme 165 Gigawattstunden Solarstrom lokal selbstverbraucht. (Niels H. Petersen)
=> 400.000 kWh ./. 61.000 Systeme gleich 6,55 kWh pro System
=> 165 GWh ./. 61.000 Systeme gleich 2.705 kWh pro System, geteilt durch 6,55 kWh pro System ergibt 413 malige Nutzung der Kapazität pro Jahr ...
mehr als einmal pro Tag ???
Oder meinen sie nur PV-System, die auch einen Speicher haben, aber die kWh nicht zwingend da durch muss?
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 55.450.518 von R-BgO am 03.08.17 12:34:50
hier ist der Link zum Bericht:
http://www.speichermonitoring.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Speic…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 55.450.518 von R-BgO am 03.08.17 12:34:50Selbst Google macht mit: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/2017/07/alphabe…
"Alphabet Inc.'s secretive X skunk works has another idea that could save the world. This one, code named Malta, involves vats of salt and antifreeze.
The research lab, which hatched Google's driverless car almost a decade ago, is developing a system for storing renewable energy that would otherwise be wasted. It can be located almost anywhere, has the potential to last longer than lithium-ion batteries and compete on price with new hydroelectric plants and other existing clean energy storage methods, according to X executives and researchers.
...
Two tanks are filled with salt, and two are filled with antifreeze or a hydrocarbon liquid. The system takes in energy in the form of electricity and turns it into separate streams of hot and cold air. The hot air heats up the salt, while the cold air cools the antifreeze, a bit like a refrigerator. The jet engine part: Flip a switch and the process reverses. Hot and cold air rush toward each other, creating powerful gusts that spin a turbine and spit out electricity when the grid needs it. Salt maintains its temperature well, so the system can store energy for many hours, and even days, depending on how much you insulate the tanks."
"Alphabet Inc.'s secretive X skunk works has another idea that could save the world. This one, code named Malta, involves vats of salt and antifreeze.
The research lab, which hatched Google's driverless car almost a decade ago, is developing a system for storing renewable energy that would otherwise be wasted. It can be located almost anywhere, has the potential to last longer than lithium-ion batteries and compete on price with new hydroelectric plants and other existing clean energy storage methods, according to X executives and researchers.
...
Two tanks are filled with salt, and two are filled with antifreeze or a hydrocarbon liquid. The system takes in energy in the form of electricity and turns it into separate streams of hot and cold air. The hot air heats up the salt, while the cold air cools the antifreeze, a bit like a refrigerator. The jet engine part: Flip a switch and the process reverses. Hot and cold air rush toward each other, creating powerful gusts that spin a turbine and spit out electricity when the grid needs it. Salt maintains its temperature well, so the system can store energy for many hours, and even days, depending on how much you insulate the tanks."
Northvolt will eine "Gigafactory" in Schweden bauen: http://northvolt.com/about
Bloom installiert Fuel Cells bei Equinix: https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/bloom-energy-an…
Auszug:
"On Wednesday, the partners announced they’ve landed the biggest client yet for that offering, in the form of a 37-megawatt fuel cell deal with data center company Equinix.
Over the next two years, the partners will install Bloom’s solid-oxide, natural-gas-fueled “energy servers” at 12 Equinix data centers in California and New York, with the goal of reducing the company’s carbon footprint, offering it more control over its energy supply, and keeping its electricity bills at or lower their current rates via 15-year power purchase agreements.
It’s one of the biggest fuel cell installations to date, both for Bloom and for the industry as a whole.
The U.S. had about 235 megawatts of large-scale stationary fuel cells operating in the U.S. as of mid-2016, most of them in California, according to a November report from the Department of Energy. But the largest single projects to date are in Connecticut, with nearly 15 megawatts from FuelCell Energy, and in Delaware, where Bloom set the previous record with a 30-megawatt deployment with Delmarva Power to deploy its fuel cells at utility substations."
Auszug:
"On Wednesday, the partners announced they’ve landed the biggest client yet for that offering, in the form of a 37-megawatt fuel cell deal with data center company Equinix.
Over the next two years, the partners will install Bloom’s solid-oxide, natural-gas-fueled “energy servers” at 12 Equinix data centers in California and New York, with the goal of reducing the company’s carbon footprint, offering it more control over its energy supply, and keeping its electricity bills at or lower their current rates via 15-year power purchase agreements.
It’s one of the biggest fuel cell installations to date, both for Bloom and for the industry as a whole.
The U.S. had about 235 megawatts of large-scale stationary fuel cells operating in the U.S. as of mid-2016, most of them in California, according to a November report from the Department of Energy. But the largest single projects to date are in Connecticut, with nearly 15 megawatts from FuelCell Energy, and in Delaware, where Bloom set the previous record with a 30-megawatt deployment with Delmarva Power to deploy its fuel cells at utility substations."
Energy Storage Firm Alevo Shutters Operations
August 22, 2017
http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/pt/2017/08/ener…
By Associated Press with Commentary by Jennifer Runyon
RALEIGH, N.C. (AP) - A startup company is giving up plans to build boxcar-sized batteries that help power companies save energy or shift to wind and solar power. Alevo Manufacturing Inc. informed state officials Friday that it was immediately shutting down its factory inside a massive, former Philip Morris USA cigarette plant and filing for bankruptcy protection.
August 22, 2017
http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/pt/2017/08/ener…
By Associated Press with Commentary by Jennifer Runyon
RALEIGH, N.C. (AP) - A startup company is giving up plans to build boxcar-sized batteries that help power companies save energy or shift to wind and solar power. Alevo Manufacturing Inc. informed state officials Friday that it was immediately shutting down its factory inside a massive, former Philip Morris USA cigarette plant and filing for bankruptcy protection.
Solar Philippines working on Asia’s ‘largest solar, diesel, battery micro-grid’ without subsidies
Published: 23 Aug 2017, 15:05
By:Tom Kenning
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/solar-philippines-worki…
Filipino renewable energy firm Solar Philippines is developing an off-grid solar, battery and diesel micro-grid in the Philippines that could be the largest of its kind in Asia, according to the company head.
Solar Philippines founder and CEO Leandro Leviste told Energy-Storage.News that the micro-grid system on the island of Mindoro will include an 8MWh energy storage battery, a 4MW solar PV plant and diesel capacity – enough to power a whole town.
Leviste added: “We are going to be replicating a lot of these that are unserved, without subsidies and without any government programmes. So we are doing all on a deregulated basis.”
He also gave new details about the nation’s first utility-scale solar plant combined with storage at Concepcion,Tarlac, which the company started constructing in March. While it was already known that the PV project would be 150MW, Leviste revealed that the storage element would include a 50MWh battery. Commissioning is due in the next few months, he added.
Solar Philippines claims that this was in fact the first project to start construction after the government’s Feed-in-Tariff (FiT) programme came to an end, under President Duterte’s administration.
Today, Duterte was present to inaugurate the newly expanded Solar Philippines solar module factory at Batangas - the first such facility in the Philippines - that now has 800MW capacity.
Published: 23 Aug 2017, 15:05
By:Tom Kenning
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/solar-philippines-worki…
Filipino renewable energy firm Solar Philippines is developing an off-grid solar, battery and diesel micro-grid in the Philippines that could be the largest of its kind in Asia, according to the company head.
Solar Philippines founder and CEO Leandro Leviste told Energy-Storage.News that the micro-grid system on the island of Mindoro will include an 8MWh energy storage battery, a 4MW solar PV plant and diesel capacity – enough to power a whole town.
Leviste added: “We are going to be replicating a lot of these that are unserved, without subsidies and without any government programmes. So we are doing all on a deregulated basis.”
He also gave new details about the nation’s first utility-scale solar plant combined with storage at Concepcion,Tarlac, which the company started constructing in March. While it was already known that the PV project would be 150MW, Leviste revealed that the storage element would include a 50MWh battery. Commissioning is due in the next few months, he added.
Solar Philippines claims that this was in fact the first project to start construction after the government’s Feed-in-Tariff (FiT) programme came to an end, under President Duterte’s administration.
Today, Duterte was present to inaugurate the newly expanded Solar Philippines solar module factory at Batangas - the first such facility in the Philippines - that now has 800MW capacity.
...die Jungs dürften >200 MEUR Umsatz machen und sind profitabel!:
BMZ bündelt Kompetenzen für Batterieforschung
22.08.2017 11:01 -
Ab September 2017 startet im Hauptquartier der BMZ Group das E-Volution Center. In Karlstein am Main bei Aschaffenburg werden über 150 Entwickler demnach die Energiespeicher der Zukunft entwickeln. Denn Lithiumakkus werden immer kleiner, leichter und besser.
Im E-Volution Center werden laut BMZ jährlich rund 200 neue Batteriesysteme für Autos, Fahrräder, Gartengeräte, Medizinprodukte und weitere Anwendungen entwickelt. „Die Batteriesysteme werden immer kleiner und leichter und dies mit längeren Laufzeiten, einem besseren Temperaturbereich und sie können schneller geladen werden - um nur einige Innovationen zu nennen“, erklärt Sven Bauer, Geschäftsführer und Gründer der BMZ Group. BMZ sei durch diese Innovationen der größte Hersteller von Systemlösungen in Europa geworden und wachse jedes Jahr um 30 bis 50 Prozent.
Produktion mit Schweißrobotern
Die Mitarbeiter des Centers entwickeln demnach alle Komponenten einer Lithium-Ionen Batterie: vom Konzept bis zur Serienfertigung. Neben Batteriezellen-Experten arbeiten Konstrukteure, Hard- und Softwareentwickler, Testingenieure und Prototypentechniker sowie Spezialisten für Schweißtechnik. Thermomanagement, Ladetechnik und viele weitere innovative Themen. Auch um das Thema Recycling und die Wiederverwendung (second life) von Batterien. Technischer Leiter des Centers wird Dirk Oestreich.
Durch das Schweißen mit Laserschweißrobotern seien hohe Schweißgeschwindigkeiten sowie ein hoher Automatisierungsgrad möglich. Weitere Vorteile sind laut BMZ eine hohe Prozesssicherheit, eine gute Verbindungsqualität sowie die Maßgenauigkeiten und schlanke Schweißnahten. Zudem arbeitet der Hersteller eng mit der Batteryuniversity zusammen, um alle Sicherheitsanforderungen und Zulassungen für den weltweiten Versand zu ermöglichen. (N. Petersen)
BMZ bündelt Kompetenzen für Batterieforschung
22.08.2017 11:01 -
Ab September 2017 startet im Hauptquartier der BMZ Group das E-Volution Center. In Karlstein am Main bei Aschaffenburg werden über 150 Entwickler demnach die Energiespeicher der Zukunft entwickeln. Denn Lithiumakkus werden immer kleiner, leichter und besser.
Im E-Volution Center werden laut BMZ jährlich rund 200 neue Batteriesysteme für Autos, Fahrräder, Gartengeräte, Medizinprodukte und weitere Anwendungen entwickelt. „Die Batteriesysteme werden immer kleiner und leichter und dies mit längeren Laufzeiten, einem besseren Temperaturbereich und sie können schneller geladen werden - um nur einige Innovationen zu nennen“, erklärt Sven Bauer, Geschäftsführer und Gründer der BMZ Group. BMZ sei durch diese Innovationen der größte Hersteller von Systemlösungen in Europa geworden und wachse jedes Jahr um 30 bis 50 Prozent.
Produktion mit Schweißrobotern
Die Mitarbeiter des Centers entwickeln demnach alle Komponenten einer Lithium-Ionen Batterie: vom Konzept bis zur Serienfertigung. Neben Batteriezellen-Experten arbeiten Konstrukteure, Hard- und Softwareentwickler, Testingenieure und Prototypentechniker sowie Spezialisten für Schweißtechnik. Thermomanagement, Ladetechnik und viele weitere innovative Themen. Auch um das Thema Recycling und die Wiederverwendung (second life) von Batterien. Technischer Leiter des Centers wird Dirk Oestreich.
Durch das Schweißen mit Laserschweißrobotern seien hohe Schweißgeschwindigkeiten sowie ein hoher Automatisierungsgrad möglich. Weitere Vorteile sind laut BMZ eine hohe Prozesssicherheit, eine gute Verbindungsqualität sowie die Maßgenauigkeiten und schlanke Schweißnahten. Zudem arbeitet der Hersteller eng mit der Batteryuniversity zusammen, um alle Sicherheitsanforderungen und Zulassungen für den weltweiten Versand zu ermöglichen. (N. Petersen)
aus einem GMO-Paper vergangenen Woche:
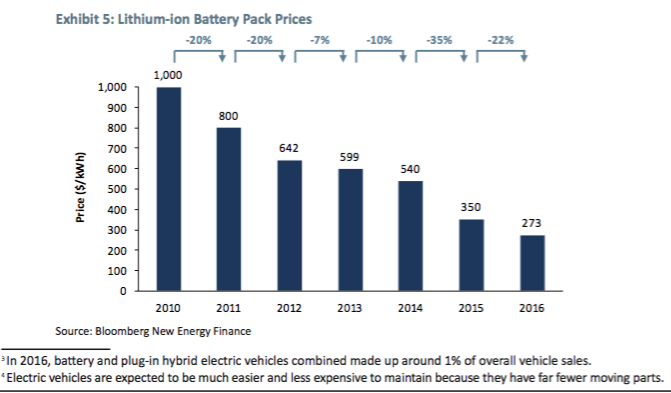
Li-Ion start-up mit SpaceX, Tesla, Apple, Amazon und Samsung Veteranen...
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/former-spacex-battery-e…California-based Romeo Power is currently building a 113,000 square-foot, fully automated manufacturing facility, scheduled to be completed by the end of this year. Once opened, it should produce 1GWh of battery capacity on a single shift, reaching 4GWh capacity per shift during 2018.
...
Claiming that partly due to lessons learned from aerospace, Harris’ team has been able to make some breakthroughs, Romeo Power says that energy density in its batteries can be 25% higher than competing lithium-ion providers, has thermal performance good enough to improve (reduce) charging times by anywhere from 15% to 30% and have inbuilt protection against thermal runaway, which can cause batteries to catch fire, and is also well-protected against cross cell propagation.
wasset nich alles jibt: http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/2017/08/why-ene… 


Auszug:
"Grid operators and traders thought they were totally prepped for the historic U.S. solar eclipse. There was just this one thing they didn’t completely factor in: “irregular human-behavior patterns.”
That’s the technical definition, from the folks who manage the electricity network at the Southwest Power Pool, for the conduct of millions of Americans who were outdoors ogling the moon shadowing the sun instead of cranking up the A/C in homes and offices.
Demand, of course, tends to rise heading into the hottest part of a summer day. On Monday, it developed a weird U-shaped dip over a two-hour period across the country."



Auszug:
"Grid operators and traders thought they were totally prepped for the historic U.S. solar eclipse. There was just this one thing they didn’t completely factor in: “irregular human-behavior patterns.”
That’s the technical definition, from the folks who manage the electricity network at the Southwest Power Pool, for the conduct of millions of Americans who were outdoors ogling the moon shadowing the sun instead of cranking up the A/C in homes and offices.
Demand, of course, tends to rise heading into the hottest part of a summer day. On Monday, it developed a weird U-shaped dip over a two-hour period across the country."
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/flow-batteries-leading-…
"Of the 13 leading companies selected for a close look, the vast majority are flow batteries, sometimes also called flow machines. In fact, of the top 10-ranked of those companies, six are producing variations on redox flow battery energy storage.
Two companies among these non-lithium energy storage vendors have emerged as clear leaders, according to Navigant’s research and methodology. Japan’s Sumitomo Electric, which in 2013 installed a 60MWh flow battery in northern Japan and US company Vizn Energy, which recently claimed it could pair energy storage with solar and wind for US$0.04 per kilowatt-hour.
Other notable inclusions range from Eos Energy Storage (zinc hybrid cathode batteries), NGK Insulators (sodium-sulfur NaS batteries), FIAMM (molten salt) and Fluidic Energy (metal-air batteries)."
"Of the 13 leading companies selected for a close look, the vast majority are flow batteries, sometimes also called flow machines. In fact, of the top 10-ranked of those companies, six are producing variations on redox flow battery energy storage.
Two companies among these non-lithium energy storage vendors have emerged as clear leaders, according to Navigant’s research and methodology. Japan’s Sumitomo Electric, which in 2013 installed a 60MWh flow battery in northern Japan and US company Vizn Energy, which recently claimed it could pair energy storage with solar and wind for US$0.04 per kilowatt-hour.
Other notable inclusions range from Eos Energy Storage (zinc hybrid cathode batteries), NGK Insulators (sodium-sulfur NaS batteries), FIAMM (molten salt) and Fluidic Energy (metal-air batteries)."
Ich glaube, am meisten hätte St. Elon the Liar verdient,
wenn er sich den Begriff "Gigafactory" hätte schützen lassen:TerraE formt Konsortium für Gigafactory: https://www.terrae.com/2017/07/26/terrae-formt-konsortium-fu…
Northvolt is going to build Europe’s largest and most advanced lithium-ion battery factory in Sweden. http://northvolt.com/news#/news/abb-and-northvolt-partner-fo…
Lithium-Schwefelbatterien versprechen hohe Energiedichte
28.09.2017
https://www.photovoltaik.eu/Archiv/Meldungsarchiv/article-78…
Das von der Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft geförderte Verbundprojekt Liscell hat drei Jahre lang die innovative Lithium-Schwefel-Technologie untersucht. Ergebnis: Mit geringen Materialkosten und hoher Energiedichte könnte ein attraktiver Stromspeicher für Mobilität entstehen.
Ein effizienter Stromspeicher ist der Flaschenhals für alle mobilen elektronischen Anwendungen. Gewicht und Kosten pro Kilowattstunde Speicherkapazität der Batterie begrenzen den Einsatz der Akkus. Eine Lösung dafür können neuartige Lithium-Schwefel-Batterien sein. Laut den Forschern sind Energiedichten von bis zu 500 Wattstunden pro Kilogramm erwartet werden. Gleichzeitig wird bei dieser Technologie das teure Kathodenmaterial der Lithium-Ionen-Zellen durch kostengünstigen, ungiftigen und nahezu unbegrenzt verfügbaren Schwefel abgelöst.
Lithium-Schwefel-Zellen erreichen zwar bereits heute bis zu 40 Prozent höhere Energiedichten als die besten Lithium-Ionen-Zellen. Allerdings können sie nur 50 bis 100 Mal wiederaufgeladen werden. Grund dafür sind Zersetzungsreaktionen des Elektrolyten an der Anoden-Oberfläche, die aus metallischem Lithium besteht. An der Weiterentwicklung der Lithium-Schwefel-Batteriezellen auf der Basis neuer Kathoden, Elektrolyten und Anoden wurde im Rahmen des Verbundprojektes Liscell in den letzten drei Jahren geforscht.
Die drei Fraunhofer-Institute ICT, FEP und IVI beschäftigten sich neben der Materialentwicklung auch mit skalierbaren Herstellungsverfahren für Anoden und Kathoden als Rollenware und dem Aufbau von Batteriemodulen. Dabei wurde die Möglichkeit Batterien wieder aufzuladen, um ein Vielfaches erhöht und die Herstellungskosten durch das günstige Rolle-zu-Rolle-Fertigungsverfahren gesenkt. Damit sei ein weiterer Schritt für den Einsatz dieser Energiespeicher in der Elektromobilität getan, erklären die Fraunhofer-Wissenschaftler. (nhp)
28.09.2017
https://www.photovoltaik.eu/Archiv/Meldungsarchiv/article-78…
Das von der Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft geförderte Verbundprojekt Liscell hat drei Jahre lang die innovative Lithium-Schwefel-Technologie untersucht. Ergebnis: Mit geringen Materialkosten und hoher Energiedichte könnte ein attraktiver Stromspeicher für Mobilität entstehen.
Ein effizienter Stromspeicher ist der Flaschenhals für alle mobilen elektronischen Anwendungen. Gewicht und Kosten pro Kilowattstunde Speicherkapazität der Batterie begrenzen den Einsatz der Akkus. Eine Lösung dafür können neuartige Lithium-Schwefel-Batterien sein. Laut den Forschern sind Energiedichten von bis zu 500 Wattstunden pro Kilogramm erwartet werden. Gleichzeitig wird bei dieser Technologie das teure Kathodenmaterial der Lithium-Ionen-Zellen durch kostengünstigen, ungiftigen und nahezu unbegrenzt verfügbaren Schwefel abgelöst.
Lithium-Schwefel-Zellen erreichen zwar bereits heute bis zu 40 Prozent höhere Energiedichten als die besten Lithium-Ionen-Zellen. Allerdings können sie nur 50 bis 100 Mal wiederaufgeladen werden. Grund dafür sind Zersetzungsreaktionen des Elektrolyten an der Anoden-Oberfläche, die aus metallischem Lithium besteht. An der Weiterentwicklung der Lithium-Schwefel-Batteriezellen auf der Basis neuer Kathoden, Elektrolyten und Anoden wurde im Rahmen des Verbundprojektes Liscell in den letzten drei Jahren geforscht.
Die drei Fraunhofer-Institute ICT, FEP und IVI beschäftigten sich neben der Materialentwicklung auch mit skalierbaren Herstellungsverfahren für Anoden und Kathoden als Rollenware und dem Aufbau von Batteriemodulen. Dabei wurde die Möglichkeit Batterien wieder aufzuladen, um ein Vielfaches erhöht und die Herstellungskosten durch das günstige Rolle-zu-Rolle-Fertigungsverfahren gesenkt. Damit sei ein weiterer Schritt für den Einsatz dieser Energiespeicher in der Elektromobilität getan, erklären die Fraunhofer-Wissenschaftler. (nhp)
‘Flow machine’ maker redT supplies vanadium-lithium hybrid energy storage system in Australia
Published: 4 Oct 2017, 11:27, By: Andy Colthorpe
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/flow-machine-maker-redt…
Four months after its CEO declared to Energy-Storage.News that hybrid vanadium redox flow-lithium systems would be the “optimal” way to deliver multiple applications for energy storage, redT has delivered equipment to its first such project.
UK-headquartered redT, which makes energy storage systems based on the redox flow technology said yesterday that it has sold a 300kW / 1MWh “hybrid” energy storage system to Melbourne’s Monash University in Australia. The company said this marks two firsts: the delivery of Australia’s first flow-lithium hybrid system and redT’s first deal in the country.
CEO Scott McGregor, who has famously banned employees from defining the systems as “batteries”, instead calling them “flow machines”, said in a June interview that combining the “workhorse” properties of vanadium systems with the more high power capabilities of lithium could deliver the “the lowest cost, highest function out of the two technologies”.
The system at Monash uses 900kWh of redT energy storage, combined with a 120kW C-1 rated lithium battery, to be installed at a biomedical research and learning facility at the university. It will be paired to on-site PV generation and will help maximise the use of renewables, reducing energy costs in a country where abundant sunshine, high electricity costs and isolated grid networks have created a sort of perfect storm of market conditions for PV and latterly for energy storage.
It is hoped the hybrid system will generate both revenues and savings for the university, with plans to offer its capabilities into markets for merchant and contracted grid services in future. It is being integrated into a university-wide microgrid project, which is being deployed in partnership with Monash Energy Materials and Systems Institute (MEMSI). Under that project, the reliability and stability of the local grid is being boosted by the integration of renewables and there is also intent to create a peer-to-peer energy trading network using the microgrid.
“Why you would look at hybrid is if you think of the flow machine as your workhorse, it’ll do 60%-80% of the work, it’s really boring, just sit there pumping energy and liquid all the way round many times a day, it will never degrade and you want to utilise that as much as you can,” McGregor had said earlier in the year in explaining the appeal and potential strengths of the hybrid concept.
“Whereas you will get small little peaks during the day. If you actually service them through a power technology, it could be lithium, gel lead acid or a supercapacitor maybe, depending on what your power need is. If you only have short spurts during the day, you’re better off using a power technology for that and using your flow to do the PV and shifting and peaking and your reserve and everything else.”
Speaking about the Monash project yesterday, McGregor said redT believed “hybrid energy storage solutions such as this are a major development for the energy market as a whole and we are pleased to be at the forefront of this, launching this important project in Australia, one of the fastest growing energy storage markets globally.”
US research firm Navigant put out a report this summer which predicted that by 2026, there could be 2.1GW of hybrid energy storage systems deployed worldwide using various configurations and combinations of technologies.
Monash University programme director Tony Fullelove said the hybrid system and microgrid would be useful in investigating how Australia could deal with its ongoing energy ‘trilemma’ of “providing sustainable power whilst keeping costs low and maintaining energy security".
“The hybrid solution offered by redT is particularly exciting as Monash will be using the energy component (flow machine) to shape the building load profile to minimise costs on a daily basis, whilst using the power component (lithium) to assist with the connection of the building to a highly intermittent and sustainable embedded generation network,” Fullelove said.
In late September, redT sent 14 units of its 40kWh vanadium flow machines to Botswana, to be deployed alongside rooftop PV installations, each of 11kWp capacity. RedT called Sub-Saharan Africa a "key growth market for the company".
Published: 4 Oct 2017, 11:27, By: Andy Colthorpe
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/flow-machine-maker-redt…
Four months after its CEO declared to Energy-Storage.News that hybrid vanadium redox flow-lithium systems would be the “optimal” way to deliver multiple applications for energy storage, redT has delivered equipment to its first such project.
UK-headquartered redT, which makes energy storage systems based on the redox flow technology said yesterday that it has sold a 300kW / 1MWh “hybrid” energy storage system to Melbourne’s Monash University in Australia. The company said this marks two firsts: the delivery of Australia’s first flow-lithium hybrid system and redT’s first deal in the country.
CEO Scott McGregor, who has famously banned employees from defining the systems as “batteries”, instead calling them “flow machines”, said in a June interview that combining the “workhorse” properties of vanadium systems with the more high power capabilities of lithium could deliver the “the lowest cost, highest function out of the two technologies”.
The system at Monash uses 900kWh of redT energy storage, combined with a 120kW C-1 rated lithium battery, to be installed at a biomedical research and learning facility at the university. It will be paired to on-site PV generation and will help maximise the use of renewables, reducing energy costs in a country where abundant sunshine, high electricity costs and isolated grid networks have created a sort of perfect storm of market conditions for PV and latterly for energy storage.
It is hoped the hybrid system will generate both revenues and savings for the university, with plans to offer its capabilities into markets for merchant and contracted grid services in future. It is being integrated into a university-wide microgrid project, which is being deployed in partnership with Monash Energy Materials and Systems Institute (MEMSI). Under that project, the reliability and stability of the local grid is being boosted by the integration of renewables and there is also intent to create a peer-to-peer energy trading network using the microgrid.
“Why you would look at hybrid is if you think of the flow machine as your workhorse, it’ll do 60%-80% of the work, it’s really boring, just sit there pumping energy and liquid all the way round many times a day, it will never degrade and you want to utilise that as much as you can,” McGregor had said earlier in the year in explaining the appeal and potential strengths of the hybrid concept.
“Whereas you will get small little peaks during the day. If you actually service them through a power technology, it could be lithium, gel lead acid or a supercapacitor maybe, depending on what your power need is. If you only have short spurts during the day, you’re better off using a power technology for that and using your flow to do the PV and shifting and peaking and your reserve and everything else.”
Speaking about the Monash project yesterday, McGregor said redT believed “hybrid energy storage solutions such as this are a major development for the energy market as a whole and we are pleased to be at the forefront of this, launching this important project in Australia, one of the fastest growing energy storage markets globally.”
US research firm Navigant put out a report this summer which predicted that by 2026, there could be 2.1GW of hybrid energy storage systems deployed worldwide using various configurations and combinations of technologies.
Monash University programme director Tony Fullelove said the hybrid system and microgrid would be useful in investigating how Australia could deal with its ongoing energy ‘trilemma’ of “providing sustainable power whilst keeping costs low and maintaining energy security".
“The hybrid solution offered by redT is particularly exciting as Monash will be using the energy component (flow machine) to shape the building load profile to minimise costs on a daily basis, whilst using the power component (lithium) to assist with the connection of the building to a highly intermittent and sustainable embedded generation network,” Fullelove said.
In late September, redT sent 14 units of its 40kWh vanadium flow machines to Botswana, to be deployed alongside rooftop PV installations, each of 11kWp capacity. RedT called Sub-Saharan Africa a "key growth market for the company".
MIT entwickelt ein:
...new design is a rechargeable flow battery, meaning its cathode and anode components are liquids (catholyte and anolyte) that pass ions back and forth to store or release energy. In this case, the anolyte is made up of sulfur dissolved in water, and the hunt for an equally abundant material for the catholyte led the team to an oxygenated liquid salt solution.
"We went on a search for a positive electrode that would also have exceptionally low cost that we could use with sulfur as the negative electrode," says Yet-Ming Chiang, co-author of the study. "Through an accidental laboratory discovery, we figured out that it could actually be oxygen, and therefore air. We needed to add one other component, which was a charge carrier to go back and forth between the sulfur and air electrode, and that turned out to be sodium."
The clever part of the battery is the fact that the catholyte "breathes" in air in from outside while discharging, and exhales while recharging. By this mechanism, the battery creates negatively-charged hydroxide ions in the catholyte while inhaling, and while recharging that oxygen is released, creating hydrogen ions which then send electrons back into the anolyte.
"This battery literally inhales and exhales air, but it doesn't exhale carbon dioxide, like humans — it exhales oxygen," says Chiang. "What this does is create a charge balance by taking oxygen in and out of the system."
Lithium-air batteries use the same mechanism, but sulfur, water and salt are far cheaper materials, and cost-cutting is key to scaling up energy storage systems for use with the grid. The researchers say their battery would cost far less to make and run than lithium-ion batteries, while retaining almost the same energy density. Once in use, they estimate a scaled-up version of their flow battery would cost between US$20 and $30 per kWh stored to run, compared to about $100 per kWh for other storage systems.
http://www.cell.com/joule/fulltext/S2542-4351(17)30032-6
...new design is a rechargeable flow battery, meaning its cathode and anode components are liquids (catholyte and anolyte) that pass ions back and forth to store or release energy. In this case, the anolyte is made up of sulfur dissolved in water, and the hunt for an equally abundant material for the catholyte led the team to an oxygenated liquid salt solution.
"We went on a search for a positive electrode that would also have exceptionally low cost that we could use with sulfur as the negative electrode," says Yet-Ming Chiang, co-author of the study. "Through an accidental laboratory discovery, we figured out that it could actually be oxygen, and therefore air. We needed to add one other component, which was a charge carrier to go back and forth between the sulfur and air electrode, and that turned out to be sodium."
The clever part of the battery is the fact that the catholyte "breathes" in air in from outside while discharging, and exhales while recharging. By this mechanism, the battery creates negatively-charged hydroxide ions in the catholyte while inhaling, and while recharging that oxygen is released, creating hydrogen ions which then send electrons back into the anolyte.
"This battery literally inhales and exhales air, but it doesn't exhale carbon dioxide, like humans — it exhales oxygen," says Chiang. "What this does is create a charge balance by taking oxygen in and out of the system."
Lithium-air batteries use the same mechanism, but sulfur, water and salt are far cheaper materials, and cost-cutting is key to scaling up energy storage systems for use with the grid. The researchers say their battery would cost far less to make and run than lithium-ion batteries, while retaining almost the same energy density. Once in use, they estimate a scaled-up version of their flow battery would cost between US$20 and $30 per kWh stored to run, compared to about $100 per kWh for other storage systems.
http://www.cell.com/joule/fulltext/S2542-4351(17)30032-6
Windturbinen mit Pumpspeicher
https://www.euwid-energie.de/max-boegl-wind-nimmt-windrad-mi…Auszug:
"Erstmals wird die Produktion von Strom aus erneuerbaren Energien mit einem modernen Pumpspeicherkraftwerk kombiniert. Das neue Speicherkonzept nutzt die Turmfundamente der Windanlagen als Wasserspeicher. So werden zusätzliche 40 Meter Höhe gewonnen. Das ist lukrativ, denn mit jedem Meter Nabenhöhe, den eine Windenergieanlage gewinnt, steigt der jährliche Stromertrag um 0,5 bis 1 Prozent. Weniger Windturbulenzen und eine deutlich bessere Windausbeute sprechen für hohe Nabenhöhen, gerade an windschwächeren Binnenlandstandorten."
China scheint Flow-Batterien zu pushen:
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/chinese-governments-str… diverse News von flow-battery Playern
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/flood-of-announcements-… neue Li-Ion Fabriken in:
L.A. (4 GWh, Romeo Power) und Langen (0,6 GWh, Akasol)
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/lithium-battery-factori…
ESS (Iron-Flow) erhält 13 MUSD B-Runde: https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/money-flows-to-…
"The money will go to automate and expand the manufacturing facilities where the Oregon company makes its containerized long-duration storage product, the Energy Warehouse. If all goes according to plan, the improvements will raise the six-year-old company's annual output to 900 megawatt-hours."
"The money will go to automate and expand the manufacturing facilities where the Oregon company makes its containerized long-duration storage product, the Energy Warehouse. If all goes according to plan, the improvements will raise the six-year-old company's annual output to 900 megawatt-hours."
for perspective:
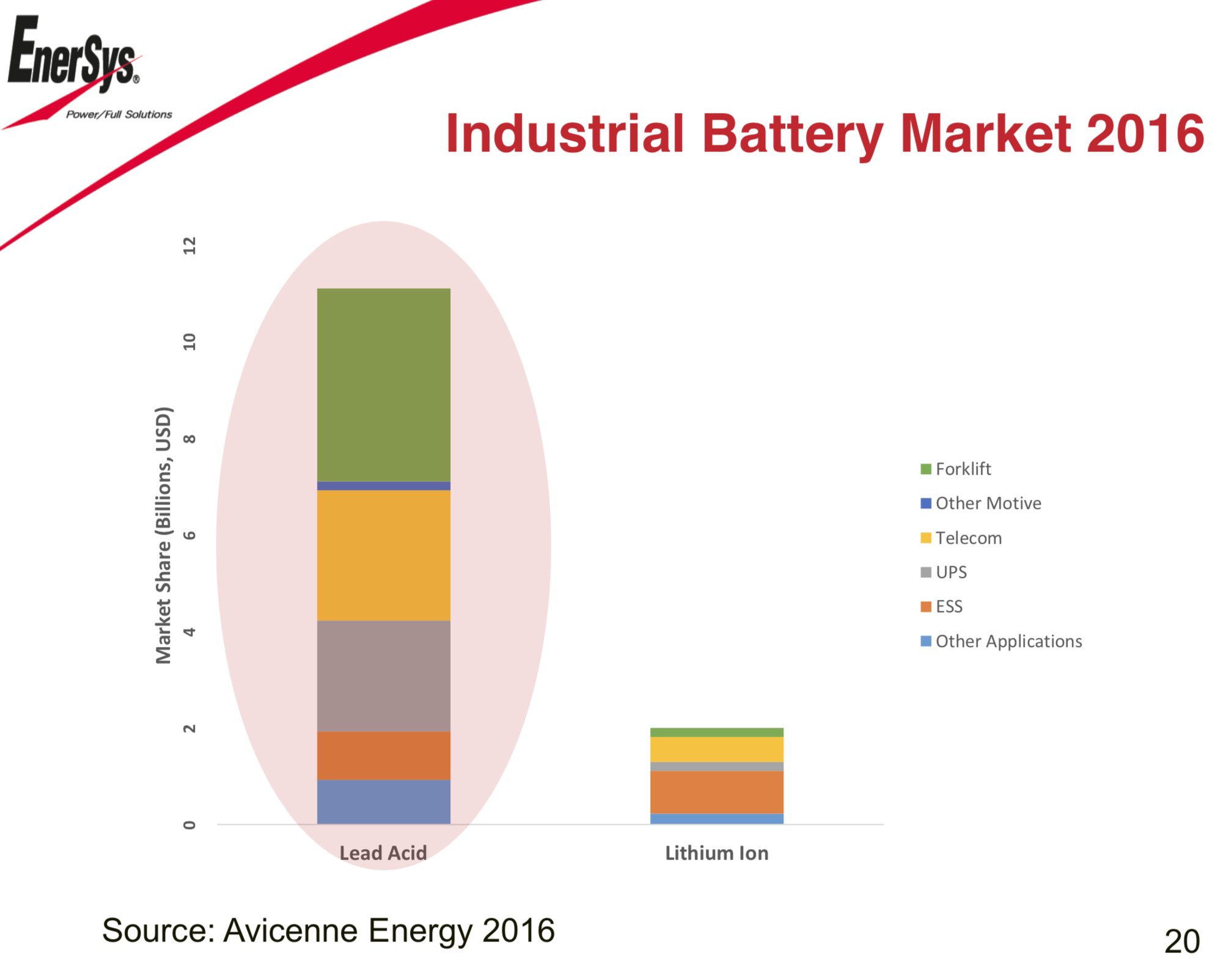
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 52.296.139 von R-BgO am 28.04.16 10:24:43Lockheed Martin eyes solar partners for new flow battery
By John Parnell Jan 16, 2018
Lockheed Martin Energy is looking for development and manufacturing partners in the solar industry as it readies its long-duration flow battery at the end of the year.
The company has an established lithium-ion business but will add a flow battery to its line-up after several years of development.
“We’re in this market already with Li-ion, we know what investors expect so we’re fully prepared to offer long-term warranties, long-term performance guarantees, you have to,” said John Battaglini director of business development for Lockheed Martin Energy. “We know the requirements, the company has made a sizeable investment and we’re committed to this technology.”
Unlike many venture capital-backed start-ups in the flow battery sector, Lockheed Martin is also extremely bankable as a company with 97,000 employees and a market capitalisation of almost US$100 billion.
“The four primary applications we see for long-duration energy storage are wind and solar shifting, T&D deferral and microgrids,” said Battaglini. “As more renewables come online the first two will only increase. We’re targeting wind and solar developers directly but we also want to talk to solar and wind manufacturers, we’re seeing a lot more hybrid systems coming into the market. Not just sharing and interconnect but an integrated system. When you look at these four applications, there is clearly a lot of demand for long-duration storage in the next 5-10 years.”
“We acquired [MIT spin-out] Sun Catalytix in 2014 and we have been investing in that product for four years now. We have prototypes up and running at our Massachusetts facility and we are targeting a commercial launch of the product in late 2018,” Battaglini said on the sidelines of the World Future Energy Summit (WFES) in Abu Dhabi.
Battaglini claimed its flow systems will be price competitive “right out of the gate” and expects that cost to continue to fall. But upfront costs alone don’t offer a fair comparison of storage technologies he warns.
“We’ve done a lot of education with customers about lifetime cost, not just looking at upfront cost. You have to take a 20-30 year view when comparing lithium and flow. Lithium batteries need replaced perhaps every seven years so you need to make sure you are comparing apples to apples,” he said.
By John Parnell Jan 16, 2018
Lockheed Martin Energy is looking for development and manufacturing partners in the solar industry as it readies its long-duration flow battery at the end of the year.
The company has an established lithium-ion business but will add a flow battery to its line-up after several years of development.
“We’re in this market already with Li-ion, we know what investors expect so we’re fully prepared to offer long-term warranties, long-term performance guarantees, you have to,” said John Battaglini director of business development for Lockheed Martin Energy. “We know the requirements, the company has made a sizeable investment and we’re committed to this technology.”
Unlike many venture capital-backed start-ups in the flow battery sector, Lockheed Martin is also extremely bankable as a company with 97,000 employees and a market capitalisation of almost US$100 billion.
“The four primary applications we see for long-duration energy storage are wind and solar shifting, T&D deferral and microgrids,” said Battaglini. “As more renewables come online the first two will only increase. We’re targeting wind and solar developers directly but we also want to talk to solar and wind manufacturers, we’re seeing a lot more hybrid systems coming into the market. Not just sharing and interconnect but an integrated system. When you look at these four applications, there is clearly a lot of demand for long-duration storage in the next 5-10 years.”
“We acquired [MIT spin-out] Sun Catalytix in 2014 and we have been investing in that product for four years now. We have prototypes up and running at our Massachusetts facility and we are targeting a commercial launch of the product in late 2018,” Battaglini said on the sidelines of the World Future Energy Summit (WFES) in Abu Dhabi.
Battaglini claimed its flow systems will be price competitive “right out of the gate” and expects that cost to continue to fall. But upfront costs alone don’t offer a fair comparison of storage technologies he warns.
“We’ve done a lot of education with customers about lifetime cost, not just looking at upfront cost. You have to take a 20-30 year view when comparing lithium and flow. Lithium batteries need replaced perhaps every seven years so you need to make sure you are comparing apples to apples,” he said.
Stem (Li-Ion-Systeme) sammelt 80 MUSD ein: https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/stem-lands-80-m…
Belectric baut Großspeicher für Primärregelenergie
7.02.2018 10:56 -
Der fränkische Systemintegrator hat im Auftrag von RWE einen Großspeicher installiert, der sieben Megawattstunden elektrische Energie aus dem Stromnetz aufnehmen kann. Verbaut wurden 550 Lithiumbatterien für Fahrzeuge. Die Kapazität entspricht rund 700.000 Smartphones.
RWE Generation hat auf dem Gelände ihres Pumpspeicherkraftwerks am Hengsteysee in Herdecke einen Batteriespeicher mit einer elektrischen Speichermenge von sieben Megawattstunden in Betrieb genommen.
Sechs Millionen Euro für sieben Megawattstunden
Die Investition für die neue Anlage belief sich auf rund sechs Millionen Euro. „Der neue Batteriespeicher hilft, die schwankende Einspeisung aus Solar- und Windkraftanlagen auszugleichen und stabilisiert das Netz“, sagt Roger Miesen, Vorstandsvorsitzender von RWE Generation. „Die Anlage ist unser erstes Referenzprojekt im Markt für Batteriespeicher. Wir sehen im Betrieb und der Vermarktung von Speichern sowie Batterien großes Potenzial.“
Errichtet wurde die Anlage von der Firma Belectric aus Kolitzheim bei Würzburg. Frank Amend, in der Geschäftsführung von Belectric für Speicher und Hybridsysteme zuständig, erklärt: „Speichertechnologien sind das Bindeglied zwischen modernen Netzen und einer volatilen Erzeugung aus erneuerbaren Energien.“ Insgesamt besteht der Batteriespeicher aus drei gleichen Systemen. Jedes System besteht aus einem Übersee-Container, einem Umrichter und einem Transformator.
Anschluss in der Mittelspannung
Die Transformatoren sind über eine Mittelspannungsschaltanlage an das Netz angeschlossen. Das Herz des Batteriespeichers sind 552 Batteriemodule mit je 100 Lithium-Ionen-Zellen aus dem Automotive-Bereich. Der Batteriespeicher kann rund sieben Megawattstunden speichern und etwa eine Stunde lang wieder ins Netz abgeben.
Die Refinanzierung erfolgt im Markt für Primärregelleistung. Der Großspeicher reagiert auf Frequenzveränderungen im Stromnetz und speichert bei Bedarf Strom ein oder speist ihn wieder ins Netz. Die verfügbare Leistung des Batteriespeichers ist beim Übertragungsnetz-betreiber Amprion gemeldet und wird von der RWE Supply & Trading von Essen aus vermarktet. (HS)
7.02.2018 10:56 -
Der fränkische Systemintegrator hat im Auftrag von RWE einen Großspeicher installiert, der sieben Megawattstunden elektrische Energie aus dem Stromnetz aufnehmen kann. Verbaut wurden 550 Lithiumbatterien für Fahrzeuge. Die Kapazität entspricht rund 700.000 Smartphones.
RWE Generation hat auf dem Gelände ihres Pumpspeicherkraftwerks am Hengsteysee in Herdecke einen Batteriespeicher mit einer elektrischen Speichermenge von sieben Megawattstunden in Betrieb genommen.
Sechs Millionen Euro für sieben Megawattstunden
Die Investition für die neue Anlage belief sich auf rund sechs Millionen Euro. „Der neue Batteriespeicher hilft, die schwankende Einspeisung aus Solar- und Windkraftanlagen auszugleichen und stabilisiert das Netz“, sagt Roger Miesen, Vorstandsvorsitzender von RWE Generation. „Die Anlage ist unser erstes Referenzprojekt im Markt für Batteriespeicher. Wir sehen im Betrieb und der Vermarktung von Speichern sowie Batterien großes Potenzial.“
Errichtet wurde die Anlage von der Firma Belectric aus Kolitzheim bei Würzburg. Frank Amend, in der Geschäftsführung von Belectric für Speicher und Hybridsysteme zuständig, erklärt: „Speichertechnologien sind das Bindeglied zwischen modernen Netzen und einer volatilen Erzeugung aus erneuerbaren Energien.“ Insgesamt besteht der Batteriespeicher aus drei gleichen Systemen. Jedes System besteht aus einem Übersee-Container, einem Umrichter und einem Transformator.
Anschluss in der Mittelspannung
Die Transformatoren sind über eine Mittelspannungsschaltanlage an das Netz angeschlossen. Das Herz des Batteriespeichers sind 552 Batteriemodule mit je 100 Lithium-Ionen-Zellen aus dem Automotive-Bereich. Der Batteriespeicher kann rund sieben Megawattstunden speichern und etwa eine Stunde lang wieder ins Netz abgeben.
Die Refinanzierung erfolgt im Markt für Primärregelleistung. Der Großspeicher reagiert auf Frequenzveränderungen im Stromnetz und speichert bei Bedarf Strom ein oder speist ihn wieder ins Netz. Die verfügbare Leistung des Batteriespeichers ist beim Übertragungsnetz-betreiber Amprion gemeldet und wird von der RWE Supply & Trading von Essen aus vermarktet. (HS)
so langsam wird es interessant:
Mix of Solar and Batteries Is Beating Natural Gas
February 13, 2018
By Chris Martin and Mark Chediak, Bloomberg
http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/2018/02/mix-of-…
Natural gas is getting edged out of power markets across the U.S. by two energy sources that, together, are proving to be an unbeatable mix: solar and batteries.
In just the latest example, First Solar Inc. won a power contract to supply Arizona’s biggest utility when electricity demand on its system typically peaks, between 3 p.m. and 8 p.m. The panel maker beat out bids from even power plants burning cheap gas by proposing to build a 65-MW solar farm that will, in turn, feed a 50-MW battery system. [MWh rating was not released.]
It’s a powerful combination for meeting peak demand because of when the sun shines. Here’s how it’ll work: The panels will generate solar power when the sun’s out to charge the batteries. The utility will draw on those batteries as the sun starts to set and demand starts to rise.
Just last week, NextEra Energy Inc.’s Florida utility similarly installed a battery system that’ll back up a solar farm and boost generation. In California, regulators have called on PG&E Corp. to use batteries or other non-fossil fuel resources instead of supplies from gas-fired plants to meet peak demand.
And batteries may be about to get even more competitive. Federal Energy Regulatory Commission Chairman Kevin McIntyre said he expects the agency to decide Thursday on a proposed rule that could remove barriers to energy storage participating more in wholesale markets.
Arizona Public Service Co. spokeswoman Annie DeGraw said the bid the utility received from First Solar was “very competitive, and it had the added benefit of being clean.”
Mix of Solar and Batteries Is Beating Natural Gas
February 13, 2018
By Chris Martin and Mark Chediak, Bloomberg
http://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/2018/02/mix-of-…
Natural gas is getting edged out of power markets across the U.S. by two energy sources that, together, are proving to be an unbeatable mix: solar and batteries.
In just the latest example, First Solar Inc. won a power contract to supply Arizona’s biggest utility when electricity demand on its system typically peaks, between 3 p.m. and 8 p.m. The panel maker beat out bids from even power plants burning cheap gas by proposing to build a 65-MW solar farm that will, in turn, feed a 50-MW battery system. [MWh rating was not released.]
It’s a powerful combination for meeting peak demand because of when the sun shines. Here’s how it’ll work: The panels will generate solar power when the sun’s out to charge the batteries. The utility will draw on those batteries as the sun starts to set and demand starts to rise.
Just last week, NextEra Energy Inc.’s Florida utility similarly installed a battery system that’ll back up a solar farm and boost generation. In California, regulators have called on PG&E Corp. to use batteries or other non-fossil fuel resources instead of supplies from gas-fired plants to meet peak demand.
And batteries may be about to get even more competitive. Federal Energy Regulatory Commission Chairman Kevin McIntyre said he expects the agency to decide Thursday on a proposed rule that could remove barriers to energy storage participating more in wholesale markets.
Arizona Public Service Co. spokeswoman Annie DeGraw said the bid the utility received from First Solar was “very competitive, and it had the added benefit of being clean.”
Coole Quelle:
https://www.smard.de/blueprint/servlet/page/home/46
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 55.593.868 von R-BgO am 24.08.17 21:44:28Alevo-Assets leben weiter:
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/imperium3-new-y…
"A battery development consortium called Imperium3 New York (IM3NY) has fast-tracked plans for a gigafactory after picking up Alevo’s North Carolina factory machinery in auction.
Australian consortium member Magnis Resources, which is planning to launch three gigafactories worldwide, said IM3NY bought the assets, worth more than $200 million, for just $5 million. "
=> Thread: Magnis Resources
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/imperium3-new-y…
"A battery development consortium called Imperium3 New York (IM3NY) has fast-tracked plans for a gigafactory after picking up Alevo’s North Carolina factory machinery in auction.
Australian consortium member Magnis Resources, which is planning to launch three gigafactories worldwide, said IM3NY bought the assets, worth more than $200 million, for just $5 million. "
=> Thread: Magnis Resources
Navigant sieht aktuell LG Chem und Samsung SDI vorne:
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/lg-chem-samsung-sdi-at-…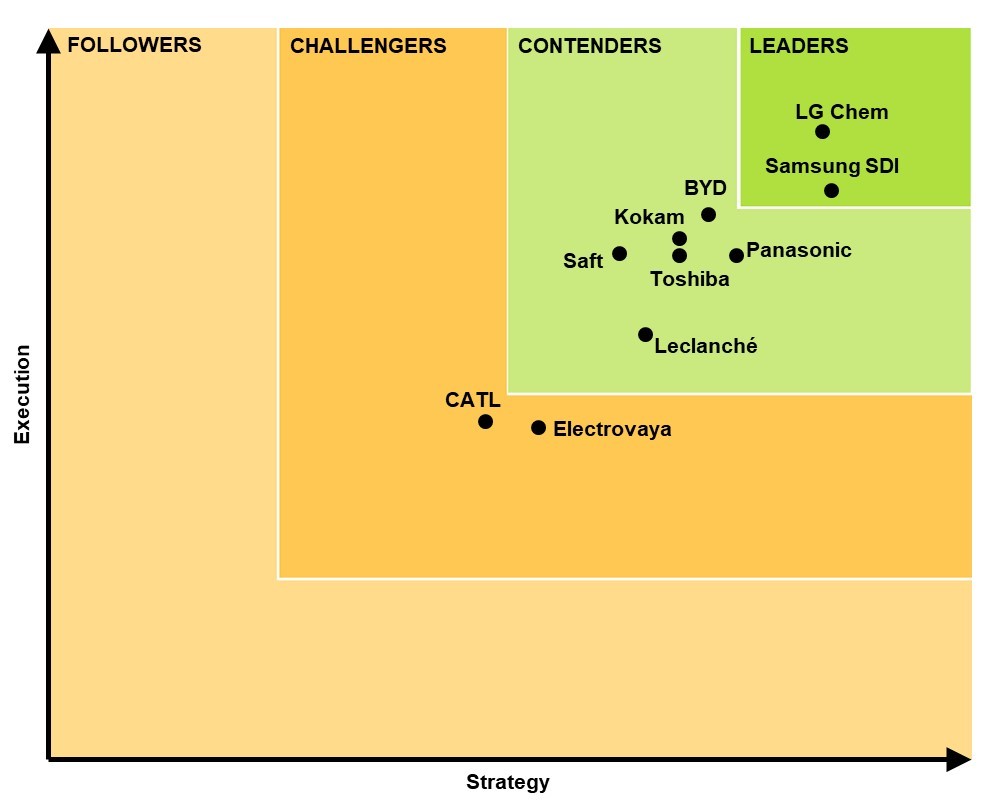
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 57.099.975 von R-BgO am 23.02.18 11:22:36
aufgemacht;
die sind groß
Habe für CATL mal einen eigenen
Thread: CATL - Contemporary Amperex Technology Ltd.aufgemacht;
die sind groß
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 57.099.975 von R-BgO am 23.02.18 11:22:36https://www.bloomberg.com/news/features/2018-02-01/the-break…
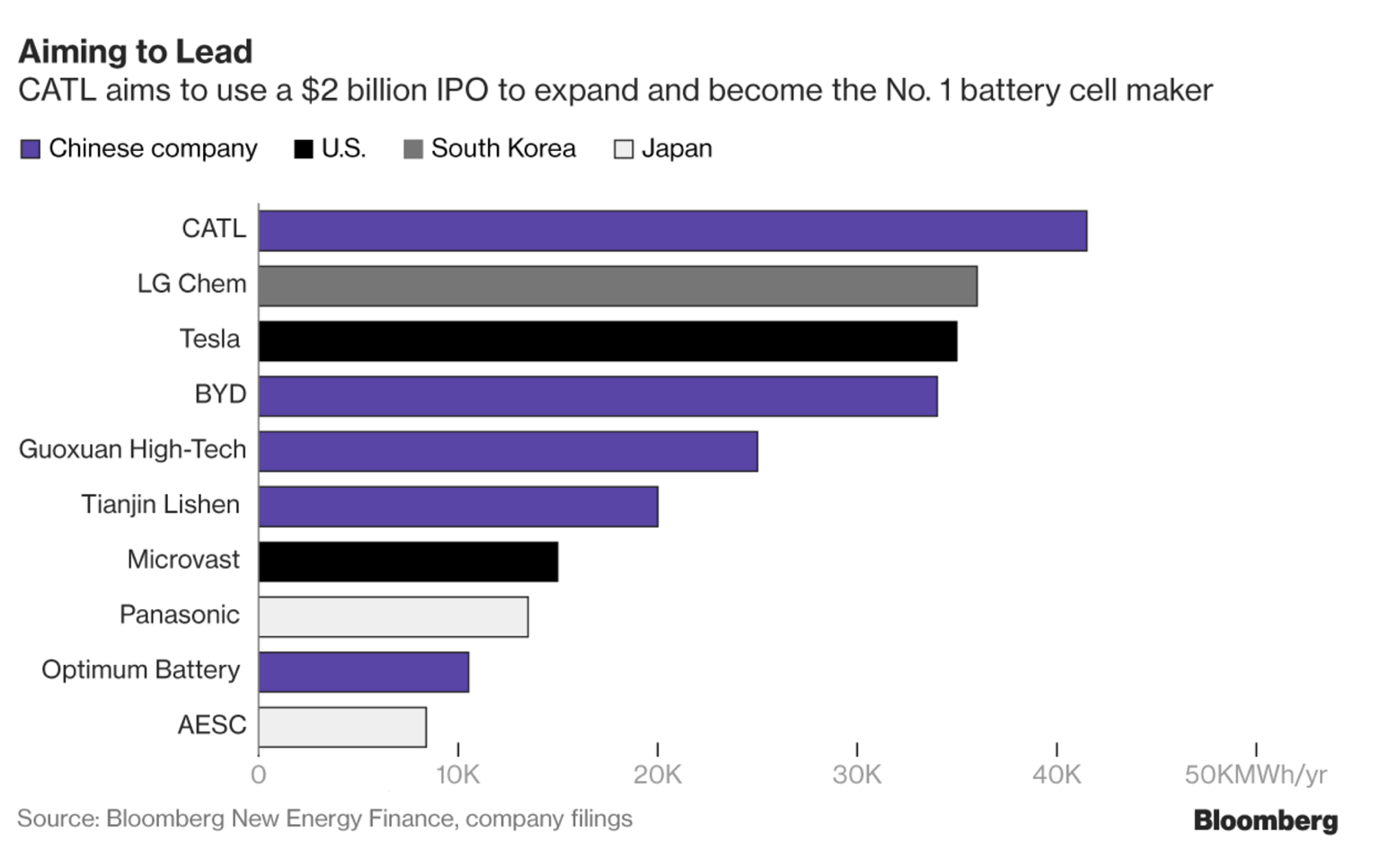

Buzzword-Alarm:
Stem liefert AI-gesteuerte Speicher: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20180227005432/en/INO…
Murata macht auch in Li-Ion : http://www.datacenterdynamics.com/content-tracks/power-cooli…
"Fortelion lithium-ion cells use a cathode composed of olivine-type iron phosphate, which the company says negates the risk of fire and ensures a lifespan of up to fifteen years. "
"Fortelion lithium-ion cells use a cathode composed of olivine-type iron phosphate, which the company says negates the risk of fire and ensures a lifespan of up to fifteen years. "
Highview Power bietet LAES (Liquid Air Energy Storage) System an: https://www.windpowerengineering.com/uncategorized/highview-…
"Highview Power’s proprietary LAES technology is based on the principle of air liquefaction, which enables the easy storage of gases in cryogenic liquid form. The process involves a 700-fold expansion in volume from liquid back to gas, which releases the stored energy, powering turbines and generating electricity. This enables Highview’s system to store energy in increments measured in days rather than hours, at half the cost of lithium-ion batteries, and while releasing zero emissions in the process. It utilizes long-proven technology with a system lifespan of over 30 years."
"Highview Power’s proprietary LAES technology is based on the principle of air liquefaction, which enables the easy storage of gases in cryogenic liquid form. The process involves a 700-fold expansion in volume from liquid back to gas, which releases the stored energy, powering turbines and generating electricity. This enables Highview’s system to store energy in increments measured in days rather than hours, at half the cost of lithium-ion batteries, and while releasing zero emissions in the process. It utilizes long-proven technology with a system lifespan of over 30 years."
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 57.102.774 von R-BgO am 23.02.18 15:20:25
"Dem weltweit größten Autozulieferer Bosch ist eine eigene Batteriezellfertigung zu teuer und zu riskant. Das Unternehmen habe sich nach reiflicher Überlegung gegen eine eigene Produktion entschieden, erklärte Bosch-Manager, Rolf Bulander. "Wir müssen die Zelle technisch verstehen, wir müssen sie nicht fertigen", begründete er die Entscheidung. Bosch werde auch ohne eigene Produktion in der Elektromobilität bis 2020 der führende Zulieferer sein. Die Zelle sei die einzige Komponente von Elektroauto-Systemen, die Bosch fehle und die weiterhin zugekauft werden könne. "Wir sagen Nein zur eigenen Zellfertigung, wir sagen aber Ja zur Batterie bei Bosch", sagte Bulander."
und Bosch steigt aus:
http://www.spiegel.de/wirtschaft/unternehmen/zu-teuer-bosch-…"Dem weltweit größten Autozulieferer Bosch ist eine eigene Batteriezellfertigung zu teuer und zu riskant. Das Unternehmen habe sich nach reiflicher Überlegung gegen eine eigene Produktion entschieden, erklärte Bosch-Manager, Rolf Bulander. "Wir müssen die Zelle technisch verstehen, wir müssen sie nicht fertigen", begründete er die Entscheidung. Bosch werde auch ohne eigene Produktion in der Elektromobilität bis 2020 der führende Zulieferer sein. Die Zelle sei die einzige Komponente von Elektroauto-Systemen, die Bosch fehle und die weiterhin zugekauft werden könne. "Wir sagen Nein zur eigenen Zellfertigung, wir sagen aber Ja zur Batterie bei Bosch", sagte Bulander."
Senec wird übernommen von Thread: EnBW - einer der groeßten deutschen Versorger
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 56.731.638 von R-BgO am 16.01.18 16:19:04Cypress Creek setzt Lockheed ein: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/cypress-creeks-first-so…
Vanadium-Flow:
TORONTO, April 3, 2018 /CNW/ - Stina Resources Ltd. ("Stina" or the "Company") (CSE: SQA) (OTCQB: STNUF) (Frankfurt: 01X) is pleased to report and provide an update on the acquisition of the Gildemeister assets. Gildemeister was one of the world's first and largest researchers, developers, manufacturers and distributors of vanadium flow batteries. As industry leaders, they installed vanadium flow batteries at over 100 sites around the world.
The finalization of the acquisition of the assets of Gildemeister GmbH from the Austrian administrator is progressing. In February 2018, Stina created a subsidiary to assume the assets and operations of Gildemeister. The subsidiary, Enerox GmbH, is an Austrian company headquartered in Vienna.
The receiver transferred all the operational functions to Enerox GmbH on April 1, 2018. The transfer included employee contracts, rental agreements, and all related contractual obligations that Enerox agreed to accept. Stina expects to close the transaction on or about April 11, 2018. The closing and transitional requirements have been implemented quite smoothly and on time. Once the transfer of assets is completed, Enerox will be able to resume full production and sales of CellCube vanadium flow batteries.
"Enerox CellCube is one of a few proven technologies on all scales and sizes of vanadium flow battery storage requirements. Gildemeister had over 100 installations worldwide. We are on the threshold of an immense opportunity as the world embraces green energy and develops the efficient means to store it. We want Stina and Enerox to be the green energy solution," stated Brian Stecyk, President and CEO of Stina.
...
https://www.newswire.ca/news-releases/stina-to-close-battery…

NEC ES: Future lies in creating Amazon-style ‘enterprise platforms’
Published: 22 Mar 2018, 14:25
By: Andy Colthorpe
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/nec-es-future-lies-in-c…
(NEC ES was originally spun out of the acquired start-up, A123 Systems before joining the Japan-headquartered NEC Corporation.)
The energy industry is evolving towards more ‘enterprise platform’-based business models, enabling energy storage to play a vital role for businesses and the grid, NEC Energy Solutions (NEC ES) CEO Steve Fludder has said.
NEC ES, the NEC Corporation’s energy storage system integration and technology business, relies increasingly on machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI), Fludder said in an interview and presentation at last month’s Energy Storage Summit in London. Fludder took over as CEO in November, replacing temporary boss Hiro Ezawa, who in turn replaced longstanding leader Budd Collins.
...
Published: 22 Mar 2018, 14:25
By: Andy Colthorpe
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/nec-es-future-lies-in-c…
(NEC ES was originally spun out of the acquired start-up, A123 Systems before joining the Japan-headquartered NEC Corporation.)
The energy industry is evolving towards more ‘enterprise platform’-based business models, enabling energy storage to play a vital role for businesses and the grid, NEC Energy Solutions (NEC ES) CEO Steve Fludder has said.
NEC ES, the NEC Corporation’s energy storage system integration and technology business, relies increasingly on machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI), Fludder said in an interview and presentation at last month’s Energy Storage Summit in London. Fludder took over as CEO in November, replacing temporary boss Hiro Ezawa, who in turn replaced longstanding leader Budd Collins.
...
‘All-iron’ flow battery maker ESS Inc nets BASF project contracts in Germany
Published: 21 Mar 2018, 15:51
By: Andy Colthorpe
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/all-iron-flow-battery-m…
ESS Inc, US manufacturer of a novel iron flow battery for stationary energy storage applications, has entered the German market via an agreement with investor, chemical company BASF.
The company’s ‘all-iron’ batteries, housed and sold in a solution called Energy Warehouse, are intended to offer long durations of energy storage beyond the limits of around 2-4 hours typically seen in grid or commercial-scale lithium battery storage.
ESS Inc claims it can comfortably go beyond six hours and is also suitable for microgrids. Durability advantages give it a potential 20,000+ cycle life, approximately over 20 years of operation. ESS said it also responds quickly to signals and the company offers full turnkey installation services. The battery’s proprietary electrolyte is made with iron, salt and water...
Published: 21 Mar 2018, 15:51
By: Andy Colthorpe
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/all-iron-flow-battery-m…
ESS Inc, US manufacturer of a novel iron flow battery for stationary energy storage applications, has entered the German market via an agreement with investor, chemical company BASF.
The company’s ‘all-iron’ batteries, housed and sold in a solution called Energy Warehouse, are intended to offer long durations of energy storage beyond the limits of around 2-4 hours typically seen in grid or commercial-scale lithium battery storage.
ESS Inc claims it can comfortably go beyond six hours and is also suitable for microgrids. Durability advantages give it a potential 20,000+ cycle life, approximately over 20 years of operation. ESS said it also responds quickly to signals and the company offers full turnkey installation services. The battery’s proprietary electrolyte is made with iron, salt and water...
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 57.189.088 von R-BgO am 05.03.18 14:28:23
Auszug:
“This is a pretty bold step by Bosch,” said Mitalee Gupta, energy storage analyst at GTM Research, after the German multinational announced plans to give up on in-house battery manufacturing.
“However,” she said, “it is important to understand that capital investments are required at both the cell and battery pack level to meet the growing battery demand from EV and stationary energy storage market.”
With established battery manufacturers pouring hundreds of millions of dollars into new gigafactories around the world, new entrants could find it hard to muscle into the market, said Gupta.
“Unless a company brings new, commercially viable chemistries or makes great strides in energy density improvements, the lithium-ion cell market will be largely dominated by Chinese and South Korean manufacturers,” she said.
Bosch had hoped to crack the market with a next-generation solid-state lithium-ion battery developed by Seeo, a U.S. startup. Bosch bought Seeo in 2015 and has now put it up for sale again. Reuters reports Seeo “already has potential buyers.”"
weiterer Background zum Bosch-Ausstieg:
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/bosch-abandons-…Auszug:
“This is a pretty bold step by Bosch,” said Mitalee Gupta, energy storage analyst at GTM Research, after the German multinational announced plans to give up on in-house battery manufacturing.
“However,” she said, “it is important to understand that capital investments are required at both the cell and battery pack level to meet the growing battery demand from EV and stationary energy storage market.”
With established battery manufacturers pouring hundreds of millions of dollars into new gigafactories around the world, new entrants could find it hard to muscle into the market, said Gupta.
“Unless a company brings new, commercially viable chemistries or makes great strides in energy density improvements, the lithium-ion cell market will be largely dominated by Chinese and South Korean manufacturers,” she said.
Bosch had hoped to crack the market with a next-generation solid-state lithium-ion battery developed by Seeo, a U.S. startup. Bosch bought Seeo in 2015 and has now put it up for sale again. Reuters reports Seeo “already has potential buyers.”"
Übersichtsartikel zu Flow
https://www.energy-storage.news/blogs/flow-in-flux-life-on-t…
Vizn in Trouble:
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/distressed-vizn…
Zinc redox flow battery maker ViZn Energy Systems is scrambling to find backers after the lead investor pulled out of its latest funding round.
...
Although ViZn has not filed for Chapter 11 insolvency protection, the company has sacked all but two of its 70-person team. Local paper Flathead Beacon last Friday reported staff were told to stop working on March 16.
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/distressed-vizn…
Zinc redox flow battery maker ViZn Energy Systems is scrambling to find backers after the lead investor pulled out of its latest funding round.
...
Although ViZn has not filed for Chapter 11 insolvency protection, the company has sacked all but two of its 70-person team. Local paper Flathead Beacon last Friday reported staff were told to stop working on March 16.
http://www.elektroniknet.de/markt-technik/power/lithium-ione…
Im ersten Quartal 2018 sind die Preise von Kobalt um 20 Prozent gestiegen. Das kann auch zu steigenden Kosten für Li-Ionen-Batterien und E-Autos führen.
Deshalb arbeiten laut den Analysten von Energytrend auch schon daran, ihr Abhängigkeit von Kobalt zu reduzieren. Sie entwickeln Batterie mit einem hohen Nickelanteil sowie lithium-Ionen-Batterien mit Siliziumoxid als Kathodenmaterial und experimentieren mit beigemischten Polymeren. Im Moment aber besteht der bevorzugte Weg, um die Energiedichte der Lithium-Ionen Batterien zu erhöhen, darin Kobalt einzusetzen. Den Markt aber dominiert eine kleine Anzahl von Lieferanten und er ist von kurzfristigen Spekulationen geprägt...
Im ersten Quartal 2018 sind die Preise von Kobalt um 20 Prozent gestiegen. Das kann auch zu steigenden Kosten für Li-Ionen-Batterien und E-Autos führen.
Deshalb arbeiten laut den Analysten von Energytrend auch schon daran, ihr Abhängigkeit von Kobalt zu reduzieren. Sie entwickeln Batterie mit einem hohen Nickelanteil sowie lithium-Ionen-Batterien mit Siliziumoxid als Kathodenmaterial und experimentieren mit beigemischten Polymeren. Im Moment aber besteht der bevorzugte Weg, um die Energiedichte der Lithium-Ionen Batterien zu erhöhen, darin Kobalt einzusetzen. Den Markt aber dominiert eine kleine Anzahl von Lieferanten und er ist von kurzfristigen Spekulationen geprägt...
Scatec ist recht optimistisch
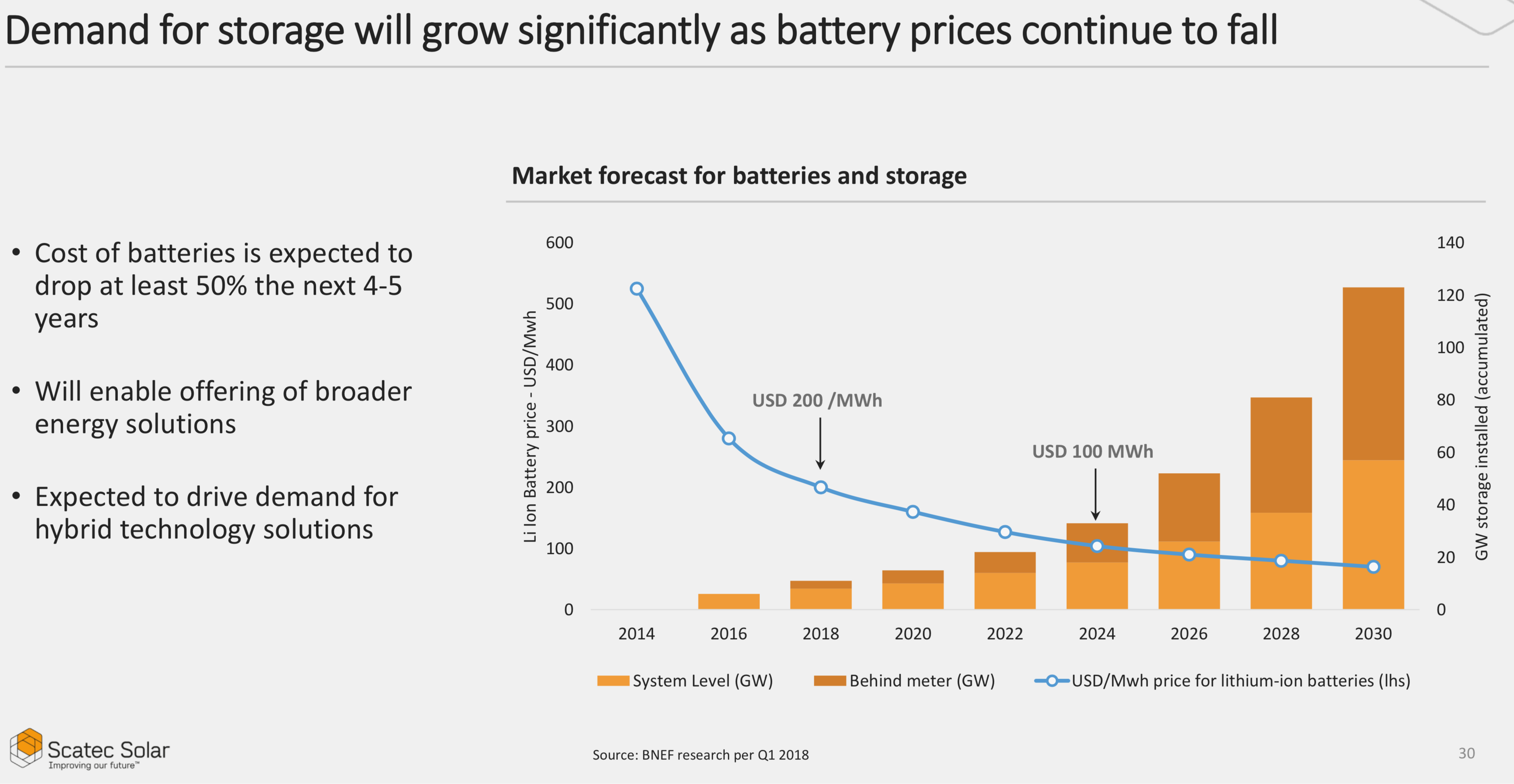
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 57.863.367 von R-BgO am 30.05.18 09:01:37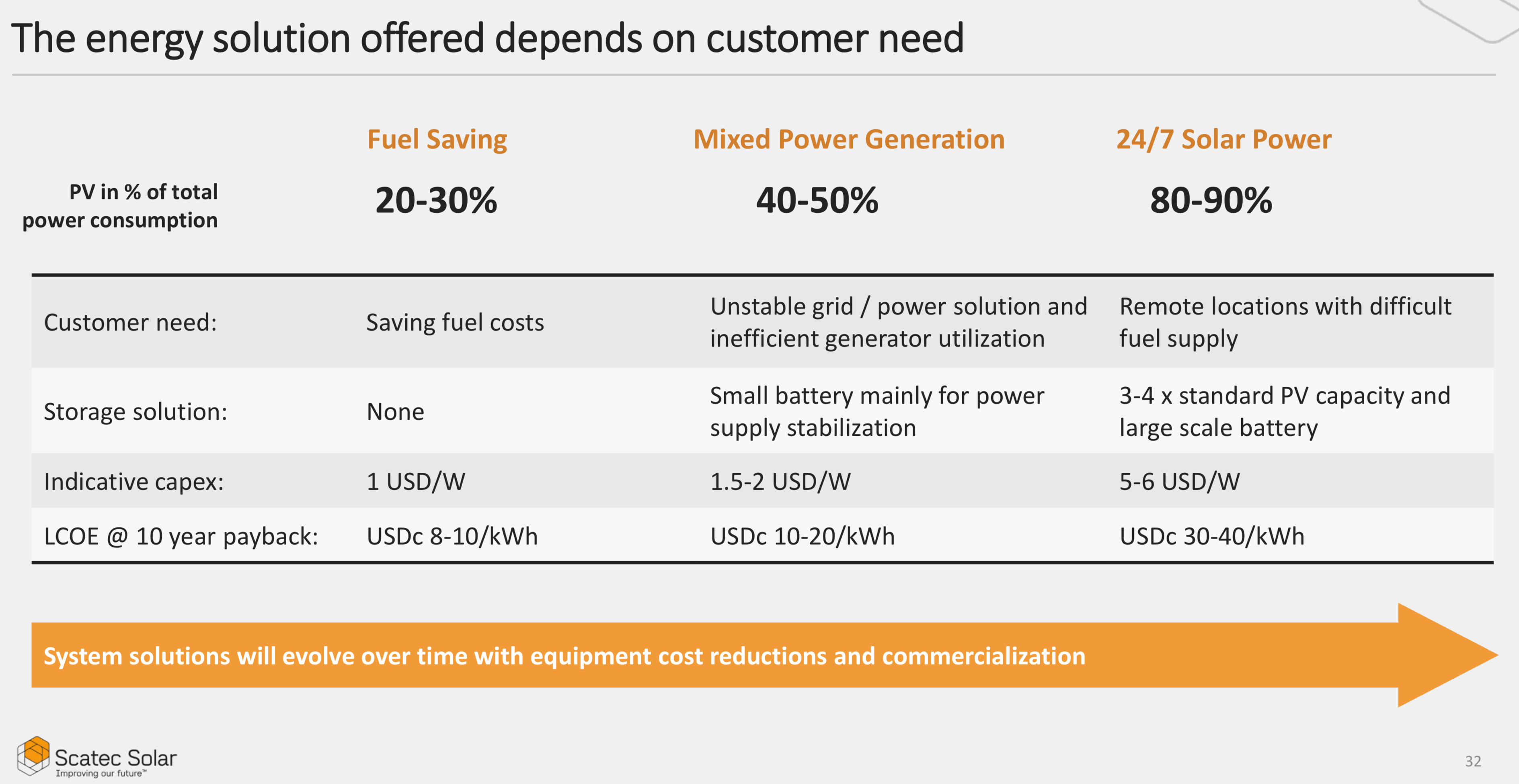

Siemens steigt bei Northvolt ein: http://www.handelsblatt.com/unternehmen/energie/northvolt-si…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 57.167.874 von R-BgO am 02.03.18 10:02:04Highview Power's LAES ist in Betrieb:
World first grid-scale liquid air energy storage project completed in northern England
Published: 5 Jun 2018, 16:35
By: David Pratt
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/world-first-grid-scale-…
The UK's energy storage sector took “a great step forward” after completing what is thought to be the world’s first grid-scale liquid air energy storage (LAES) plant at the Pilsworth landfill gas site in Bury, near Manchester, the two companies involved have said.
After technology provider Highview Power and waste management specialist Viridor finished working on the 5MW/15MWh LAES plant, it was officially unveiled today by Professor John Loughhead, Chief Scientific Adviser at the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS), almost three years after Highview revealed work was well underway on the demonstrator with backing from General Electric.
The project which was developed in partnership with Viridor, used £8 million of government funding to become the first operational demonstration of the LAES technology.
“We’re pleased to have been able to support the Pilsworth demonstrator through our Energy Innovation Programme aimed at accelerating the commercialisation of innovative clean energy technologies and processes,” Loughhead said.
“The deployment of smart, flexible technologies, such as energy storage, will help to ensure the UK has a secure, affordable and clean energy system now and in the future in keeping with the priorities within UK Government’s Modern Industrial Strategy.”
LAES converts air, which is stored as a liquid, into gas using an expansion process that releases stored energy to drive a turbine and generate clean electricity. Unlike battery storage, the process does not use any potentially harmful metals or chemical elements, being comprised mostly of steel.
This offers a lifespan of 30-40 years in comparison to around 10 for lithium-ion batteries, while at the end of life the plant can be easily decommissioned and the steel elements recycled.
Meanwhile, the long duration nature of the facility allows it to provide high levels of energy storage capacity to a number of reserve, grid balancing and regulation services.
In addition to providing energy storage, the LAES plant also converts waste heat to power using heat from the on-site landfill gas engines.
Gareth Brett, chief executive at Highview Power, said, “Support from government, our partners and our supply chain has enabled Highview Power to successfully design and build the world’s first grid-scale LAES plant here in the UK. The plant is the only large scale, true long-duration, locatable energy storage technology available today, at acceptable cost.”
'Sustainability and innovation' at the the heart of the project
Aggregator Kiwi Power has been selected to take the facility into the ancillary services market, where CEO Yoav Zingher says the technology will allow the future grid, with high levels of renewables, to maintain system inertia and ensure the lights stay on while accruing “predictable, annual, recurring revenue”.
“LAES technology is a great step forward in the creation of a truly de-centralised energy system in the UK allowing end-users to balance the national electricity network at times of peak demand,” he said.
Richard Pennells, managing director, energy at Viridor, agreed and said: “The innovative LAES technology which has been developed through the Highview Power project could play an important role in supporting UK growth in low carbon, renewable energy sources and in maintaining the security of the United Kingdom’s electricity supply.
“Sustainability and innovation has been at the heart of this project and it is this focus which is required to reduce our carbon footprint and deliver the long-term energy security the UK requires.”
Taking on global demand
With the Bury LAES project completed, Highview Power expects a surge in interest in the technology as global energy storage demand grows and shifts towards long duration grid-connected systems.
In a recent report published by our publisher Solar Media’s Market Research division, analyst Lauren Cook pointed to this changing trend, noting that in megawatt-hours, battery energy storage capacities installed in the UK by the end of 2022 will be 50 times what they were as 2017 ended.
Brett added: “The market opportunity for LAES technology is exciting – we estimate that 60% of the global energy storage market comprises long-duration, grid connected storage and that our LAES technology is ready to meet almost half of this (45%).”
He went on to claim that utilities, which have been assessing “the unique solution” offered by LAES technology for some time, are now using the operating data from the site to confirm their expectations.
“We are therefore already in detailed negotiations to build plants ten times the size of this one for utility customers of several nationalities and for various different applications,” Brett revealed.
World first grid-scale liquid air energy storage project completed in northern England
Published: 5 Jun 2018, 16:35
By: David Pratt
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/world-first-grid-scale-…
The UK's energy storage sector took “a great step forward” after completing what is thought to be the world’s first grid-scale liquid air energy storage (LAES) plant at the Pilsworth landfill gas site in Bury, near Manchester, the two companies involved have said.
After technology provider Highview Power and waste management specialist Viridor finished working on the 5MW/15MWh LAES plant, it was officially unveiled today by Professor John Loughhead, Chief Scientific Adviser at the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS), almost three years after Highview revealed work was well underway on the demonstrator with backing from General Electric.
The project which was developed in partnership with Viridor, used £8 million of government funding to become the first operational demonstration of the LAES technology.
“We’re pleased to have been able to support the Pilsworth demonstrator through our Energy Innovation Programme aimed at accelerating the commercialisation of innovative clean energy technologies and processes,” Loughhead said.
“The deployment of smart, flexible technologies, such as energy storage, will help to ensure the UK has a secure, affordable and clean energy system now and in the future in keeping with the priorities within UK Government’s Modern Industrial Strategy.”
LAES converts air, which is stored as a liquid, into gas using an expansion process that releases stored energy to drive a turbine and generate clean electricity. Unlike battery storage, the process does not use any potentially harmful metals or chemical elements, being comprised mostly of steel.
This offers a lifespan of 30-40 years in comparison to around 10 for lithium-ion batteries, while at the end of life the plant can be easily decommissioned and the steel elements recycled.
Meanwhile, the long duration nature of the facility allows it to provide high levels of energy storage capacity to a number of reserve, grid balancing and regulation services.
In addition to providing energy storage, the LAES plant also converts waste heat to power using heat from the on-site landfill gas engines.
Gareth Brett, chief executive at Highview Power, said, “Support from government, our partners and our supply chain has enabled Highview Power to successfully design and build the world’s first grid-scale LAES plant here in the UK. The plant is the only large scale, true long-duration, locatable energy storage technology available today, at acceptable cost.”
'Sustainability and innovation' at the the heart of the project
Aggregator Kiwi Power has been selected to take the facility into the ancillary services market, where CEO Yoav Zingher says the technology will allow the future grid, with high levels of renewables, to maintain system inertia and ensure the lights stay on while accruing “predictable, annual, recurring revenue”.
“LAES technology is a great step forward in the creation of a truly de-centralised energy system in the UK allowing end-users to balance the national electricity network at times of peak demand,” he said.
Richard Pennells, managing director, energy at Viridor, agreed and said: “The innovative LAES technology which has been developed through the Highview Power project could play an important role in supporting UK growth in low carbon, renewable energy sources and in maintaining the security of the United Kingdom’s electricity supply.
“Sustainability and innovation has been at the heart of this project and it is this focus which is required to reduce our carbon footprint and deliver the long-term energy security the UK requires.”
Taking on global demand
With the Bury LAES project completed, Highview Power expects a surge in interest in the technology as global energy storage demand grows and shifts towards long duration grid-connected systems.
In a recent report published by our publisher Solar Media’s Market Research division, analyst Lauren Cook pointed to this changing trend, noting that in megawatt-hours, battery energy storage capacities installed in the UK by the end of 2022 will be 50 times what they were as 2017 ended.
Brett added: “The market opportunity for LAES technology is exciting – we estimate that 60% of the global energy storage market comprises long-duration, grid connected storage and that our LAES technology is ready to meet almost half of this (45%).”
He went on to claim that utilities, which have been assessing “the unique solution” offered by LAES technology for some time, are now using the operating data from the site to confirm their expectations.
“We are therefore already in detailed negotiations to build plants ten times the size of this one for utility customers of several nationalities and for various different applications,” Brett revealed.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 57.863.367 von R-BgO am 30.05.18 09:01:37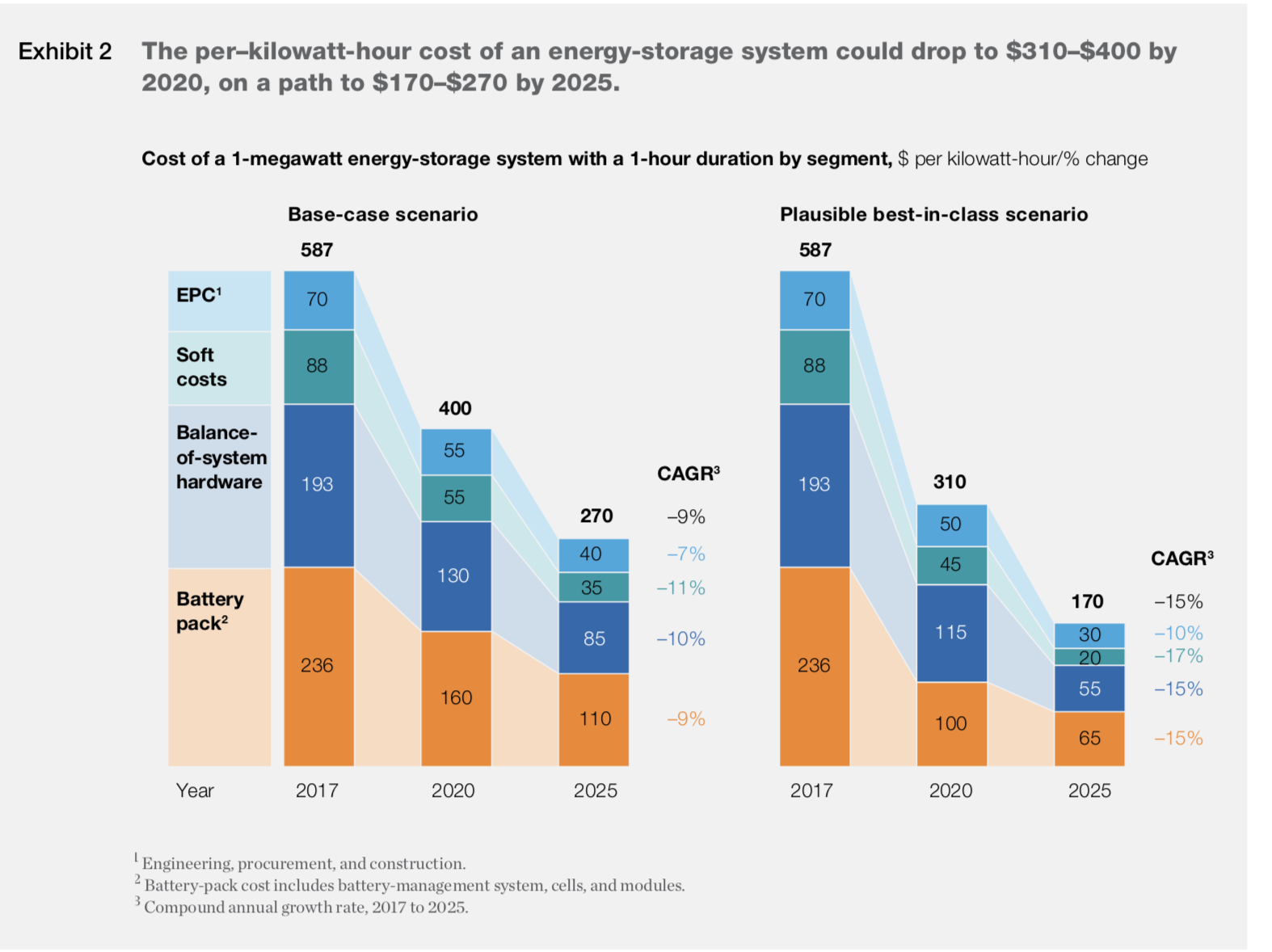
https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/electric-power-and-natur…
McKinsey haut in die gleiche Kerbe:

https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/electric-power-and-natur…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 57.959.412 von R-BgO am 11.06.18 17:20:19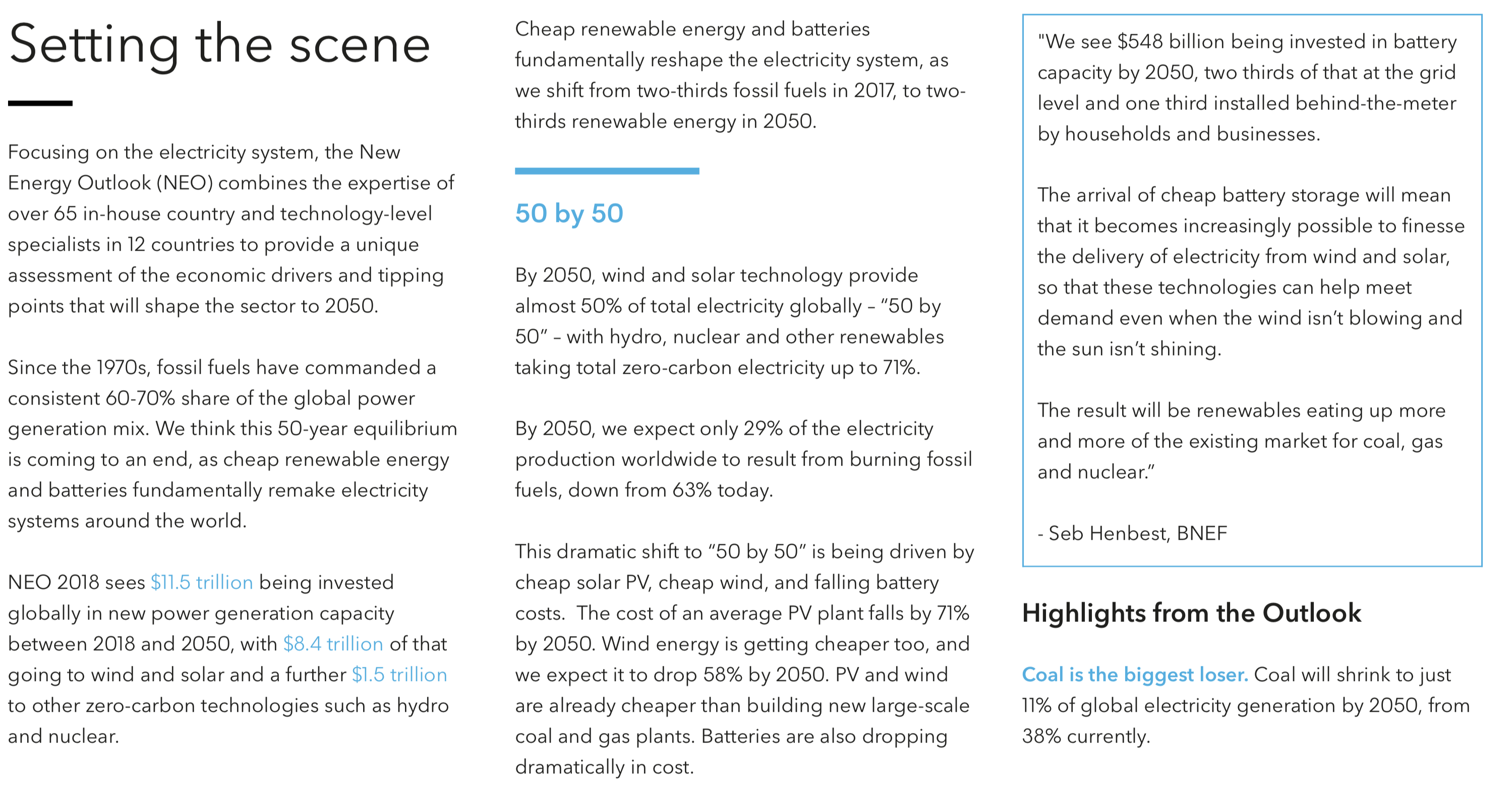

Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 58.024.477 von R-BgO am 20.06.18 10:42:02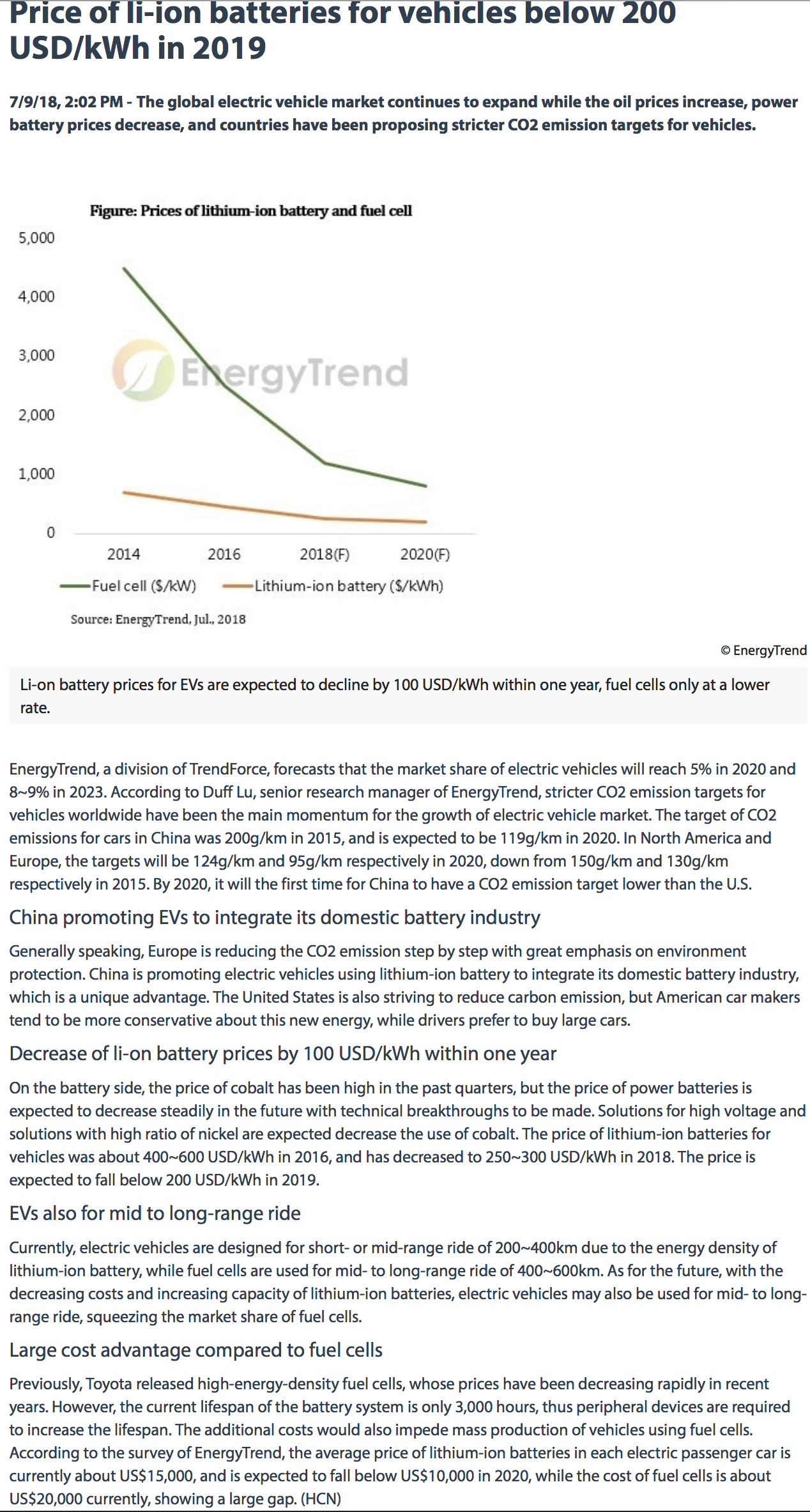

RedT:
Long duration energy storage will be put to use in Germany’s grid, with RedT, a UK-headquartered maker of flow energy storage ‘machines’, announcing an initial 80MWh deployment to the country.
Through a two-phase deal brokered with developer Energy System Management – a subsidiary of WWF Solar – RedT will deliver 1,066 of its Gen 3 tank units to form two 40MWh grid-scale projects in the first phase. The second phase is a much bigger deal, comprising a further 690MWh of projects.
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/redts-vanadium-flow-ene…
Long duration energy storage will be put to use in Germany’s grid, with RedT, a UK-headquartered maker of flow energy storage ‘machines’, announcing an initial 80MWh deployment to the country.
Through a two-phase deal brokered with developer Energy System Management – a subsidiary of WWF Solar – RedT will deliver 1,066 of its Gen 3 tank units to form two 40MWh grid-scale projects in the first phase. The second phase is a much bigger deal, comprising a further 690MWh of projects.
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/redts-vanadium-flow-ene…
Eine CO2-Auffangtechnologie: https://www.cell.com/joule/fulltext/S2542-4351(18)30225-3
"Highlights
Detailed engineering and cost analysis for a 1 Mt-CO2/year direct air capture plant
Levelized costs of $94 to $232 per ton CO2 from the atmosphere
First DAC paper with commercial engineering cost breakdown
Full mass and energy balance with pilot plant data for each unit operation"
"Highlights
Detailed engineering and cost analysis for a 1 Mt-CO2/year direct air capture plant
Levelized costs of $94 to $232 per ton CO2 from the atmosphere
First DAC paper with commercial engineering cost breakdown
Full mass and energy balance with pilot plant data for each unit operation"
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 58.370.847 von R-BgO am 03.08.18 18:40:33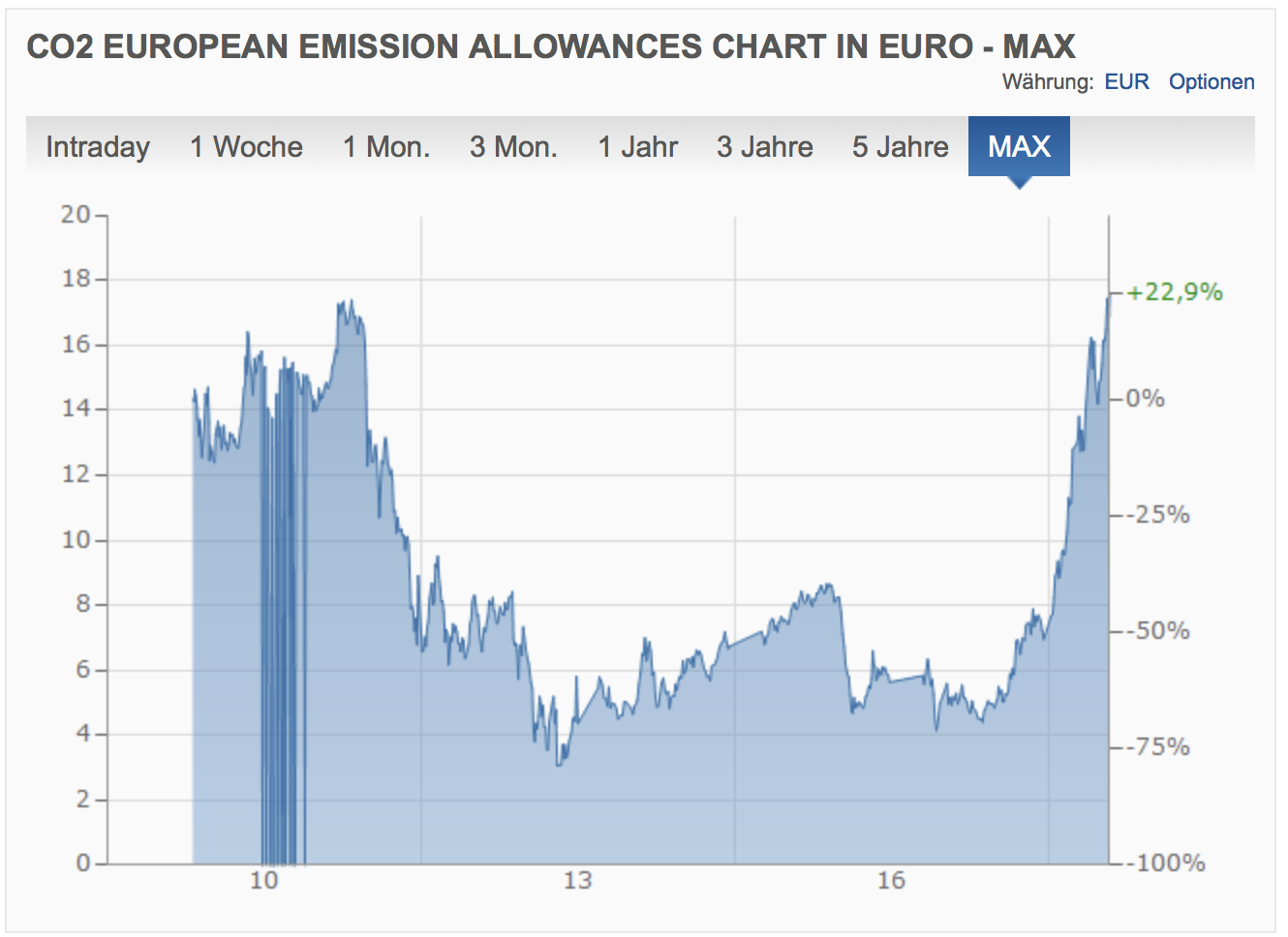
https://www.finanzen.net/rohstoffe/co2-emissionsrechte
bisheriger Preisverlauf für CO2-Emissionsrechte:

https://www.finanzen.net/rohstoffe/co2-emissionsrechte
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 58.370.811 von R-BgO am 03.08.18 18:36:00Haben Sie RedT im Blick?
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/after-original-buyer-bi…
After original buyer bid fails, Nissan & NEC’s Li-ion battery business (=AESC) acquired by China’s Envision...
After original buyer bid fails, Nissan & NEC’s Li-ion battery business (=AESC) acquired by China’s Envision...
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 58.379.967 von Popeye82 am 06.08.18 00:17:10
Qinous kannte ich noch nicht

Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 58.928.763 von R-BgO am 11.10.18 12:27:03und Kokam auch nicht...
SolarEdge to Acquire Kokam, a Provider of Li-ion Cells, Batteries, and Energy Storage Solutions
FREMONT, Calif. & SEOUL, Korea--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Oct. 11, 2018--
SolarEdge Technologies, Inc. (“SolarEdge”) (NASDAQ:SEDG), a global leader in smart energy technology, announced today that it has entered into definitive agreements to acquire a major stake in Kokam Co., Ltd. Headquartered in South Korea, Kokam is a provider of Lithium-ion battery cells, batteries and energy storage solutions.
Founded in 1989, Kokam has been manufacturing Lithium-ion cells and providing reliable, safe, high-performance battery solutions for the past twenty-nine years. Kokam provides battery solutions for a wide-variety of industries, including ESS (energy storage systems), UPS, electric vehicles (EV), aerospace, marine and more.
“The acquisition of Kokam will enable us to grow our offering, adding already proven battery storage to our product portfolio,” said Guy Sella, CEO, Chairman and Founder of SolarEdge. “Our technological innovation combined with Kokam’s world-class team and renowned battery storage solutions, will enable seamless integration with our current solutions, taking us a further step toward making solar installations smarter and more beneficial.”
The acquisition of approximately 75% of outstanding equity shares of Kokam reflects an aggregate investment of approximately $88 million, including related transaction expenses. The transaction is subject to customary closing conditions and is expected to close in the coming weeks. Over time, the Company intends to purchase the remaining outstanding equity shares of Kokam that are currently listed on the Korean over the counter exchange through open-market purchases and otherwise, eventually resulting in Kokam becoming a wholly-owned subsidiary of SolarEdge.
SolarEdge to Acquire Kokam, a Provider of Li-ion Cells, Batteries, and Energy Storage Solutions
FREMONT, Calif. & SEOUL, Korea--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Oct. 11, 2018--
SolarEdge Technologies, Inc. (“SolarEdge”) (NASDAQ:SEDG), a global leader in smart energy technology, announced today that it has entered into definitive agreements to acquire a major stake in Kokam Co., Ltd. Headquartered in South Korea, Kokam is a provider of Lithium-ion battery cells, batteries and energy storage solutions.
Founded in 1989, Kokam has been manufacturing Lithium-ion cells and providing reliable, safe, high-performance battery solutions for the past twenty-nine years. Kokam provides battery solutions for a wide-variety of industries, including ESS (energy storage systems), UPS, electric vehicles (EV), aerospace, marine and more.
“The acquisition of Kokam will enable us to grow our offering, adding already proven battery storage to our product portfolio,” said Guy Sella, CEO, Chairman and Founder of SolarEdge. “Our technological innovation combined with Kokam’s world-class team and renowned battery storage solutions, will enable seamless integration with our current solutions, taking us a further step toward making solar installations smarter and more beneficial.”
The acquisition of approximately 75% of outstanding equity shares of Kokam reflects an aggregate investment of approximately $88 million, including related transaction expenses. The transaction is subject to customary closing conditions and is expected to close in the coming weeks. Over time, the Company intends to purchase the remaining outstanding equity shares of Kokam that are currently listed on the Korean over the counter exchange through open-market purchases and otherwise, eventually resulting in Kokam becoming a wholly-owned subsidiary of SolarEdge.
neuer US Energy-Storage Player
Hecate Energy: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/hecate-energy-infrared-… Si als Anodenmaterial?
-neu für mich-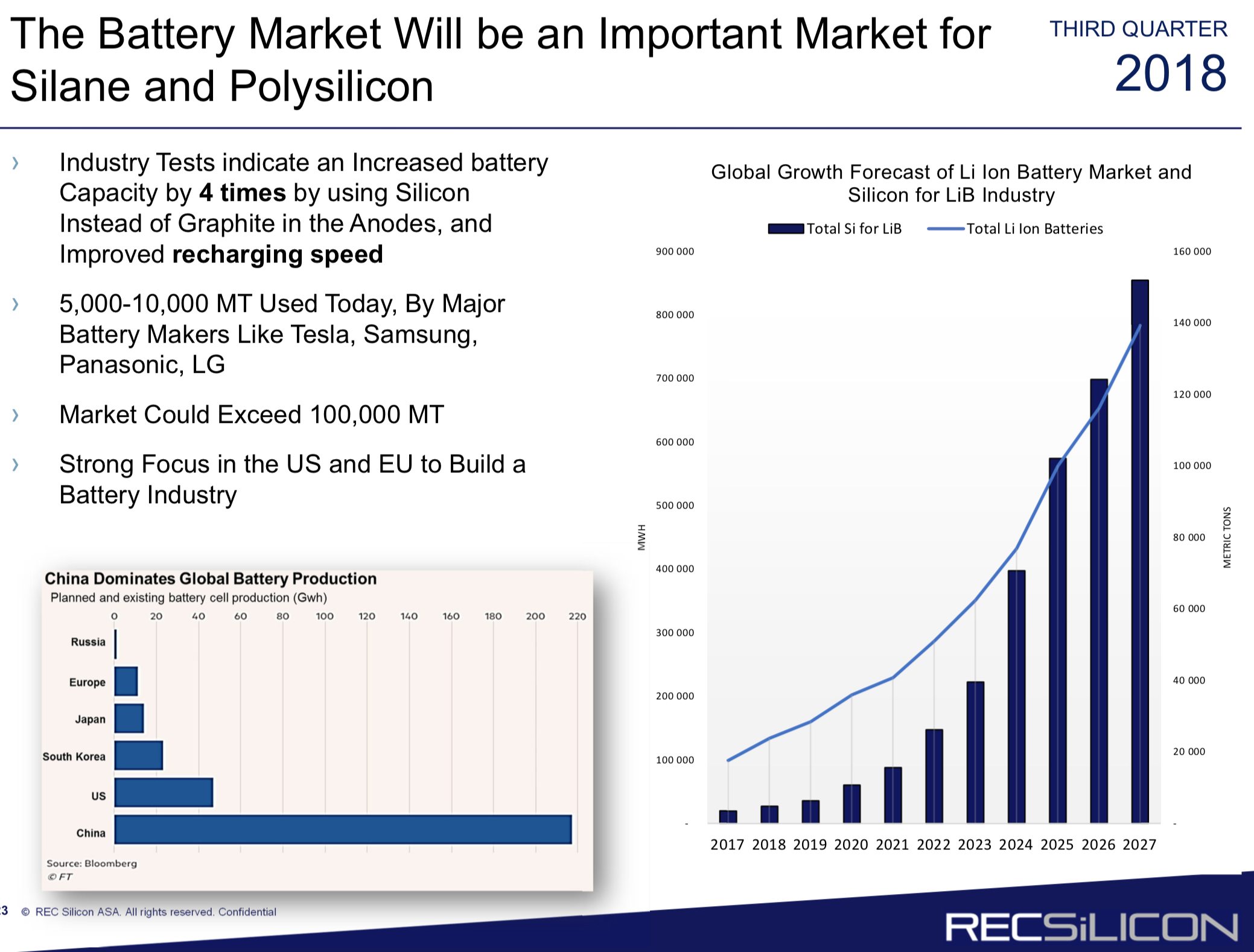
Trojan Battery wird von C&D Technologies übernommen: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/trojan-battery-acquired…
letztere sind seit 2017 PE-owned, die Grippe soll rund ! Mrd. USD p.a. Umsatz machen.
Kommt bestimmt irgendwann auf den Kurszettel
letztere sind seit 2017 PE-owned, die Grippe soll rund ! Mrd. USD p.a. Umsatz machen.
Kommt bestimmt irgendwann auf den Kurszettel
BNEF forecastet mal wieder:
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/energy-storage-economic…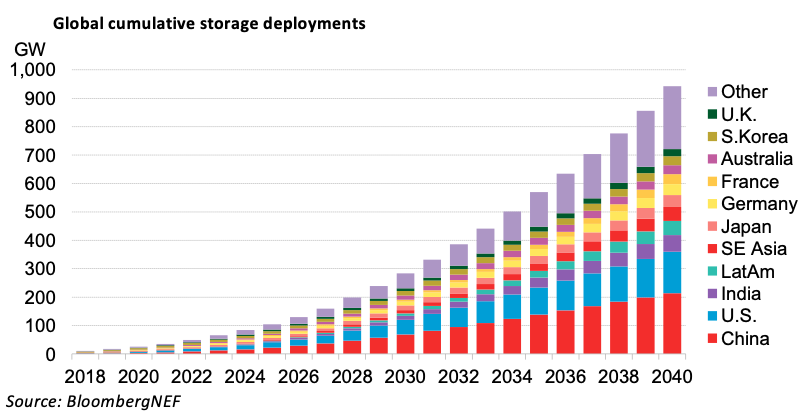
nehme an, die y-Achse sollen GWh sein...
das geht schon eindeutig über Pilotprojektcharakter hinaus:
PG&E ersetzt Gasturbinen durch Batterienhttps://www.utilitydive.com/news/storage-will-replace-3-cali…
Auszug
"The PG&E projects, however, are the first time a utility and its regulators have sought to directly replace multiple major power plants with battery storage.
The projects would take the place of three plants owned by generator Calpine — the 580 MW Metcalf plant and the Feather River and Yuba City generators, both 48 MW.
Calpine and the California ISO last year asked the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission to approve reliability-must-run (RMR) contracts for the plants, arguing they are essential to maintain power reliability. The one-year contracts would see California ratepayers finance the continued operation of the generators, which are losing money in the ISO's wholesale market.
FERC approved the request in April, but California regulators were already planning for when the plants retire. In January, they ordered PG&E to seek alternatives to the generators, writing that the lack of competition in RMR contracts could mean higher prices for customers.
Without a replacement plan, "it is likely that the Calpine plants could need to be RMR'd year after year," CPUC spokesman Christopher Chow told Utility Dive at the time. "The new procurement would eliminate the shortfalls in the local areas that would result in future RMRs, if not addressed."
Approval of the storage plan gives PG&E the green light to proceed with the projects — all lithium-ion battery facilities.
Once completed, the Vistra and Tesla projects will be the largest in the world, according to the Department of Energy's global database of energy storage projects. The largest lithium-ion battery currently in service is Tesla's 100 MW / 127 MWh facility in South Australia, while Japan's Kyushu Electric Power Co. has a 50 MW / 300 MWh sodium-sulfur battery facility that it installed in 2016.
In addition to those projects, the PG&E solicitation includes a 75 MW / 300 MWh facility from Hummingbird Energy Solutions and a 10 MW / 40 MWh facility from battery provider mNOC. PG&E will own the Tesla facility, while the developers will own the other projects.
The two largest facilities will be sited in Moss Landing, a transmission-constrained region south of San Francisco, while the Hummingbird facility will be placed in the city of Morgan Hill, and the mNOC capacity will come from multiple behind-the-meter projects in PG&E's service area.
PG&E will be allowed to recover all the costs for the facilities from ratepayers, but analysts say that's likely less expensive than the gas plants they will replace.
"Storage at this scale is likely now cheaper than the total cost to run the gas plants," Alex Eller, senior energy research analyst at Navigant, told Utility Dive when the solicitation was announced. "
Mitsubishi Electric - sehr groß:


100 MW CSP mit Speicher in Südafrika: https://www.renewableenergyworld.com/articles/2018/11/south-…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 59.257.156 von R-BgO am 20.11.18 11:49:31Thread: BMZ Group
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 59.257.156 von R-BgO am 20.11.18 11:49:31Lumenion macht Speicher auf Basis flüssigen Stahls: https://lumenion.com/produkt-2
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 59.334.971 von R-BgO am 30.11.18 14:38:15
"Der Lumenion Stahlspeicher speichert “Stromspitzen” für weniger als 2 Cent/KWh kosten- und platzeffizient mit bis zu 650° Celsius als Wärme, die bei Bedarf mittels Turbinen-Einheit rückverstromt – oder zur Gänze als Wärme genutzt werden kann. Als Mitgründer von, unter anderem, Solon, Q-Cells und Younicos hat Voigt schon seit den 90er Jahren Solarmodule und Speicher erfolgreich in den Markt eingeführt."
angeblich:
https://lumenion.com/pressemitteilung-22-oktober-2018"Der Lumenion Stahlspeicher speichert “Stromspitzen” für weniger als 2 Cent/KWh kosten- und platzeffizient mit bis zu 650° Celsius als Wärme, die bei Bedarf mittels Turbinen-Einheit rückverstromt – oder zur Gänze als Wärme genutzt werden kann. Als Mitgründer von, unter anderem, Solon, Q-Cells und Younicos hat Voigt schon seit den 90er Jahren Solarmodule und Speicher erfolgreich in den Markt eingeführt."
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 59.334.971 von R-BgO am 30.11.18 14:38:15https://www.energy-storage.news/news/vattenfall-pilots-high-…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 59.283.382 von R-BgO am 23.11.18 10:17:03GV Yuasa - ebenfalls ziemlich groß:


Alphabet (!) probiert es mit flüssigem Salz: https://www.engadget.com/2018/12/19/alphabet-malta-energy-st…
"Alphabet's X division has played host to a string of experimental ideas, and another one is spinning out as an independent business. Malta uses cheap, abundant materials including salt, anti-freeze and steel to store power at grid scale.
Malta taps into the laws of thermodynamics to store renewable and fossil energy as heat in molten salt and cold in low-temperature anti-freeze until it's needed -- you probably still need electricity at night, when the sun isn't shining on your local solar farm. The company is working on a pilot plant, backed by $26 million from its first funding round, which was led by a fund Jeff Bezos, Bill Gates and Michael Bloomberg are involved with."
"Alphabet's X division has played host to a string of experimental ideas, and another one is spinning out as an independent business. Malta uses cheap, abundant materials including salt, anti-freeze and steel to store power at grid scale.
Malta taps into the laws of thermodynamics to store renewable and fossil energy as heat in molten salt and cold in low-temperature anti-freeze until it's needed -- you probably still need electricity at night, when the sun isn't shining on your local solar farm. The company is working on a pilot plant, backed by $26 million from its first funding round, which was led by a fund Jeff Bezos, Bill Gates and Michael Bloomberg are involved with."
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 59.490.930 von R-BgO am 21.12.18 16:03:33Kyocera, Itochu und North Bridge Venture Partners investieren in 24M, die es mit "semi-solid lithium cells"versuchen: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/japanese-solar-names-in…
""“Standard Li-ion cells contain films of solid electrode materials in contact with liquid electrolytes. 24M's patented innovation replaces these films with semi-solid electrodes made of Li-ion cathode and anode materials suspended in conventional liquid electrolytes. The company claims this design is easier and cheaper to manufacture,” Lilia Xie wrote.
According to 24M, using electrolyte as the processing solvent can eliminate several steps in the standard process for lithium battery production which can be capital and energy intensive, including drying and electrolyte filling. The design of 24M’s cells reduces or eliminates the need for certain inactive materials in batteries such as cell separators or copper and aluminium parts. 24M also says the addition of electrolyte at an early stage of the manufacturing process, during slurry mixing, aids the creation of high energy density devices.
""“Standard Li-ion cells contain films of solid electrode materials in contact with liquid electrolytes. 24M's patented innovation replaces these films with semi-solid electrodes made of Li-ion cathode and anode materials suspended in conventional liquid electrolytes. The company claims this design is easier and cheaper to manufacture,” Lilia Xie wrote.
According to 24M, using electrolyte as the processing solvent can eliminate several steps in the standard process for lithium battery production which can be capital and energy intensive, including drying and electrolyte filling. The design of 24M’s cells reduces or eliminates the need for certain inactive materials in batteries such as cell separators or copper and aluminium parts. 24M also says the addition of electrolyte at an early stage of the manufacturing process, during slurry mixing, aids the creation of high energy density devices.
Klingt ein bisschen nach snake-oil,
aber wer weiß...: https://energy.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/power/innov…Gegadyne Energy will eine Technologie schaffen,
(that) "combines the quick charging capability of supercapacitors with the high energy density of conventional batteries. It uses the concept of electrostatic charge storage & rapid kinetic Faraday reaction, said Varghese.
He said the goal is to have the first commercial iteration of the battery by 2020. "
ein paar Datenpunkte zu Solar+Storage aus Hawaii:
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/proposed-solar-plus-sto…"While fossil fuel generation in the state comes in at a price of around US$0.15 per kilowatt-hour, two of the proposed projects hit prices of US$0.08 per kilowatt-hour, with even the most expensive, Paeahu Solar on Maui by Canadian developer Innergex coming in at an expected US$0.12 per kWh. It is also worth noting that Paeahu Solar is the smallest project on the list by some way at 15MW / 60MWh, implying that scale plays some part in setting prices.
Every few months the prolific deployment of solar in Hawaii appears to set new benchmarks for low-cost energy from solar-plus-storage projects. In late June Energy-Storage.news reported that Hawaii electric cooperative KIUC will pay less than US$0.11 per kWh for power from a new solar-plus-storage facility on Kaua’i. In August, a 4.88MW solar PV project with a 3MW / 15MWh battery energy storage system on Molokai, one of the smaller islands, reached prices of US$0.17 per kWh, again still competitive on that island with fossil fuel costs."
Fraunhofer IKTS macht Na/NiCl und NaS:
https://www.ikts.fraunhofer.de/de/departments/energy_bio-med…
"cerenergy® ist die Technologieplattform des Fraunhofer IKTS für Keramik-basierte Hochtemperaturbatterien. Die Idee basiert auf der »Neuentwicklung« von Na/NiCl2- und Na/S-Batterien unter der Maßgabe, Zellen und Systeme so kostengünstig wie möglich herzustellen. Dabei werden das Zell- und Systemdesign, die verwendeten Materialien sowie die Fertigungstechnologien gesamthaft betrachtet. Die Zielkosten sollen deutlich unter 100 €/kWh auf Zellebene liegen.
Diese Vorgabe wird durch eine hoch automatisierte Fertigungstechnologie bei der Herstellung des keramischen Elektrolyten und ein »schlankes« Zell- und Systemdesign erreicht.
Die benötigten Rohstoffe sind kostengünstig und gut verfügbar. So wird die Speicherkapazität in Na/NiCl2-Batterien durch den Gehalt an NaCl-Kochsalz definiert. Weitere wesentliche Bestandteile sind ein keramischer Na‑Ionen leitender Elektrolyt aus einem dotierten Aluminiumoxid sowie Nickel und Eisen.
Die Batterien sind frei von Seltenen Erden oder anderen strategischen Rohstoffen.
Die Energiedichten von ca. 130 Wh/kg (auf Zellebene) sind im Vergleich zu Li-Ionen-Batterien durchaus wettbewerbsfähig. Lade- und Entladeraten von 0,25 bis maximal 1 C beschränken die Leistungsdichte, spielen allerdings bei der stationären Energiespeicherung eine eher untergeordnete Rolle. Die erhöhten Arbeitstemperaturen von 300 °C werden durch eine gestützte Vakuumisolation verlustarm realisiert und im Betrieb vom Endverbraucher nicht wahrgenommen. Im Gegensatz zu Lithium-Ionen-Batterien können die cerenergy®-Batterien daher auch unter extremen Umgebungsbedingungen ohne Klimatisierung eingesetzt werden."
https://www.ikts.fraunhofer.de/de/departments/energy_bio-med…
"cerenergy® ist die Technologieplattform des Fraunhofer IKTS für Keramik-basierte Hochtemperaturbatterien. Die Idee basiert auf der »Neuentwicklung« von Na/NiCl2- und Na/S-Batterien unter der Maßgabe, Zellen und Systeme so kostengünstig wie möglich herzustellen. Dabei werden das Zell- und Systemdesign, die verwendeten Materialien sowie die Fertigungstechnologien gesamthaft betrachtet. Die Zielkosten sollen deutlich unter 100 €/kWh auf Zellebene liegen.
Diese Vorgabe wird durch eine hoch automatisierte Fertigungstechnologie bei der Herstellung des keramischen Elektrolyten und ein »schlankes« Zell- und Systemdesign erreicht.
Die benötigten Rohstoffe sind kostengünstig und gut verfügbar. So wird die Speicherkapazität in Na/NiCl2-Batterien durch den Gehalt an NaCl-Kochsalz definiert. Weitere wesentliche Bestandteile sind ein keramischer Na‑Ionen leitender Elektrolyt aus einem dotierten Aluminiumoxid sowie Nickel und Eisen.
Die Batterien sind frei von Seltenen Erden oder anderen strategischen Rohstoffen.
Die Energiedichten von ca. 130 Wh/kg (auf Zellebene) sind im Vergleich zu Li-Ionen-Batterien durchaus wettbewerbsfähig. Lade- und Entladeraten von 0,25 bis maximal 1 C beschränken die Leistungsdichte, spielen allerdings bei der stationären Energiespeicherung eine eher untergeordnete Rolle. Die erhöhten Arbeitstemperaturen von 300 °C werden durch eine gestützte Vakuumisolation verlustarm realisiert und im Betrieb vom Endverbraucher nicht wahrgenommen. Im Gegensatz zu Lithium-Ionen-Batterien können die cerenergy®-Batterien daher auch unter extremen Umgebungsbedingungen ohne Klimatisierung eingesetzt werden."
VRB Energy macht Vanadium-Redox-Battteries: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/first-phase-of-chinas-b…
"VRB Energy, a maker of flow batteries headquartered in Canada and owned by a metal resources and mining company, said the first phase of a 40MWh flow battery project in China has now been commissioned.
VRB Energy (VRB), 82% owned by High Power Exploration, a base metals-focused exploration company led by noted mining financier Robert Friedland, provided Energy-Storage.news with a progress update from Hubei Province at the end of last week.
The company said that it has now successfully commissioned a 3MW / 12MWh vanadium redox flow battery energy storage project which represents Phase 1 of the Hubei Zaoyang Utility-scale Solar and Storage Integration Demonstration Project, set to be 10MW / 40MWh when completed. It represents the latest step since the previous update on the project, when the first 250kW / 1MWh battery module was commissioned a few months ago.
"
"VRB Energy, a maker of flow batteries headquartered in Canada and owned by a metal resources and mining company, said the first phase of a 40MWh flow battery project in China has now been commissioned.
VRB Energy (VRB), 82% owned by High Power Exploration, a base metals-focused exploration company led by noted mining financier Robert Friedland, provided Energy-Storage.news with a progress update from Hubei Province at the end of last week.
The company said that it has now successfully commissioned a 3MW / 12MWh vanadium redox flow battery energy storage project which represents Phase 1 of the Hubei Zaoyang Utility-scale Solar and Storage Integration Demonstration Project, set to be 10MW / 40MWh when completed. It represents the latest step since the previous update on the project, when the first 250kW / 1MWh battery module was commissioned a few months ago.
"
UAE integrates 648MWh of sodium sulfur batteries in one swoop
Published: 28 Jan 2019, 15:10
By: Andy Colthorpe
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/uae-integrates-648mwh-o…
Sodium sulfur (NAS) batteries produced by Japan’s NGK Insulators are being put into use on a massive scale in Abu Dhabi, the capital of the United Arab Emirates.
The company’s battery systems have been deployed across 10 locations – 15 systems in total – adding up to 108MW / 648MWh in total, with each system able to store energy for six hours. The total undertaking includes 12 x 4MW systems and three 20MW systems. The official government Emirates News Agency described the project as the “world’s largest Virtual Battery Plant” as it opened earlier this month.
A representative at NGK’s power business division told Energy-Storage.news the ‘virtual’ description is correct in the sense that the 15 systems in 10 locations “can be controlled as a single plant. While of course they can still be controlled individually when local support to the grid is needed”.
Critical to this aggregation of the systems is the CISC (Centralised Integrated System Controller) which will be located at a control room in Mussafah, an industrial district in Abu Dhabi’s southwest where some of the battery systems are also located, with the rest in nearby Sila. CISC and the NAS systems are “ready to be operated by the TSO (transmission system operator)”, the NGK representative said.
Operational parameters increased from original scope
Awaidha Al Marar, chairman of Abu Dhabi’s Department of Energy, attended an inauguration event on 17 January, as a number of events including Abu Dhabi Sustainability Week and World Future Energy Summit (WFES) took place in the region.
The NGK CISC 648MWh project will help the city load balance across its networks during the daytime, as well as providing up to six hours backup in the case of grid outages. As with many energy storage system projects, it is primarily about reducing the strain on the grid at times of peak demand.
According to the NGK representative, the project was originally planned as thermal generation investment deferral, to reduce the cost of network operations and maintenance (O&M) and to increase total system efficiency, “as well securing that diesel will not be used anymore for peak load”. However, as the project was mapped out and development began, other services were added: frequency control, operating reserve and voltage control.
Why sodium sulfur over lithium-ion
While many grid-scale battery projects around the world are currently being executed with lithium-ion batteries, in this instance, the use of sodium sulfur, allowing for six hours of storage, is “mandatory for thermal generation investment deferral”, the NGK spokesman said, with the peak demand period being shifted itself lasting around six hours.
“[Deploying] 1MW of battery energy storage systems allows avoiding the investment in about 1.1MW of combined cycle (gas and steam) thermal power plants,” by increasing availability by about 10%, while O&M costs for battery systems “are much lower” than equivalent costs for thermal generation plants.
Energy-Storage.news asked what made the NAS battery particularly suitable for the Abu Dhabi project. The NGK representative said that the six hours of storage in each battery cell reduces total system cost versus lithium batteries. Lithium-ion systems tend to combine several one-hour duration battery cells, “which increases the integration costs”. NAS battery systems are also less sensitive to external temperature conditions. There is no need for air-conditioning to keep cells at the right operating temperature – unlike lithium batteries, NAS batteries are insulated and operate at about 300 degrees centigrade. Due to the insulation, it is still safe to touch the exterior of the module with bare hands. The NGK representative explained further that the rugged nature of the batteries and the ways they can be used provide further compelling reasons to use them in the Middle East.
NAS batteries are robust for the kind of heavy use – charging and discharging the battery each day in a full cycle from 100% state-of-charge to 0% i.e. a full 100% depth of discharge (DOD), which make generation investment deferral possible. The batteries are expected to last “15 years without degradation at system level”.
In November, Energy-Storage.news reported on the inauguration of a 20MWh NGK NAS battery project in Niedersachsen, Germany, combined with 7.5MW / 2.5MWh of lithium-ion batteries from Hitachi Chemical. That will be a three-year demonstration, developed through Japan’s NEDO (New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation) and Niedersachsen’s Ministry for Economics, Labour and Transport, as well as authorities in the City of Varel where the demonstration project is located.
Seeds of energy storage’s future
The 648MWh project marks the second announced deployment of NGK NAS batteries in the Emirates, with Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) announcing in August last year that it will test a 1.2MW / 7.2MWh NGK sodium sulfur battery system at Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park.
Also during January, a Smart Grid Station (SGS) was inaugurated in Al Ruwayyah, Dubai by Dubai Supreme Council of Energy chairman Sheikh Ahmed bin Saeed Al Maktoum. Again, a DEWA project, the SGS was deployed in partnership with South Korea’s state-owned Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO).
DEWA and KEPCO have been exchanging experiences and best practises knowledge with each other on smart city and smart grid topics, including standardisation. The Internet-of-things technology-backed SGS combines a 200kW PV system with 9kW of wind energy and a 500kWh battery energy storage system. It also uses a large thermal energy storage system which provides cooling and a smart chiller system integrated into the SGS’ building management system. The DWA-KEPCO project has been in the making since November 2015.
Published: 28 Jan 2019, 15:10
By: Andy Colthorpe
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/uae-integrates-648mwh-o…
Sodium sulfur (NAS) batteries produced by Japan’s NGK Insulators are being put into use on a massive scale in Abu Dhabi, the capital of the United Arab Emirates.
The company’s battery systems have been deployed across 10 locations – 15 systems in total – adding up to 108MW / 648MWh in total, with each system able to store energy for six hours. The total undertaking includes 12 x 4MW systems and three 20MW systems. The official government Emirates News Agency described the project as the “world’s largest Virtual Battery Plant” as it opened earlier this month.
A representative at NGK’s power business division told Energy-Storage.news the ‘virtual’ description is correct in the sense that the 15 systems in 10 locations “can be controlled as a single plant. While of course they can still be controlled individually when local support to the grid is needed”.
Critical to this aggregation of the systems is the CISC (Centralised Integrated System Controller) which will be located at a control room in Mussafah, an industrial district in Abu Dhabi’s southwest where some of the battery systems are also located, with the rest in nearby Sila. CISC and the NAS systems are “ready to be operated by the TSO (transmission system operator)”, the NGK representative said.
Operational parameters increased from original scope
Awaidha Al Marar, chairman of Abu Dhabi’s Department of Energy, attended an inauguration event on 17 January, as a number of events including Abu Dhabi Sustainability Week and World Future Energy Summit (WFES) took place in the region.
The NGK CISC 648MWh project will help the city load balance across its networks during the daytime, as well as providing up to six hours backup in the case of grid outages. As with many energy storage system projects, it is primarily about reducing the strain on the grid at times of peak demand.
According to the NGK representative, the project was originally planned as thermal generation investment deferral, to reduce the cost of network operations and maintenance (O&M) and to increase total system efficiency, “as well securing that diesel will not be used anymore for peak load”. However, as the project was mapped out and development began, other services were added: frequency control, operating reserve and voltage control.
Why sodium sulfur over lithium-ion
While many grid-scale battery projects around the world are currently being executed with lithium-ion batteries, in this instance, the use of sodium sulfur, allowing for six hours of storage, is “mandatory for thermal generation investment deferral”, the NGK spokesman said, with the peak demand period being shifted itself lasting around six hours.
“[Deploying] 1MW of battery energy storage systems allows avoiding the investment in about 1.1MW of combined cycle (gas and steam) thermal power plants,” by increasing availability by about 10%, while O&M costs for battery systems “are much lower” than equivalent costs for thermal generation plants.
Energy-Storage.news asked what made the NAS battery particularly suitable for the Abu Dhabi project. The NGK representative said that the six hours of storage in each battery cell reduces total system cost versus lithium batteries. Lithium-ion systems tend to combine several one-hour duration battery cells, “which increases the integration costs”. NAS battery systems are also less sensitive to external temperature conditions. There is no need for air-conditioning to keep cells at the right operating temperature – unlike lithium batteries, NAS batteries are insulated and operate at about 300 degrees centigrade. Due to the insulation, it is still safe to touch the exterior of the module with bare hands. The NGK representative explained further that the rugged nature of the batteries and the ways they can be used provide further compelling reasons to use them in the Middle East.
NAS batteries are robust for the kind of heavy use – charging and discharging the battery each day in a full cycle from 100% state-of-charge to 0% i.e. a full 100% depth of discharge (DOD), which make generation investment deferral possible. The batteries are expected to last “15 years without degradation at system level”.
In November, Energy-Storage.news reported on the inauguration of a 20MWh NGK NAS battery project in Niedersachsen, Germany, combined with 7.5MW / 2.5MWh of lithium-ion batteries from Hitachi Chemical. That will be a three-year demonstration, developed through Japan’s NEDO (New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organisation) and Niedersachsen’s Ministry for Economics, Labour and Transport, as well as authorities in the City of Varel where the demonstration project is located.
Seeds of energy storage’s future
The 648MWh project marks the second announced deployment of NGK NAS batteries in the Emirates, with Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) announcing in August last year that it will test a 1.2MW / 7.2MWh NGK sodium sulfur battery system at Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park.
Also during January, a Smart Grid Station (SGS) was inaugurated in Al Ruwayyah, Dubai by Dubai Supreme Council of Energy chairman Sheikh Ahmed bin Saeed Al Maktoum. Again, a DEWA project, the SGS was deployed in partnership with South Korea’s state-owned Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO).
DEWA and KEPCO have been exchanging experiences and best practises knowledge with each other on smart city and smart grid topics, including standardisation. The Internet-of-things technology-backed SGS combines a 200kW PV system with 9kW of wind energy and a 500kWh battery energy storage system. It also uses a large thermal energy storage system which provides cooling and a smart chiller system integrated into the SGS’ building management system. The DWA-KEPCO project has been in the making since November 2015.
SHELL übernimmt sonnen: https://www.shell.com/media/news-and-media-releases/2019/sma…
Sachen gibt's:
http://www.sonnenseite.com/de/wissenschaft/mit-eierschalen-e…"...die vielversprechenden elektrochemischen Eigenschaften von Hühnereierschalen, die Lithium durch einen hohen Anteil an CaCO3 gut speichern können. Das Eierschalenpulver wurde als Elektrode gegen eine metallische Lithium-Anode in einem nichtwässrigen Elektrolyten verwendet. Bei über 1 000 Lade- und Entladezyklen hielt die Testzelle eine Kapazität von 92 Prozent aufrecht."
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 60.108.382 von R-BgO am 15.03.19 10:14:34Thread: Cellcube Energy Storage Systems, Energiespeicher der Zukunft?!
24 M, a startup battery company founded as a spin-off from MIT, claims it has made a breakthrough in creating semi-solid lithium-ion battery cells with an energy density exceeding 350Wh per kg.
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/24m-claims-energy-densi…
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/24m-claims-energy-densi…
Auch eine Möglichkeit ist es,
Salz aufzuheizen und als Antrieb für vorhandene Kraftwerke zu nutzen: http://www.sonnenseite.com/de/wissenschaft/waermespeicherkra…Wirkungsgrad natürlich unterirdisch, aber in der Gedamtkalkulation? Wer weiß....
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 57.916.293 von R-BgO am 05.06.18 22:42:33Highview Power skaliert (angeblich) hoch: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/cryogenic-storage-1bn-j…
Auszug:
"Liquid air energy storage (LAES), so far only deployed at scale at two sites in England, will be available in a number of new territories after manufacturer Highview Power signed a deal claimed to be worth €1 billion (US$1.12 billion).
Highview Power, headquartered in the UK, said earlier this month that it has signed a deal with an engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) partner, TSK, for marketing the LAES systems into Spain, the Middle East and South Africa.
Teasing the possibility of days and weeks of storage from ‘giga-hour scale’ facilities, making possible the kind of long-term storage not possible or economically viable with lithium-ion or even flow batteries, the JV is targeting the replacement of thermal power plants and even nuclear. Highview Power has so far built one 2.5MWh demonstrator and a further 15MWh project in northern England.
TSK has executed projects across numerous sectors, including a 103.19MW PV plant in Jordan, as well as large projects in oil and gas and for industrial infrastructure such as ports. Headquartered in Spain with a turnover of €1 billion in 2018, the company has been active in the Middle East since 2010."
Auszug:
"Liquid air energy storage (LAES), so far only deployed at scale at two sites in England, will be available in a number of new territories after manufacturer Highview Power signed a deal claimed to be worth €1 billion (US$1.12 billion).
Highview Power, headquartered in the UK, said earlier this month that it has signed a deal with an engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) partner, TSK, for marketing the LAES systems into Spain, the Middle East and South Africa.
Teasing the possibility of days and weeks of storage from ‘giga-hour scale’ facilities, making possible the kind of long-term storage not possible or economically viable with lithium-ion or even flow batteries, the JV is targeting the replacement of thermal power plants and even nuclear. Highview Power has so far built one 2.5MWh demonstrator and a further 15MWh project in northern England.
TSK has executed projects across numerous sectors, including a 103.19MW PV plant in Jordan, as well as large projects in oil and gas and for industrial infrastructure such as ports. Headquartered in Spain with a turnover of €1 billion in 2018, the company has been active in the Middle East since 2010."
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 60.223.348 von R-BgO am 28.03.19 20:42:47
Innolith macht in "anorganisch": https://innolith.com/de/technology/
90% Mumpitz-Wahrscheinlichkeit
mal wieder einer mit dem Stein der Weisen:
(oder Sack der Zwerge)Innolith macht in "anorganisch": https://innolith.com/de/technology/
90% Mumpitz-Wahrscheinlichkeit
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 60.274.464 von R-BgO am 04.04.19 10:33:47
99% Mumpitz
den Vorturner kennt man schon von Alevo:
https://www.bzbasel.ch/basel/basel-stadt/wie-ein-oligarch-vo…99% Mumpitz
http://www.sonnenseite.com/de/wissenschaft/hochleistungsfaeh…
"...hochleistungsfähige Siliziumanoden entwickelt. In Kombination mit Schwefel-Kathoden erreichen sie eine zwei- bis dreimal höhere Energiedichte, bis zu 90 Prozent kürzere Ladezeiten und 20 Prozent geringeres Gewicht. "
"...hochleistungsfähige Siliziumanoden entwickelt. In Kombination mit Schwefel-Kathoden erreichen sie eine zwei- bis dreimal höhere Energiedichte, bis zu 90 Prozent kürzere Ladezeiten und 20 Prozent geringeres Gewicht. "
Datenpunkt von McKinsey:
https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/McKinsey/Email/Shortlist/39…"With prices dropping faster than anyone expected—battery-pack costs were recently $230 per kilowatt-hour, down from $1,000—battery storage is playing a bigger role in energy markets, moving from niche uses like grid balancing to broader ones such as replacing conventional power generators for reliability, providing power-quality services, and supporting renewables integration. And as the rise of renewables—solar and wind—continues, so will the need to store all that decarbonized electricity."
SaltX aims to compete with pumped hydro’s economics as 10MWh pilot launches
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/saltx-aims-to-compete-w…
Published: 15 Apr 2019, 16:16
By: Andy Colthorpe
Electrical and heat storage using specially nanocoated salt (NCS) could be economically competitive with pumped hydro, SaltX has said, with a large-scale demonstration facility inaugurated in Berlin, Germany.
Headquartered in Sweden, SaltX has been “working with salts for 15 years”, the company’s marketing director Eric Jacobson told Energy-Storage.news today. This specific application for the salt-based energy storage technology has been in development since customers began expressing an interest in seeing it scaled up a couple of years ago, Jacobson said.
Last Thursday, SaltX and its project partner Vattenfall inaugurated the first 10MWh system based on the technology, in Spandau, Berlin. The pilot plant has an output of 0.5MW, Jacobson said, with energy utility Vattenfall installing the system at one of its combined heat and power (CHP) plants, Reuter-C.
“It’s been known for a while that you can store energy in salt, and there’s been two problems with doing that,” Jacobson said.
“First, the salt is highly corrosive so the application itself has been really expensive because you need special material as the salt starts to corrode the metal and eventually it will be destroyed. Secondly, when you are discharging this thermal battery the salt content has agglomerated, started to lump together. So after 60 cycles you lose the properties of the salt and it starts to not be so efficient.”
Claiming to have solved this problem by applying a proprietary material – patented as far back as 2013 – as a nanocoating to salt crystals, which prevents this corrosion and the agglomeration, Jacobson said that it will require tanks of inexpensive metal to store the material, without the need for pressurisation inside. SaltX claims this will make the technology easier to scale up to larger and larger capacities of storage.
“We use a technology where, it’s similar to an engine and a fuel tank, so the salt is the fuel and it’s really easy to scale this tank up and then we have a reactor or engine where we can take out the energy or the power.
"Whether we want 10MWh or 100MWh of storage, that’s not a big deal for us. That’s one of our advantages.”
Local wind power becomes local power and heat
The pilot project is sited in a region with high penetration of wind energy on the grid. It charges with electricity from the grid and absorbs excess wind energy, while also outputting heat into the local district heating network.
With the system operating at 500 degrees, it can also output high-temperature steam commonly used in industrial processes. For maximum efficiency – claimed to be as high as 90% – the system outputs 30% of the stored energy as electrical power and the rest as heat, to be used either domestically or industrially.
Energy stored chemically in this way can retain its heat for “a day, week or even a year without losing the energy over time”, unlike water, which cools rapidly by comparison. Jacobson also claims the technology and level of engineering required to create scalable systems is superior to molten salt, which some others are investigating, or attempting to commercialise.
“We are really different [to molten salt] because they heat up salt and they keep their salt isolated. So that’s not a form of chemical storage, it’s a latent heat storage. Molten salt cannot go down in temperature below 200 degrees then the salt crystallises then the system will fail and they need to keep their system hot. We can go down to 0 degrees in temperature and restart the process where we were – so it’s really easy for us to start and stop the process.”
While SaltX had considered trying to make the electrical storage component a bigger part of the output equation, the company found that customers in China, Europe and Great Britain all said that partly due to planned coal power station retirements, ways of cheaply generating, storing and dispatching heat are desired.
SaltX seeks system developer, EPC partners
The Spandau project is a pre-commercial demonstrator, Eric Jacobson pointed out, and it will take “roughly three to four months” of operation for meaningful data to emerge. The next step will be to create a commercialised design for testing.
The company is currently looking for partners that will help them to do that. SaltX itself would like to stick to its core expertise in creating the salt and related materials, with an EPC and system developer partners to deliver the systems’ engines (or reactors), and to engineer, construct and build the complete systems for markets in Europe and in China.
Vattenfall is seeking solutions to help it play a role in the transition to decarbonised and decentralised energy and as such was “really kind in letting” SaltX trial its technology in Spandau, Jacobson said. Other partners in the pilot include French engineering consultancy ETIA and the Swedish Energy Agency.
The system can take one to five minutes to start up, making it not suitable for fast-response applications such as frequency control on the grid, whereas it could be a good fit for peak shifting, from one time of day to another, or even to the next day and so on. SaltX supplied some indications of the potential the company sees for the technology privately with Energy-Storage.news and although it is pre-commercial and as yet not possible to put a number on what completed, large-scale commercial systems might cost, Jacobson said that broadly speaking, SaltX wants to be “as price competitive as pumped hydro [energy storage]”.
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/saltx-aims-to-compete-w…
Published: 15 Apr 2019, 16:16
By: Andy Colthorpe
Electrical and heat storage using specially nanocoated salt (NCS) could be economically competitive with pumped hydro, SaltX has said, with a large-scale demonstration facility inaugurated in Berlin, Germany.
Headquartered in Sweden, SaltX has been “working with salts for 15 years”, the company’s marketing director Eric Jacobson told Energy-Storage.news today. This specific application for the salt-based energy storage technology has been in development since customers began expressing an interest in seeing it scaled up a couple of years ago, Jacobson said.
Last Thursday, SaltX and its project partner Vattenfall inaugurated the first 10MWh system based on the technology, in Spandau, Berlin. The pilot plant has an output of 0.5MW, Jacobson said, with energy utility Vattenfall installing the system at one of its combined heat and power (CHP) plants, Reuter-C.
“It’s been known for a while that you can store energy in salt, and there’s been two problems with doing that,” Jacobson said.
“First, the salt is highly corrosive so the application itself has been really expensive because you need special material as the salt starts to corrode the metal and eventually it will be destroyed. Secondly, when you are discharging this thermal battery the salt content has agglomerated, started to lump together. So after 60 cycles you lose the properties of the salt and it starts to not be so efficient.”
Claiming to have solved this problem by applying a proprietary material – patented as far back as 2013 – as a nanocoating to salt crystals, which prevents this corrosion and the agglomeration, Jacobson said that it will require tanks of inexpensive metal to store the material, without the need for pressurisation inside. SaltX claims this will make the technology easier to scale up to larger and larger capacities of storage.
“We use a technology where, it’s similar to an engine and a fuel tank, so the salt is the fuel and it’s really easy to scale this tank up and then we have a reactor or engine where we can take out the energy or the power.
"Whether we want 10MWh or 100MWh of storage, that’s not a big deal for us. That’s one of our advantages.”
Local wind power becomes local power and heat
The pilot project is sited in a region with high penetration of wind energy on the grid. It charges with electricity from the grid and absorbs excess wind energy, while also outputting heat into the local district heating network.
With the system operating at 500 degrees, it can also output high-temperature steam commonly used in industrial processes. For maximum efficiency – claimed to be as high as 90% – the system outputs 30% of the stored energy as electrical power and the rest as heat, to be used either domestically or industrially.
Energy stored chemically in this way can retain its heat for “a day, week or even a year without losing the energy over time”, unlike water, which cools rapidly by comparison. Jacobson also claims the technology and level of engineering required to create scalable systems is superior to molten salt, which some others are investigating, or attempting to commercialise.
“We are really different [to molten salt] because they heat up salt and they keep their salt isolated. So that’s not a form of chemical storage, it’s a latent heat storage. Molten salt cannot go down in temperature below 200 degrees then the salt crystallises then the system will fail and they need to keep their system hot. We can go down to 0 degrees in temperature and restart the process where we were – so it’s really easy for us to start and stop the process.”
While SaltX had considered trying to make the electrical storage component a bigger part of the output equation, the company found that customers in China, Europe and Great Britain all said that partly due to planned coal power station retirements, ways of cheaply generating, storing and dispatching heat are desired.
SaltX seeks system developer, EPC partners
The Spandau project is a pre-commercial demonstrator, Eric Jacobson pointed out, and it will take “roughly three to four months” of operation for meaningful data to emerge. The next step will be to create a commercialised design for testing.
The company is currently looking for partners that will help them to do that. SaltX itself would like to stick to its core expertise in creating the salt and related materials, with an EPC and system developer partners to deliver the systems’ engines (or reactors), and to engineer, construct and build the complete systems for markets in Europe and in China.
Vattenfall is seeking solutions to help it play a role in the transition to decarbonised and decentralised energy and as such was “really kind in letting” SaltX trial its technology in Spandau, Jacobson said. Other partners in the pilot include French engineering consultancy ETIA and the Swedish Energy Agency.
The system can take one to five minutes to start up, making it not suitable for fast-response applications such as frequency control on the grid, whereas it could be a good fit for peak shifting, from one time of day to another, or even to the next day and so on. SaltX supplied some indications of the potential the company sees for the technology privately with Energy-Storage.news and although it is pre-commercial and as yet not possible to put a number on what completed, large-scale commercial systems might cost, Jacobson said that broadly speaking, SaltX wants to be “as price competitive as pumped hydro [energy storage]”.
Anodenhersteller Sila Nanotechnologies macht 170 MUSD Finanzierungsrunde:
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/anode-materials-firm-ge…
"The company’s silicon-based anodes can replace graphite without any change to manufacturing infrastructure. It claims an average improvement of 20% dependant on the associated battery chemistry. Sila’s anodes can be used an assortment of Lithium chemistries including Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC), Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), Lithium Cobolt Oxide (LCO) and Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminium Oxide (NCA)."
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/anode-materials-firm-ge…
"The company’s silicon-based anodes can replace graphite without any change to manufacturing infrastructure. It claims an average improvement of 20% dependant on the associated battery chemistry. Sila’s anodes can be used an assortment of Lithium chemistries including Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC), Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), Lithium Cobolt Oxide (LCO) and Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminium Oxide (NCA)."
Tesvolt baut: https://www.tesvolt.com/de/presse/erste-gigafactory-fuer-bat…
"Der erste Bauabschnitt mit 12.000 m² Nutzfläche wird im Juni fertiggestellt sein, in der Endausbaustufe wird die jährliche Fertigungsleistung auf 20.000 m² Nutzfläche mehr als eine GWh betragen. Bis dahin soll die Mitarbeiterzahl von heute 60 auf 100 bis 120 ansteigen.
„Der Weltmarkt für stationäre Energiespeicher hat bereits eine Gesamtkapazität von 16 GWh erreicht. Die Menschen in Europa wollen keine rauchenden Kohlekraftwerke und Dieselskandale mehr, sie wünschen sich eine Zukunft ohne Umweltkatastrophen“, sagt Daniel Hannemann, der Tesvolt vor fünf Jahren zusammen mit Simon Schandert gegründet hat. „Mit der Gigafactory wollen wir dazu beitragen, indem wir bezahlbare, saubere Energie überall auf der Welt ermöglichen.“"
"Der erste Bauabschnitt mit 12.000 m² Nutzfläche wird im Juni fertiggestellt sein, in der Endausbaustufe wird die jährliche Fertigungsleistung auf 20.000 m² Nutzfläche mehr als eine GWh betragen. Bis dahin soll die Mitarbeiterzahl von heute 60 auf 100 bis 120 ansteigen.
„Der Weltmarkt für stationäre Energiespeicher hat bereits eine Gesamtkapazität von 16 GWh erreicht. Die Menschen in Europa wollen keine rauchenden Kohlekraftwerke und Dieselskandale mehr, sie wünschen sich eine Zukunft ohne Umweltkatastrophen“, sagt Daniel Hannemann, der Tesvolt vor fünf Jahren zusammen mit Simon Schandert gegründet hat. „Mit der Gigafactory wollen wir dazu beitragen, indem wir bezahlbare, saubere Energie überall auf der Welt ermöglichen.“"
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 60.518.307 von R-BgO am 08.05.19 17:00:04
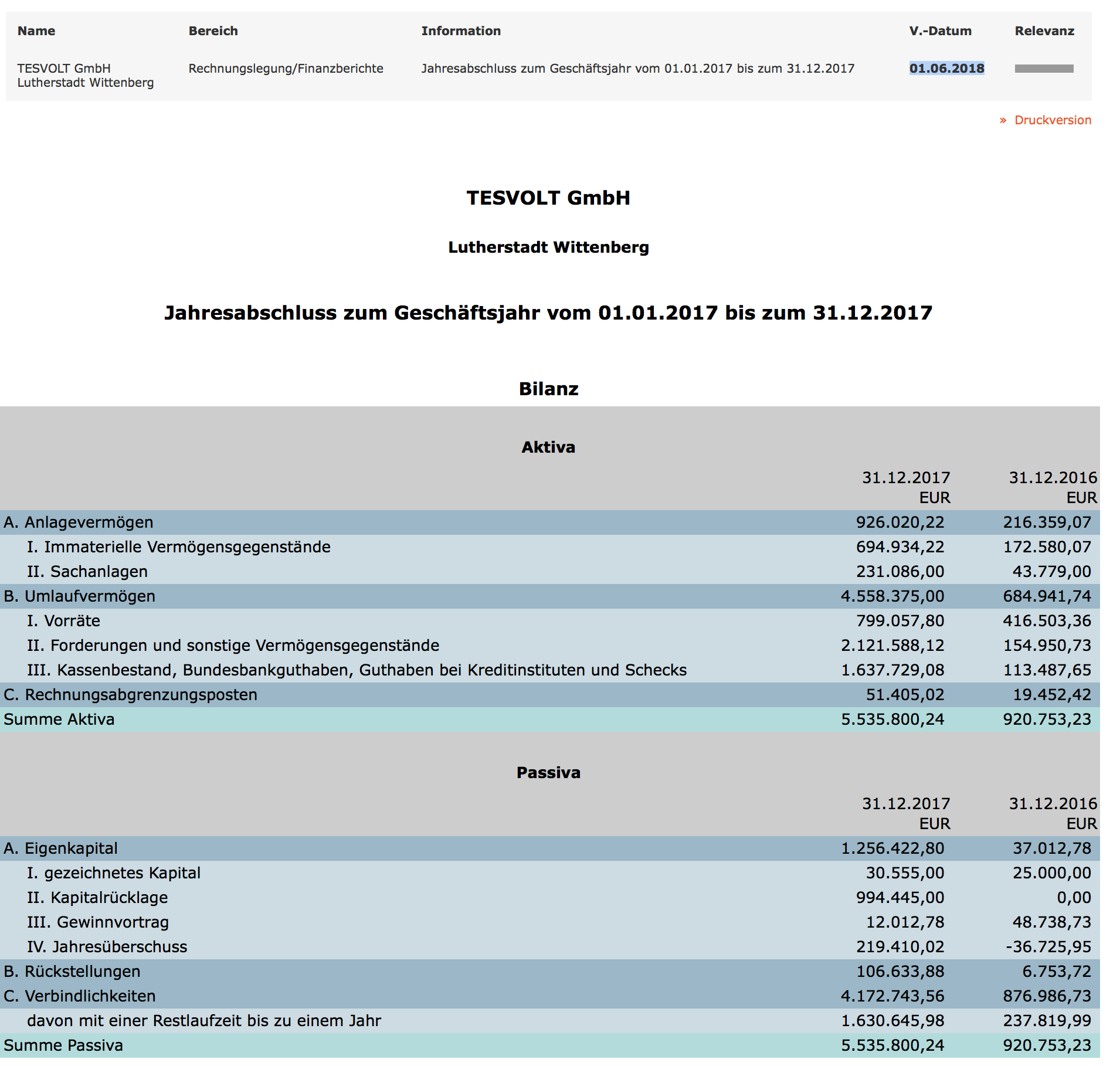
Abschluss 2017 wurde am 1.6.2018 veröffentlicht,
vielleicht wissen wir bald mehr:
Volterion macht Redox-Flow:


Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 55.520.850 von R-BgO am 14.08.17 15:03:57Northvolt wirbt EK ein: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/vw-goldman-sachs-lead-m…
Northvolt, the consortium seeking to establish significant lithium-ion battery cell manufacturing facilities in Europe, has raised US$1 billion in equity capital from parties including Volkswagen and BMW and the merchant banking division of Goldman Sachs.
Northvolt, the consortium seeking to establish significant lithium-ion battery cell manufacturing facilities in Europe, has raised US$1 billion in equity capital from parties including Volkswagen and BMW and the merchant banking division of Goldman Sachs.
24M partnert für Produktion mit Kyocera: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/24ms-semi-solid-lithium…
"...While admitting that the technology is still at the early stages of its commercialisation journey, 24M said then that it is looking to establish a 100MW pilot production plant by the end of this year."
"...While admitting that the technology is still at the early stages of its commercialisation journey, 24M said then that it is looking to establish a 100MW pilot production plant by the end of this year."
Navigant zu Kostentrends:
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/navigant-risk-of-slower…"Lithium-ion battery cell costs could fall to as little as US$76 per kWh by 2030, from around US$139 per kWh this year, according to new analysis by Navigant Research.
...
Indeed, in March, BloombergNEF's head of energy storage analysis, Logan Goldie-Scott said an 'average' lithium-ion battery pack could cost as low as US$62 per kWh by 2030, noting however that some companies will "undershoot" and price their packs even cheaper than that while others will come in with higher prices."
bin heute zufällig auf den thread aufmerksam geworden, wollte rausfinden, welche metalle außer den hinlänglich bekannten lithium und kobald für elektromobilität eine rolle spielen könnten
ein ganz guter artikel findet sich dazu auch in der sz
https://www.sueddeutsche.de/digital/batterien-weg-vom-lithiu…
ein ganz guter artikel findet sich dazu auch in der sz
https://www.sueddeutsche.de/digital/batterien-weg-vom-lithiu…
ein Überblick über die Mega und Gigafactories
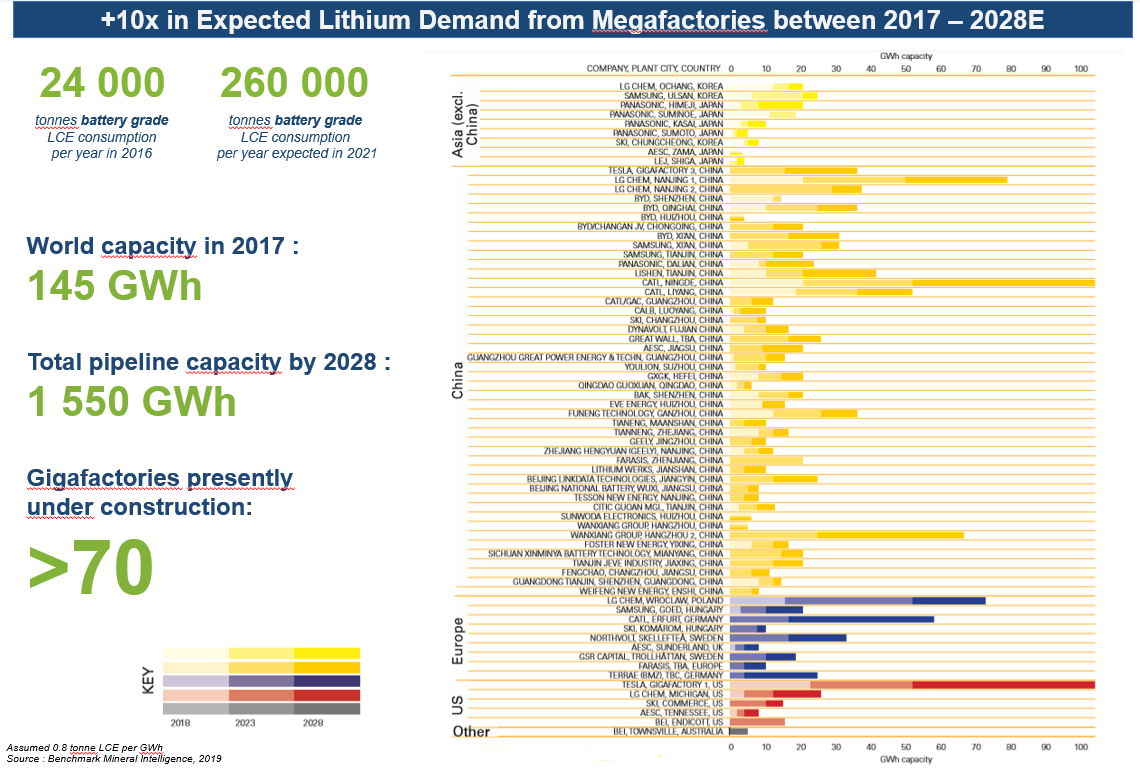

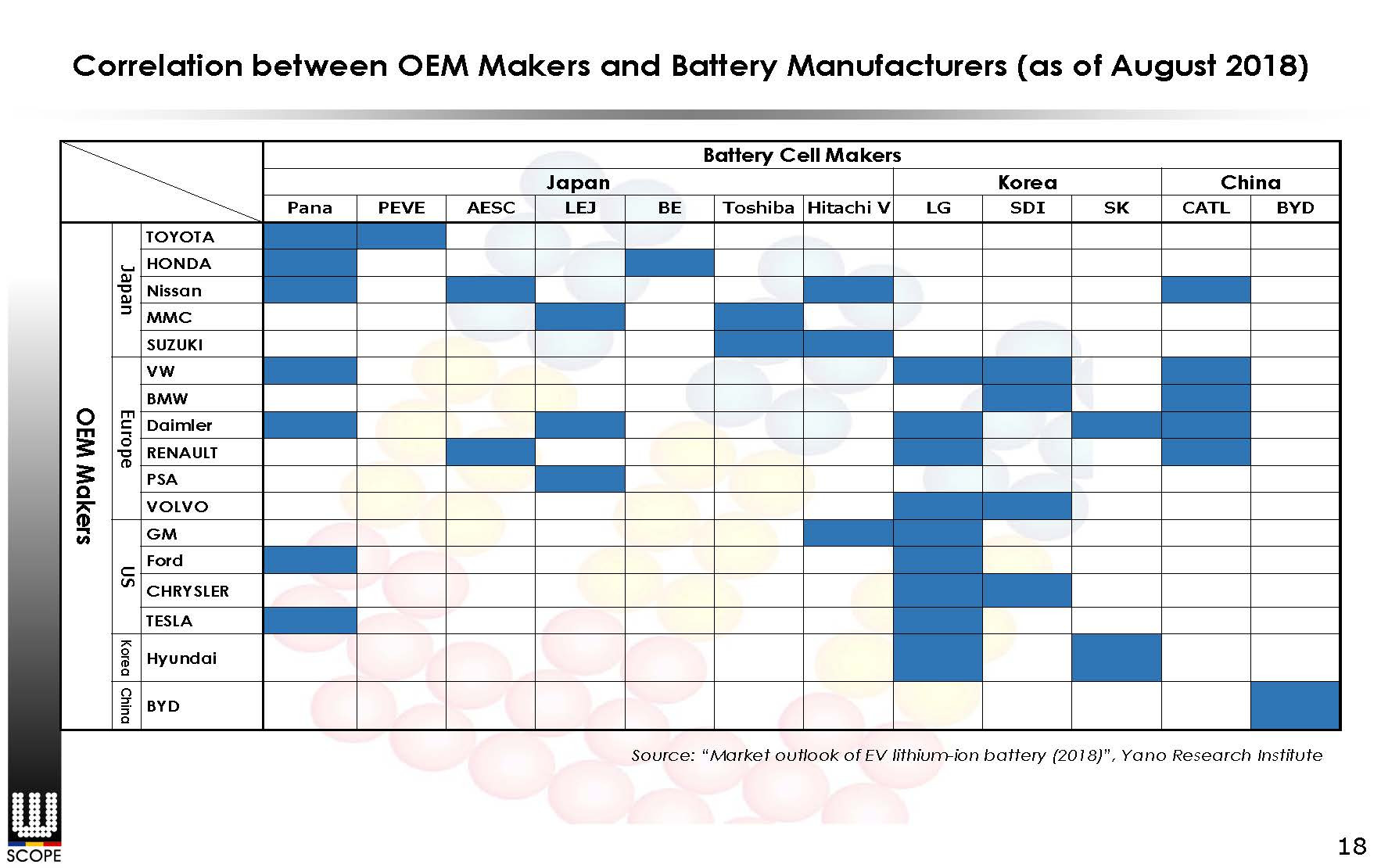
mal wieder was Neues:
https://www.energy-storage.news/news/form-energy-closes-us40…Form Energy raises $40 million USD für ultra-long-duration storage, allerdings ohne Angaben zur Technologie...
Aber Gates, Branson und Jack MA sind dabei.
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 61.377.914 von R-BgO am 30.08.19 12:17:29
älterer Artikel dazu:
https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/inside-form-ene…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 61.377.914 von R-BgO am 30.08.19 12:17:29
ich tippe mal auf irgendwas mit Schwefel:
https://www.npr.org/2019/07/22/744206049/a-new-battery-could…
Antwort auf Beitrag Nr.: 61.377.977 von R-BgO am 30.08.19 12:25:53
"Baseload isn't providing many technical details at this stage, but the key to its low cost is relying on sulfur. That's because the material is very abundant and energy-dense, Chiang says. Indeed, it's a waste product of oil and gas production that costs as little as 10 cents per kilogram.
"Based on the charge stored per dollar, sulfur was more than a factor of 10 better than the next best thing," says Chiang, a materials science professor who previously cofounded lithium-ion battery startups A123 Systems, 24M, and three other startups."
Yep;
Schwefel-Flow-Batteries: https://www.technologyreview.com/s/608962/serial-battery-ent…"Baseload isn't providing many technical details at this stage, but the key to its low cost is relying on sulfur. That's because the material is very abundant and energy-dense, Chiang says. Indeed, it's a waste product of oil and gas production that costs as little as 10 cents per kilogram.
"Based on the charge stored per dollar, sulfur was more than a factor of 10 better than the next best thing," says Chiang, a materials science professor who previously cofounded lithium-ion battery startups A123 Systems, 24M, and three other startups."
on Italy:
https://www.pv-tech.org/news/italian-utility-scale-solar-boo…"Clark seemed, however, more bullish on the economics of energy storage, which he described as the “elephant in the room”. “We’ve hardly spoken about the subject and yet people who are able to deploy storage will make money,” he remarked. “Batteries will help stabilise prices and the big question for Italian PV owners is – do you own the battery or do you rely on the market?”"
KORE Power - 6GWh NMC in Idaho: https://www.energy-storage.news/news/kore-power-targets-6gwh…
Scheint mir fast zu gut, um wahr zu sein:
https://www.pv-tech.org/news/planning-win-for-8minutenergys-…"On Tuesday, the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power (LADWP) Board of Commission unanimously voted to purchase power from 8minute Solar Energy's Eland hybrid for a 25-year period, at record-breaking fixed tariffs for solar (US$0.01997/kWh) and energy storage (US$0.013/kWh)."
...
However, some in the solar ranks have questioned whether ultra-cheap Eland can remain money-making for 8minute. Writing for PV Tech in August, Gensol Group vice president Ali Imran Naqvi examined how the US$0.01997/kWh bid will play out economically based on assumptions over component choices, investment tax credit (ITC) support, energy yield and other factors.
“Plugging these numbers in our model threw an equity return of 5%, which leaves very little room for applying sensitivities for these important factors,” Imran Naqvi remarked. “We were filled with enthusiasm at the beginning of this effort to understand the mind of the bidders but burning the midnight oil does not yield much light, it appears.”
Hatte ich bisher gar nicht auf dem Schirm:
https://splash247.com/batteries-now-in-use-across-almost-eve…"While LNG or LNG-ready ships top this chart, coming in at second place are battery-assisted vessels, which are now being installed on almost every single segment of the global merchant fleet. Battery-powered ships include fully electric vessels, and chargeable and non-chargeable hybrids. The take-up has been strongest in the ferry sector followed by OSVs to date.
Commenting on the growth of battery use in shipping, Greg Atkinson from Japan’s Eco Marine Power commented: “The use of a variety of battery technologies is likely to become more widespread across shipping especially as some ship types move towards using electrical propulsion. We are also likely to see technologies specifically developed for land-based electric vehicles including solid-state batteries being adapted for ship use also.”"
Beitrag zu dieser Diskussion schreiben
Zu dieser Diskussion können keine Beiträge mehr verfasst werden, da der letzte Beitrag vor mehr als zwei Jahren verfasst wurde und die Diskussion daraufhin archiviert wurde.
Bitte wenden Sie sich an feedback@wallstreet-online.de und erfragen Sie die Reaktivierung der Diskussion oder starten Sie eine neue Diskussion.
Meistdiskutiert
| Wertpapier | Beiträge | |
|---|---|---|
| 220 | ||
| 130 | ||
| 100 | ||
| 73 | ||
| 63 | ||
| 49 | ||
| 40 | ||
| 40 | ||
| 38 | ||
| 34 |